How to combine Go with Gin to export Mysql data to Excel table
May 26, 2023 pm 09:15 PM1. To achieve the goal
Golang uses excelize to export the table to the browser for downloading or save it locally.
The subsequent import will also be written here
2. The library used
go get github.com/xuri/excelize/v2
3. Project directory
go-excel ├─ app │ ├─ excelize │ │ └─ excelize.go │ ├─ model │ │ └─ sysUser.go │ └─ service │ └─ userService.go ├─ common │ └─ mysql.go ├─ go.mod ├─ go.sum ├─ main.go └─ setting.json
4. Main code writing
viper is used to read the configuration file
4.1. excelize.go(main Tools)
The ExportExcelByStruct function was copied directly from the Internet. It took a while to study his writing method, so I also wrote it for everyone to learn
import (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"net/url"
"reflect"
"strconv"
"time"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/xuri/excelize/v2"
)
var (
defaultSheetName = "Sheet1" //默認(rèn)Sheet名稱
defaultHeight = 25.0 //默認(rèn)行高度
)
type lzExcelExport struct {
file *excelize.File
sheetName string //可定義默認(rèn)sheet名稱
}
func NewMyExcel() *lzExcelExport {
return &lzExcelExport{file: createFile(), sheetName: defaultSheetName}
}
//導(dǎo)出基本的表格
func (l *lzExcelExport) ExportToPath(params []map[string]string, data []map[string]interface{}, path string) (string, error) {
l.export(params, data)
name := createFileName()
filePath := path + "/" + name
err := l.file.SaveAs(filePath)
return filePath, err
}
//導(dǎo)出到瀏覽器。此處使用的gin框架 其他框架可自行修改ctx
func (l *lzExcelExport) ExportToWeb(params []map[string]string, data []map[string]interface{}, c *gin.Context) {
l.export(params, data)
buffer, _ := l.file.WriteToBuffer()
//設(shè)置文件類型
c.Header("Content-Type", "application/vnd.ms-excel;charset=utf8")
//設(shè)置文件名稱
c.Header("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename="+url.QueryEscape(createFileName()))
_, _ = c.Writer.Write(buffer.Bytes())
}
//設(shè)置首行
func (l *lzExcelExport) writeTop(params []map[string]string) {
topStyle, _ := l.file.NewStyle(`{"font":{"bold":true},"alignment":{"horizontal":"center","vertical":"center"}}`)
var word = 'A'
//首行寫(xiě)入
for _, conf := range params {
title := conf["title"]
width, _ := strconv.ParseFloat(conf["width"], 64)
line := fmt.Sprintf("%c1", word)
//設(shè)置標(biāo)題
_ = l.file.SetCellValue(l.sheetName, line, title)
//列寬
_ = l.file.SetColWidth(l.sheetName, fmt.Sprintf("%c", word), fmt.Sprintf("%c", word), width)
//設(shè)置樣式
_ = l.file.SetCellStyle(l.sheetName, line, line, topStyle)
word++
}
}
//寫(xiě)入數(shù)據(jù)
func (l *lzExcelExport) writeData(params []map[string]string, data []map[string]interface{}) {
lineStyle, _ := l.file.NewStyle(`{"alignment":{"horizontal":"center","vertical":"center"}}`)
//數(shù)據(jù)寫(xiě)入
var j = 2 //數(shù)據(jù)開(kāi)始行數(shù)
for i, val := range data {
//設(shè)置行高
_ = l.file.SetRowHeight(l.sheetName, i+1, defaultHeight)
//逐列寫(xiě)入
var word = 'A'
for _, conf := range params {
valKey := conf["key"]
line := fmt.Sprintf("%c%v", word, j)
isNum := conf["is_num"]
//設(shè)置值
if isNum != "0" {
valNum := fmt.Sprintf("'%v", val[valKey])
_ = l.file.SetCellValue(l.sheetName, line, valNum)
} else {
_ = l.file.SetCellValue(l.sheetName, line, val[valKey])
}
//設(shè)置樣式
_ = l.file.SetCellStyle(l.sheetName, line, line, lineStyle)
word++
}
j++
}
//設(shè)置行高 尾行
_ = l.file.SetRowHeight(l.sheetName, len(data)+1, defaultHeight)
}
func (l *lzExcelExport) export(params []map[string]string, data []map[string]interface{}) {
l.writeTop(params)
l.writeData(params, data)
}
func createFile() *excelize.File {
f := excelize.NewFile()
// 創(chuàng)建一個(gè)默認(rèn)工作表
sheetName := defaultSheetName
index := f.NewSheet(sheetName)
// 設(shè)置工作簿的默認(rèn)工作表
f.SetActiveSheet(index)
return f
}
func createFileName() string {
name := time.Now().Format("2006-01-02-15-04-05")
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
return fmt.Sprintf("excle-%v-%v.xlsx", name, rand.Int63n(time.Now().Unix()))
}
//excel導(dǎo)出(數(shù)據(jù)源為Struct) []interface{}
func (l *lzExcelExport) ExportExcelByStruct(titleList []string, data []interface{}, fileName string, sheetName string, c *gin.Context) error {
l.file.SetSheetName("Sheet1", sheetName)
header := make([]string, 0)
for _, v := range titleList {
header = append(header, v)
}
rowStyleID, _ := l.file.NewStyle(`{"font":{"color":"#666666","size":13,"family":"arial"},"alignment":{"vertical":"center","horizontal":"center"}}`)
_ = l.file.SetSheetRow(sheetName, "A1", &header)
_ = l.file.SetRowHeight("Sheet1", 1, 30)
length := len(titleList)
headStyle := Letter(length)
var lastRow string
var widthRow string
for k, v := range headStyle {
if k == length-1 {
lastRow = fmt.Sprintf("%s1", v)
widthRow = v
}
}
if err := l.file.SetColWidth(sheetName, "A", widthRow, 30); err != nil {
fmt.Print("錯(cuò)誤--", err.Error())
}
rowNum := 1
for _, v := range data {
t := reflect.TypeOf(v)
fmt.Print("--ttt--", t.NumField())
value := reflect.ValueOf(v)
row := make([]interface {
}, 0)
for l := 0; l < t.NumField(); l++ {
val := value.Field(l).Interface()
row = append(row, val)
}
rowNum++
err := l.file.SetSheetRow(sheetName, "A"+strconv.Itoa(rowNum), &row)
_ = l.file.SetCellStyle(sheetName, fmt.Sprintf("A%d", rowNum), fmt.Sprintf("%s", lastRow), rowStyleID)
if err != nil {
return err
}
}
disposition := fmt.Sprintf("attachment; filename=%s.xlsx", url.QueryEscape(fileName))
c.Writer.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/octet-stream")
c.Writer.Header().Set("Content-Disposition", disposition)
c.Writer.Header().Set("Content-Transfer-Encoding", "binary")
c.Writer.Header().Set("Access-Control-Expose-Headers", "Content-Disposition")
return l.file.Write(c.Writer)
}
// Letter 遍歷a-z
func Letter(length int) []string {
var str []string
for i := 0; i < length; i++ {
str = append(str, string(rune('A'+i)))
}
return str
}4.2. userService.go (accepting requests)
The exported functions have been tested and are ok. They can be used directly. Just change the data to your own.
I also included the things to note. Written, lightning protection! !
import (
"go-excel/app/excelize"
"go-excel/app/model"
config "go-excel/common"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
//獲取所有用戶數(shù)據(jù)-excel
func GetAllUserExportToWeb(ctx *gin.Context) {
var users []model.TUser
db := config.GetDB()
db.Find(&users)
//定義首行標(biāo)題
dataKey := make([]map[string]string, 0)
dataKey = append(dataKey, map[string]string{
"key": "id",
"title": "索引",
"width": "20",
"is_num": "0",
})
dataKey = append(dataKey, map[string]string{
"key": "username",
"title": "用戶名",
"width": "20",
"is_num": "0",
})
dataKey = append(dataKey, map[string]string{
"key": "remark",
"title": "備注",
"width": "20",
"is_num": "0",
})
//填充數(shù)據(jù)
data := make([]map[string]interface{}, 0)
if len(users) > 0 {
for _, v := range users {
data = append(data, map[string]interface{}{
"id": v.ID,
"username": v.Username,
"remark": v.Remark,
})
}
}
ex := excelize.NewMyExcel()
// ex.ExportToWeb(dataKey, data, ctx)
//保存到D盤(pán)
ex.ExportToPath(dataKey, data, "D:/")
}
//excel 導(dǎo)出
func GetUserExcelByMap(ctx *gin.Context) {
var users []model.TUser
db := config.GetDB()
db.Find(&users)
titles := []string{"ID", "用戶名", "備注"}
ex := excelize.NewMyExcel()
var datas []interface{}
for _, v := range users {
//這里最好新建一個(gè)struct 和titles一致,不然users里面的多余的字段也會(huì)寫(xiě)進(jìn)去
datas = append(datas, model.TUser{
ID: v.ID,
Username: v.Username,
Remark: v.Remark,
})
}
ex.ExportExcelByStruct(titles, datas, "用戶數(shù)據(jù)", "用戶", ctx)
}4.2. Test results
GetAllUserExportToWeb
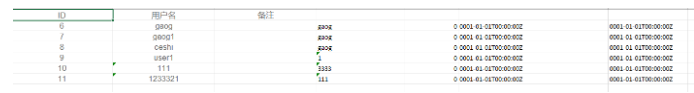
GetUserExcelByMap
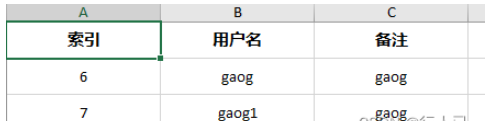
The above is the detailed content of How to combine Go with Gin to export Mysql data to Excel table. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How do you read a file line by line in Go?
Aug 02, 2025 am 05:17 AM
How do you read a file line by line in Go?
Aug 02, 2025 am 05:17 AM
Using bufio.Scanner is the most common and efficient method in Go to read files line by line, and is suitable for handling scenarios such as large files, log parsing or configuration files. 1. Open the file using os.Open and make sure to close the file via deferfile.Close(). 2. Create a scanner instance through bufio.NewScanner. 3. Call scanner.Scan() in the for loop to read line by line until false is returned to indicate that the end of the file is reached or an error occurs. 4. Use scanner.Text() to get the current line content (excluding newline characters). 5. Check scanner.Err() after the loop is over to catch possible read errors. This method has memory effect
 Troubleshooting MySQL Connection String and Driver Issues
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:30 AM
Troubleshooting MySQL Connection String and Driver Issues
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:30 AM
When you cannot connect to the MySQL database, you should first check the connection string format and driver version. 1. Check whether the connection string format is correct. Common errors include port number, database name, parameter symbol errors and driver prefix errors. It is recommended to use the generation tool to verify the format and pay attention to escaping special characters; 2. Ensure that the correct JDBC or database driver is used, different drivers are used in different languages. Pay attention to version compatibility, dependency configuration and driver class name changes, and check the log to confirm whether the driver is loading successfully; 3. Check remote access permissions and firewall settings, including MySQL user permissions, bind-address configuration and server firewall rules, and need to open port 3306 and remote access permissions; 4. Use a simple test program to quickly verify the connection.
 What is the standard project layout for a Go application?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 02:31 PM
What is the standard project layout for a Go application?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 02:31 PM
The answer is: Go applications do not have a mandatory project layout, but the community generally adopts a standard structure to improve maintainability and scalability. 1.cmd/ stores the program entrance, each subdirectory corresponds to an executable file, such as cmd/myapp/main.go; 2.internal/ stores private code, cannot be imported by external modules, and is used to encapsulate business logic and services; 3.pkg/ stores publicly reusable libraries for importing other projects; 4.api/ optionally stores OpenAPI, Protobuf and other API definition files; 5.config/, scripts/, and web/ store configuration files, scripts and web resources respectively; 6. The root directory contains go.mod and go.sum
 What are build constraints in Go?
Jul 31, 2025 am 02:53 AM
What are build constraints in Go?
Jul 31, 2025 am 02:53 AM
BuildconstraintsinGoarecommentslike//go:buildthatcontrolfileinclusionduringcompilationbasedonconditionssuchasOS,architecture,orcustomtags.2.TheyareplacedbeforethepackagedeclarationwithablanklineinbetweenandsupportBooleanoperatorslike&&,||,and
 How do you work with JSON in Go?
Jul 31, 2025 am 08:12 AM
How do you work with JSON in Go?
Jul 31, 2025 am 08:12 AM
Go provides encoding/json packages to easily process JSON data. 1. Use json.Marshal to encode the Go structure or map into JSON. The structure field must start with capital letters and the key name can be specified through the json: "name" tag. Omitempty can make the zero value field omitted; 2. Use json.Unmarshal to decode the JSON data into the Go variable, and the variable pointer must be passed in order to modify the value; 3. For JSON with unknown structure, it can be decoded into map[string]interface{} or interface{}, but type assertions are required when accessing; 4. Handle large JSO
 How do you handle routing in a Go web application?
Aug 02, 2025 am 06:49 AM
How do you handle routing in a Go web application?
Aug 02, 2025 am 06:49 AM
Routing in Go applications depends on project complexity. 1. The standard library net/httpServeMux is suitable for simple applications, without external dependencies and is lightweight, but does not support URL parameters and advanced matching; 2. Third-party routers such as Chi provide middleware, path parameters and nested routing, which is suitable for modular design; 3. Gin has excellent performance, built-in JSON processing and rich functions, which is suitable for APIs and microservices. It should be selected based on whether flexibility, performance or functional integration is required. Small projects use standard libraries, medium and large projects recommend Chi or Gin, and finally achieve smooth expansion from simple to complex.
 Implementing MySQL Data Lineage Tracking
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:37 PM
Implementing MySQL Data Lineage Tracking
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:37 PM
The core methods for realizing MySQL data blood ties tracking include: 1. Use Binlog to record the data change source, enable and analyze binlog, and trace specific business actions in combination with the application layer context; 2. Inject blood ties tags into the ETL process, and record the mapping relationship between the source and the target when synchronizing the tool; 3. Add comments and metadata tags to the data, explain the field source when building the table, and connect to the metadata management system to form a visual map; 4. Pay attention to primary key consistency, avoid excessive dependence on SQL analysis, version control data model changes, and regularly check blood ties data to ensure accurate and reliable blood ties tracking.
 How to check if a key exists in a map in Go?
Jul 31, 2025 am 06:56 AM
How to check if a key exists in a map in Go?
Jul 31, 2025 am 06:56 AM
In Go, using the "comma ok" idiom, you can safely check whether the key exists: 1. Get the value and boolean flags through value, ok:=myMap[key]; 2. If you are true, you can safely delete existing keys. This method can accurately distinguish between the absence of a key and the value is zero, which is a standard practice in Go to check the existence of a key.






