 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 CentOS
CentOS
 CentOS Interview Questions: Ace Your Linux System Administrator Interview
CentOS Interview Questions: Ace Your Linux System Administrator Interview
CentOS Interview Questions: Ace Your Linux System Administrator Interview
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:17 AMFrequently asked questions and answers to CentOS interview include: 1. Use the yum or dnf command to install the software package, such as sudo yum install nginx. 2. Manage users and groups through useradd and groupadd commands, such as sudo useradd -m -s /bin/bash newuser. 3. Use firewalld to configure the firewall, such as sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http. 4. Set automatic updates to use yum-cron, such as sudo yum install yum-cron and configure apply_updates = yes.
introduction
Are you preparing for a CentOS-related Linux system administrator interview? Do you want to know what questions you might get asked and how to answer them to stand out? In this article, I will share some common CentOS interview questions and provide detailed answers and personal experience, hoping to help you prepare for the interview better.
By reading this article, you will learn the key knowledge points of CentOS system management, master how to deal with common interview questions, and learn some practical tips and best practices from it.
Review of basic knowledge
Before we dive into the interview questions, let’s review some of the basics of CentOS. CentOS, full name is Community ENTerprise Operating System, is an open source operating system based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) source code. It is widely used in server environments because of its stability and security.
The management of CentOS involves many aspects, including but not limited to file system management, user management, network configuration, service management, etc. Understanding these basic concepts is essential to answering interview questions.
Core concept or function analysis
Key concepts of CentOS system management
In CentOS system management, there are several key concepts to master:
- File system management : Learn how to use
df,duand other commands to view and manage disk space. - User and group management : Proficient in using
useradd,groupaddand other commands to create and manage users and groups. - Network configuration : Ability to configure network interfaces, set up DNS, manage firewalls, etc.
- Service management : Use the
systemctlcommand to start, stop and restart the service.
These concepts are not only the basis of CentOS system management, but also the focus often mentioned in interviews.
How it works
Many operations managed by CentOS are done through the command line interface (CLI). Understanding how these commands work can help you manage your system more effectively. For example, the systemctl command manages system services by interacting with systemd, while the useradd command creates users and groups by modifying /etc/passwd and /etc/group files.
Example of usage
Frequent interview questions and answers
Question 1: How to install packages on CentOS?
Installing packages on CentOS usually uses the yum or dnf command. Here is an example of using yum to install nginx:
# Update package list sudo yum update # Install nginx sudo yum install nginx
This command will download and install nginx from the CentOS repository. The advantage of using yum is that it automatically handles dependencies, ensuring that all required packages are installed correctly.
Question 2: How to manage users and groups on CentOS?
Managing users and groups on CentOS can be done by following the following command:
# Create new user sudo useradd -m -s /bin/bash newuser # Set user password sudo passwd newuser # Create a new group sudo groupadd newgroup # Add user to group sudo usermod -aG newgroup newuser
These commands help you create and manage users and groups, ensuring the security and organization of your system.
Question 3: How to configure a firewall on CentOS?
CentOS uses firewalld as the default firewall management tool. Here is an example of configuring a firewall to allow HTTP traffic:
# Start and enable firewalld sudo systemctl start firewalld sudo systemctl enable firewalld # Allow HTTP traffic sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http sudo firewall-cmd --reload
These commands configure the firewall to allow HTTP traffic, ensuring that your web server can be accessed externally.
Advanced Usage
Question 4: How to set up automatic updates on CentOS?
Setting up automatic updates ensures that the system is always up to date and reduces the risk of security vulnerabilities. Here is an example of automatically updating using yum-cron :
# Install yum-cron sudo yum install yum-cron # Enable yum-cron sudo systemctl enable --now yum-cron # Edit the configuration file to enable automatic update of sudo nano /etc/yum/yum-cron.conf # Set apply_updates = yes in the configuration file
This configuration will allow the system to automatically check and apply updates every day to ensure the security and stability of the system.
Common Errors and Debugging Tips
In CentOS management, common errors include permission issues, dependency issues, and configuration errors. Here are some debugging tips:
- Permissions issue : If you encounter permission issues, check the permissions of the file or directory and use the
chmodandchowncommands to adjust. - Dependency problem : If the package installation fails, check the dependency and use the
yum deplistcommand to view the dependency. - Configuration error : If the configuration file is incorrect, use
grepandsedcommands to find and correct the error.
Performance optimization and best practices
Performance optimization and best practices are very important in CentOS system management. Here are some suggestions:
- Using LVM (Logical Volume Management) : LVM can help you manage disk space more flexibly, making it easier to expand and reduce partitions.
- Regularly clean log files : Use the
logrotatetool to clean log files regularly to prevent disk space from being filled. - Optimize network configuration : Use
ethtoolandtcpdumptools to optimize network performance to ensure network connectivity stability and speed.
With these optimizations and best practices, you can improve the performance and reliability of your CentOS system.
Summarize
Through this article, you should have mastered some key knowledge points in CentOS system management and understand how to deal with common interview questions. I hope that this information and experience sharing can help you perform well in the interview and successfully pass the CentOS-related Linux system administrator interview.
The above is the detailed content of CentOS Interview Questions: Ace Your Linux System Administrator Interview. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
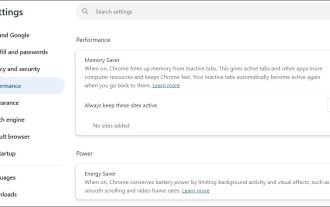 Fixed the failure to upload files in Windows Google Chrome
Jul 08, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
Fixed the failure to upload files in Windows Google Chrome
Jul 08, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
Have problems uploading files in Google Chrome? This may be annoying, right? Whether you are attaching documents to emails, sharing images on social media, or submitting important files for work or school, a smooth file upload process is crucial. So, it can be frustrating if your file uploads continue to fail in Chrome on Windows PC. If you're not ready to give up your favorite browser, here are some tips for fixes that can't upload files on Windows Google Chrome 1. Start with Universal Repair Before we learn about any advanced troubleshooting tips, it's best to try some of the basic solutions mentioned below. Troubleshooting Internet connection issues: Internet connection
 How to find my private and public IP address in Linux?
Jul 09, 2025 am 12:37 AM
How to find my private and public IP address in Linux?
Jul 09, 2025 am 12:37 AM
In Linux systems, 1. Use ipa or hostname-I command to view private IP; 2. Use curlifconfig.me or curlipinfo.io/ip to obtain public IP; 3. The desktop version can view private IP through system settings, and the browser can access specific websites to view public IP; 4. Common commands can be set as aliases for quick call. These methods are simple and practical, suitable for IP viewing needs in different scenarios.
 What is the code number of Bitcoin? What style of code is Bitcoin?
Jul 22, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
What is the code number of Bitcoin? What style of code is Bitcoin?
Jul 22, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
As a pioneer in the digital world, Bitcoin’s unique code name and underlying technology have always been the focus of people’s attention. Its standard code is BTC, also known as XBT on certain platforms that meet international standards. From a technical point of view, Bitcoin is not a single code style, but a huge and sophisticated open source software project. Its core code is mainly written in C and incorporates cryptography, distributed systems and economics principles, so that anyone can view, review and contribute its code.
 System requirements to install linux
Jul 20, 2025 am 03:49 AM
System requirements to install linux
Jul 20, 2025 am 03:49 AM
Linuxcanrunonmodesthardwarewithspecificminimumrequirements.A1GHzprocessor(x86orx86_64)isneeded,withadual-coreCPUrecommended.RAMshouldbeatleast512MBforcommand-lineuseor2GBfordesktopenvironments.Diskspacerequiresaminimumof5–10GB,though25GBisbetterforad
 How to use the `shutdown` command
Jul 15, 2025 am 12:26 AM
How to use the `shutdown` command
Jul 15, 2025 am 12:26 AM
The shutdown command of Linux/macOS can be shut down, restarted, and timed operations through parameters. 1. Turn off the machine immediately and use sudoshutdownnow or -h/-P parameters; 2. Use the time or specific time point for the shutdown, cancel the use of -c; 3. Use the -r parameters to restart, support timed restart; 4. Pay attention to the need for sudo permissions, be cautious in remote operation, and avoid data loss.
 How to make PHP container support automatic construction? Continuously integrated CI configuration method of PHP environment
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
How to make PHP container support automatic construction? Continuously integrated CI configuration method of PHP environment
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
To enable PHP containers to support automatic construction, the core lies in configuring the continuous integration (CI) process. 1. Use Dockerfile to define the PHP environment, including basic image, extension installation, dependency management and permission settings; 2. Configure CI/CD tools such as GitLabCI, and define the build, test and deployment stages through the .gitlab-ci.yml file to achieve automatic construction, testing and deployment; 3. Integrate test frameworks such as PHPUnit to ensure that tests are automatically run after code changes; 4. Use automated deployment strategies such as Kubernetes to define deployment configuration through the deployment.yaml file; 5. Optimize Dockerfile and adopt multi-stage construction
 How to build an independent PHP task container environment. How to configure the container for running PHP timed scripts
Jul 25, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
How to build an independent PHP task container environment. How to configure the container for running PHP timed scripts
Jul 25, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
Building an independent PHP task container environment can be implemented through Docker. The specific steps are as follows: 1. Install Docker and DockerCompose as the basis; 2. Create an independent directory to store Dockerfile and crontab files; 3. Write Dockerfile to define the PHPCLI environment and install cron and necessary extensions; 4. Write a crontab file to define timing tasks; 5. Write a docker-compose.yml mount script directory and configure environment variables; 6. Start the container and verify the log. Compared with performing timing tasks in web containers, independent containers have the advantages of resource isolation, pure environment, strong stability, and easy expansion. To ensure logging and error capture
 How to Securely Erase a Hard Drive on Linux
Jul 24, 2025 am 12:08 AM
How to Securely Erase a Hard Drive on Linux
Jul 24, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Confirm the target hard disk device name (such as /dev/sda) to avoid accidentally deleting the system disk; 2. Use sudoddif=/dev/zeroof=/dev/sdXbs=1Mstatus=progress to overwrite the zero value in full disk, which is suitable for most scenarios; 3. Use sudoshred-v-n3/dev/sdX for three random data overwrites to ensure that it cannot be restored; 4. Optionally execute sudobadblocks-wsv/dev/sdX for destructive write tests; finally use sudohexdump-C/dev/sdX|head to verify whether it is all zero and complete safe erasing.





