 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 HTML Tutorial
HTML Tutorial
 Best practices and common problem solutions for deploying web projects on Tomcat
Best practices and common problem solutions for deploying web projects on Tomcat
Best practices and common problem solutions for deploying web projects on Tomcat
Dec 29, 2023 am 08:21 AM
Best practices and common problem solutions for Tomcat deployment of Web projects
Introduction:
Tomcat as a lightweight Java application server, in Web applications It has been widely used in development. This article will introduce the best practices and common problem solving methods for Tomcat deployment of web projects, and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand and apply.
1. Project directory structure planning
Before deploying the Web project, we need to plan the directory structure of the project. Generally speaking, we can organize projects as follows:
-
WEB-INF directory:
- web.xml file: This file is the description of the Web project File, configure the mapping relationship between basic information of the project and components such as Servlet and Filter.
- lib directory: used to store dependent libraries (JAR files) required by the project.
- classes directory: used to store Java class files (.class files) and other resource files of the project.
-
Static resource directory:
- css directory: used to store the CSS style files of the project.
- js directory: used to store JavaScript files of the project.
- images directory: used to store image files of the project.
2. Tomcat configuration and deployment
Before deploying the Web project, we need to perform some Tomcat configuration. The specific steps are as follows:
- Set the JDK environment: Make sure that the JDK environment used by Tomcat has been configured correctly, which can be achieved by setting the JAVA_HOME environment variable.
- Confirm the Tomcat directory structure: Check whether the Tomcat directory structure meets the basic configuration requirements, including conf (configuration file), webapps (application directory), etc.
- Configure server.xml: Modify the conf/server.xml file in the Tomcat installation directory, configure the port number and other related parameters that Tomcat listens to, and ensure that there is no conflict with other services.
- Deploy the project: Copy the WAR file of the web project to Tomcat's webapps directory, and Tomcat will automatically decompress and deploy the project.
- Start Tomcat: Start Tomcat by running the catalina.sh (Linux) or catalina.bat (Windows) script.
3. Solutions to common problems and code examples
In the process of deploying Web projects on Tomcat, we may encounter some common problems. The following are some common problems and their solutions. Code example:
-
The project cannot be started or accessed:
- Confirm whether Tomcat starts successfully, which can be verified by accessing http://localhost:8080.
- Check whether the project's deployment path and file permissions are correct, and ensure that the project's directories and files have sufficient permissions.
-
The third-party library referenced in the project cannot be found:
- Place the JAR file of the third-party library in the project's WEB-INF/lib Under contents.
-
Add the dependency configuration on the library in the project's web.xml file, for example:
<listener> <listener-class>com.example.MyServletContextListener</listener-class> </listener>
Encoding appears in the project Question:
- In the tomcat/conf/server.xml file, set the URIEncoding property in Tomcat's Connector configuration to the correct encoding, such as UTF-8.
- In the project's web.xml file, configure the encoding filter to use the correct encoding by default, such as UTF-8.
The resource file cannot be loaded in the project:
- Confirm whether the resource file is placed in the correct path, for example, the image file is placed in In the project's images directory.
Configure the access path of the resource file in the project's web.xml file, for example:
<servlet> <servlet-name>ImageServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.example.ImageServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>ImageServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/images/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
Conclusion:
Tomcat deployment of Web projects is an important part of Web application development. Reasonable project directory structure planning, correct Tomcat configuration, and solutions to common problems are all keys to ensuring smooth deployment and operation of the project. Through the introduction and code examples of this article, I believe that readers will have a deeper understanding of the best practices and common problem solutions for Tomcat deployment of web projects. I hope it will be helpful to readers in developing web applications.
The above is the detailed content of Best practices and common problem solutions for deploying web projects on Tomcat. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Where is the root directory of the tomcat website?
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:27 AM
Where is the root directory of the tomcat website?
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:27 AM
The Tomcat website root directory is located in Tomcat's webapps subdirectory and is used to store web application files, static resources, and the WEB-INF directory; it can be found by looking for the docBase attribute in the Tomcat configuration file.
 How to deploy multiple projects in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:33 AM
How to deploy multiple projects in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:33 AM
To deploy multiple projects through Tomcat, you need to create a webapp directory for each project and then: Automatic deployment: Place the webapp directory in Tomcat's webapps directory. Manual deployment: Manually deploy the project in Tomcat's manager application. Once the project is deployed, it can be accessed by its deployment name, for example: http://localhost:8080/project1.
 How to configure domain name in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:52 AM
How to configure domain name in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:52 AM
To configure Tomcat to use a domain name, follow these steps: Create a server.xml backup. Open server.xml and add the Host element, replacing example.com with your domain name. Create an SSL certificate for the domain name (if required). Add an SSL connector in server.xml, change the port, keystore file, and password. Save server.xml. Restart Tomcat.
 eclipse project storage location
May 05, 2024 pm 07:36 PM
eclipse project storage location
May 05, 2024 pm 07:36 PM
Where Eclipse projects are stored depends on the project type and workspace settings. Java Project: Stored in the project folder within the workspace. Web project: stored in the project folder in the workspace, divided into multiple subfolders. Other project types: Files are stored in project folders within the workspace, and the organization may vary depending on the project type. The workspace location is located in "<home directory>/workspace" by default and can be changed through Eclipse preferences. To modify the project storage location, right-click the project and select the Resources tab in Properties.
 How to run two projects with different port numbers in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:00 AM
How to run two projects with different port numbers in tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:00 AM
Running projects with different port numbers on the Tomcat server requires the following steps: Modify the server.xml file and add a Connector element to define the port number. Add a Context element to define the application associated with the port number. Create a WAR file and deploy it to the corresponding directory (webapps or webapps/ROOT). Restart Tomcat to apply changes.
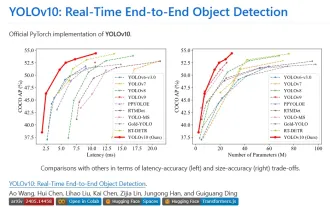 Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
1. Introduction Over the past few years, YOLOs have become the dominant paradigm in the field of real-time object detection due to its effective balance between computational cost and detection performance. Researchers have explored YOLO's architectural design, optimization goals, data expansion strategies, etc., and have made significant progress. At the same time, relying on non-maximum suppression (NMS) for post-processing hinders end-to-end deployment of YOLO and adversely affects inference latency. In YOLOs, the design of various components lacks comprehensive and thorough inspection, resulting in significant computational redundancy and limiting the capabilities of the model. It offers suboptimal efficiency, and relatively large potential for performance improvement. In this work, the goal is to further improve the performance efficiency boundary of YOLO from both post-processing and model architecture. to this end
 How to run html and jsp on tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:04 AM
How to run html and jsp on tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:04 AM
Tomcat can run HTML and JSP. The method is as follows: copy the HTML file to the corresponding subdirectory of the Tomcat directory and access it in the browser. Copy the JSP file to the corresponding subdirectory of the Tomcat directory, and use the <%@ page %> directive to specify the Java code and access it in the browser.
 Tomcat maximum number of connections and maximum number of threads
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:22 AM
Tomcat maximum number of connections and maximum number of threads
Apr 21, 2024 am 09:22 AM
The maximum number of Tomcat connections limits the number of clients connected at the same time, while the maximum number of threads limits the number of threads that can handle requests at the same time. These limits prevent server resource exhaustion and are configured by setting the maxConnections and maxThreads properties in server.xml to match server capacity and load.





