 System Tutorial
System Tutorial
 LINUX
LINUX
 Learn the basic operations of using vim editor on Linux (copy, paste, replace, line number, undo, multi-file operations)
Learn the basic operations of using vim editor on Linux (copy, paste, replace, line number, undo, multi-file operations)
Learn the basic operations of using vim editor on Linux (copy, paste, replace, line number, undo, multi-file operations)
Jan 02, 2024 pm 10:10 PMText file editing command: vim
1. Three status modes of vim
1) Command mode (default)
Note: Enter ":q!" in command mode to exit vim.
2) Editable mode (enter editable mode by entering lowercase "i" in command mode; press Esc to exit to command mode)
Remarks: Lowercase i, insert at the current cursor; lowercase a, insert after the current cursor.
3) Last line mode (enter through command mode, press Esc to exit to command mode)
Function: Execute non-text editing commands on the last line of the file, save, open the file, write the file name, etc.
For example, ":w" is used to fill in the file name;
For example, the function of ":wq" is to save and exit after filling in the file;
For example "/", search from top to bottom;
For example "?", search from bottom to top;
2. Basic operations of vim
1) Open the file
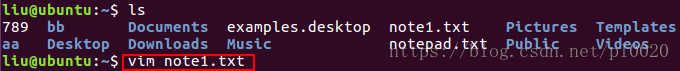
vim file name will open and enter command mode.
2) Edit file
In command mode, enter lowercase i to enter editing mode;
3) Save the file and exit
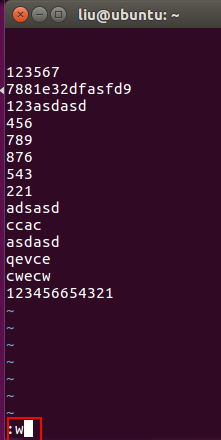
After editing is completed, press Esc to return to the command mode and enter ":w" (add the file name if there is no file name);

Enter: q to exit.
3. Vim editing operation (in command mode)
1) Copy operation
Lowercase "yy" copies a single line;
"2yy" copies the 2 lines at the cursor;
……
"nyy" copies the cursor out of n lines.
2) Paste operation
Lowercase "p" is pasted to the next line under the current cursor;
Capital "P" is pasted to the next line under the current cursor;
3) Delete operation
"dd" deletes the current line
"2dd" deletes the current two lines at the cursor;
……
4) Add line operation open
Lowercase "o", insert a blank line in the next line under the current cursor;
Capital "o", insert a blank line in the previous line at the current cursor;
4. Vim’s search and replace operation (in last line mode)
1) Search operation
Function: Find lines containing keywords;
Input "/search object" in command mode to search from top to bottom, press n to search (next);
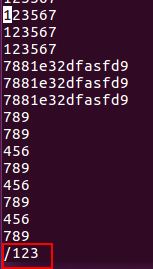
Input "? Search object" in command mode to search from top to bottom, press n to search (next);
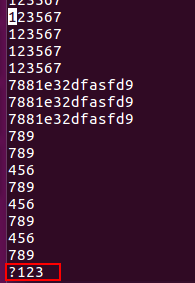
2) Replacement operation
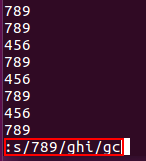
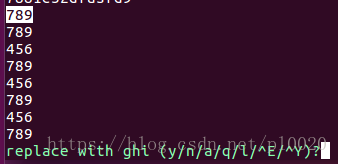
Line replacement
: s/replaced object/new object/gc, press y after the prompt to complete the replacement.
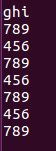
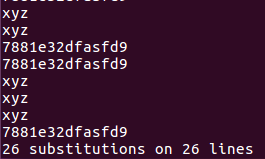
Full text replacement
: %s/replaced object/new object/gc, follow the line prompts and press y to complete the replacement.
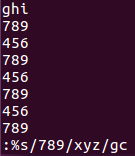
Enter: wq (save and exit).
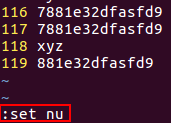
5. Advanced operations of vim 1) Line number setting
Enter ":set nu" in the last line mode to display the line number of the file;
Enter ":set nonu" in the last line mode to turn off the display of file line numbers;
vi ~/.vimrc
2) Editing settings of ~/.vimrc
3) Concurrent operations of multiple files
This operation is convenient for copying and pasting multiple files to each other.
Command: vim file name 1 file name 2 file name 3...
Command: ":args" displays the names of multiple currently opened files at the bottom, [name of current file];
Command: ":next" switches to display the next document;
Command: ":prev" switches to display the previous document;
Command: ":first" switches to display the first document;
Command: ":last" switches the display of the last document.
4) Undo and restore operations
Note: Whether it is u to undo or ctrl r to restore, the premise is that the file cannot be saved.
Lowercase u: change before (undo the most recent action by row, step by step, in timeline units) until already at oldest change (can undo multiple steps);
Uppercase U: Undo only one step;
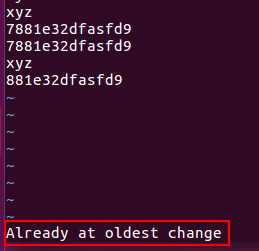
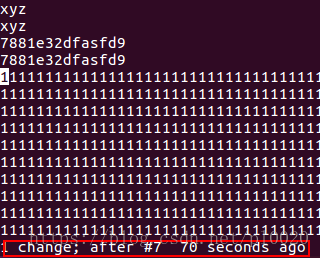
Ctrl r: change after (restore the undone action by row, step by step and in the timeline) until already at oldest change;
Ctrl R: Restore what was revoked, one step at a time;
How to copy a line, paste and delete a line of data in vi text editing under linux
When using vi, sometimes you want to copy a line of data directly, then paste a line or delete a line of data directly
How to copy a row of data
Put the cursor in front of the line you want to copy, and then press the yy letter key twice
Then place the cursor where you want to copy and press the p letter key on the keyboard
To delete a line, move the cursor to the line to be deleted and press the dd key twice
The following is a description of the relevant keys:
x,X: In a line, x is to delete one character backward (equivalent to the del key), and X is to delete one character forward (equivalent to the backspace key).
dd: Delete the entire line where the cursor is.
ndd: n is a number. Starting from the cursor, delete n columns down.
yy: Copy the line where the cursor is.
nyy: n is a number. Copy n lines down where the cursor is.
p,P: p means to paste the copied data to the line below the cursor, and P means to paste it to the line above the cursor.
u : Undo the previous operation
CTRL r: Redo the previous operation.
Decimal point '.': Repeat the previous action.
Vim common commands (delete, copy, paste, undo, search, insert, cursor movement, select, save, exit)
Basic operations of vim:
Select text
v Starting from the current position of the cursor, the place where the cursor passes will be selected, and then press v to end.
V Starting from the current line of the cursor, all lines passed by the cursor will be selected. Press V again to end.
ctrl v Starting from the current position of the cursor, select the rectangular area formed by the starting point and end point of the cursor, and then press Ctrl v to end.
ggVG selects all the text, where gg means jumping to the beginning of the line, V means selecting the entire line, and G means the end
Delete, copy, paste, undo
d Delete dd Delete the entire line ndd Delete n lines
x Delete a character
u Undo the last operation
ctrl R Undo (undo the undo operation)
y copy (copy to register)
ppaste (default taken from register)
Commonly used ESC first
i Insert text before cursor
a Insert text
after the cursor
o Start a new line below and change the current mode to Insert mode
O (capital O) will start a new line above the current line
:q exit
:q! Force quit
:wq Save and exit
ZZ Save and exit
/ Simple search /pp Search pp
in the file
Move command
$ Move the cursor to the end of the line 2$ Move to the end of the next line n$ Move to the end of the next n lines
^ Move the cursor to the first non-blank character of the current line
0 (number 0) moves the cursor to the first character of the current line
G Move the cursor to the last line. 33G Move the cursor to line 33
gg jump to the first line
Vim Select All Copy Paste Undo Back Operation
Delete all: After pressing the esc key, first press gg (reach the top), then dG
Copy all: After pressing the esc key, first press gg, then ggyG
Select all and highlight: After pressing the esc key, first press gg, then ggvG or ggVG
Single line copy: press esc key, then yy
Single line deletion: press esc key, then dd
Paste: After pressing esc key, then p
Copy to pasteboard: After selecting all and highlighting, ctrl shift c,
Problem that vim can only paste 50 lines:
Edit ~/.vimrc in the current user's home directory (if it does not exist, create a new file) and add a line
:set viminfo='1000,
As for why you need to enter '1000, this is actually not important. The most important thing is to enter
Press u in vim to undo an operation
u Undo the previous operation
Ctrl r restores the previous undone operation
Notice:
If you type "u" twice and your text returns to the original, it should be that your Vim is configured in Vi compatibility mode.
Redo
If you undo too much, you can type CTRL-R (redo) to roll back the previous command. In other words, it undoes an undo. To see an example of execution, enter CTRL-R twice. The character A and the space after it appear:
young intelligent turtle
There is a special version of the undo command: "U" (line undo). The line undo command undoes all previously edited lines
operations on. Enter these commands twice to cancel the previous "U":
A very intelligent turtle
xxxx delete very
A intelligent turtle
xxxxxx Delete turtle
A intelligent
Use "U" to restore row
A very intelligent turtle
Undo "U" with "u"
A intelligent
The "U" command changes itself, the "u" command undoes the operation, and the CTRL-R command redoes the operation. This is a bit messy, but no
Worry, you can switch to any state with the "u" and CTRL-R commands.
Popular text editors often have forward and back features that allow you to move back and forth between previously viewed locations in a file. In vim, use Ctrl-O to go backward and Ctrl-I to go forward.
Related help: :help CTRL-O :help CTRL-I :help jump-motions
The above is the detailed content of Learn the basic operations of using vim editor on Linux (copy, paste, replace, line number, undo, multi-file operations). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How does the cost of ownership differ between Linux and Windows?
Jun 09, 2025 am 12:17 AM
How does the cost of ownership differ between Linux and Windows?
Jun 09, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Linux's cost of ownership is usually lower than Windows. 1) Linux does not require license fees, saving a lot of costs, while Windows requires purchasing a license. 2) Linux has low hardware requirements and can extend the service life of the device. 3) The Linux community provides free support to reduce maintenance costs. 4) Linux is highly secure and reduces productivity losses. 5) The Linux learning curve is steep, but Windows is easier to use. The choice should be based on specific needs and budget.
 How does the performance of I/O operations differ between Linux and Windows?
Jun 07, 2025 am 12:06 AM
How does the performance of I/O operations differ between Linux and Windows?
Jun 07, 2025 am 12:06 AM
LinuxoftenoutperformsWindowsinI/Operformanceduetoitscustomizablekernelandfilesystems,whileWindowsoffersmoreuniformperformanceacrosshardware.1)LinuxexcelswithcustomizableI/OschedulerslikeCFQandDeadline,enhancingperformanceinhigh-throughputapplications
 Is Notepad still relevant in today's world of advanced text editors?
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Is Notepad still relevant in today's world of advanced text editors?
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Yes,Notepadstillhasaplaceintoday'sworldduetoitsspeed,simplicity,anduniversalavailability.1.Itloadsinstantlywithminimalsystemresources,makingitidealforquicknotesoreditswithoutdistractions.2.It'susefulforbasiccodeorscriptediting,suchasbatchscriptsorhos
 How to install Linux alongside Windows (dual boot)?
Jun 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
How to install Linux alongside Windows (dual boot)?
Jun 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The key to installing dual systems in Linux and Windows is partitioning and boot settings. 1. Preparation includes backing up data and compressing existing partitions to make space; 2. Use Ventoy or Rufus to make Linux boot USB disk, recommend Ubuntu; 3. Select "Coexist with other systems" or manually partition during installation (/at least 20GB, /home remaining space, swap optional); 4. Check the installation of third-party drivers to avoid hardware problems; 5. If you do not enter the Grub boot menu after installation, you can use boot-repair to repair the boot or adjust the BIOS startup sequence. As long as the steps are clear and the operation is done properly, the whole process is not complicated.
 How to enable the EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository?
Jun 17, 2025 am 09:15 AM
How to enable the EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository?
Jun 17, 2025 am 09:15 AM
The key to enabling EPEL repository is to select the correct installation method according to the system version. First, confirm the system type and version, and use the command cat/etc/os-release to obtain information; second, enable EPEL through dnfinstallepel-release on CentOS/RockyLinux, and the 8 and 9 version commands are the same; third, you need to manually download the corresponding version of the .repo file and install it on RHEL; fourth, you can re-import the GPG key when encountering problems. Note that the old version may not be supported, and you can also consider enabling epel-next to obtain the test package. After completing the above steps, use dnfrepolist to verify that the EPEL repository is successfully added.
 How does Linux perform compared to Windows for web server workloads?
Jun 08, 2025 am 12:18 AM
How does Linux perform compared to Windows for web server workloads?
Jun 08, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Linux usually performs better in web server performance, mainly due to its advantages in kernel optimization, resource management and open source ecosystem. 1) After years of optimization of the Linux kernel, mechanisms such as epoll and kqueue make it more efficient in handling high concurrent requests. 2) Linux provides fine-grained resource management tools such as cgroups. 3) The open source community continuously optimizes Linux performance, and many high-performance web servers such as Nginx are developed on Linux. By contrast, Windows performs well when handling ASP.NET applications and provides better development tools and commercial support.
 How to choose a Linux distro for a beginner?
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:09 AM
How to choose a Linux distro for a beginner?
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Newbie users should first clarify their usage requirements when choosing a Linux distribution. 1. Choose Ubuntu or LinuxMint for daily use; programming and development are suitable for Manjaro or Fedora; use Lubuntu and other lightweight systems for old devices; recommend CentOSStream or Debian to learn the underlying principles. 2. Stability is preferred for UbuntuLTS or Debian; you can choose Arch or Manjaro to pursue new features. 3. In terms of community support, Ubuntu and LinuxMint are rich in resources, and Arch documents are technically oriented. 4. In terms of installation difficulty, Ubuntu and LinuxMint are relatively simple, and Arch is suitable for those with basic needs. It is recommended to try it first and then decide.
 How to add a new disk to Linux
Jun 27, 2025 am 12:15 AM
How to add a new disk to Linux
Jun 27, 2025 am 12:15 AM
The steps to add a new hard disk to the Linux system are as follows: 1. Confirm that the hard disk is recognized and use lsblk or fdisk-l to check; 2. Use fdisk or parted partitions, such as fdisk/dev/sdb and create and save; 3. Format the partition to a file system, such as mkfs.ext4/dev/sdb1; 4. Use the mount command for temporary mounts, such as mount/dev/sdb1/mnt/data; 5. Modify /etc/fstab to achieve automatic mount on the computer, and test the mount first to ensure correctness. Be sure to confirm data security before operation to avoid hardware connection problems.





