 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AMDo not use SQL statements to add multiple tables in Springboot Mybatis-plus
The preparation work for the problems I encountered is broken down by simulating thinking in the test environment: Create a BrandDTO object simulation with parameters Passing parameters in the background
Problems I encountered
We all know that it is extremely difficult to perform multi-table operations in Mybatis-plus. If you do not use Mybatis-plus- For tools like join, you can only configure the corresponding Mapper. Flexibility allows us to more flexibly modify the functions required by Party A.
But if I am going to do a very ordinary small project, which does not require any flexible changes, and I do not want to write SQL statements, I want to use Mybatis directly -plus function to add multi-table (one master and multiple copies) data, then what should I do?
Looking at the database, we can know that we have a product table, but productfor Product image, Product parameter and Product type are all one-to-many or many-to-one relationships, but I want our front-end to directly submit a form You can complete the addition of data in multiple tables. Multi-table operations are inevitable
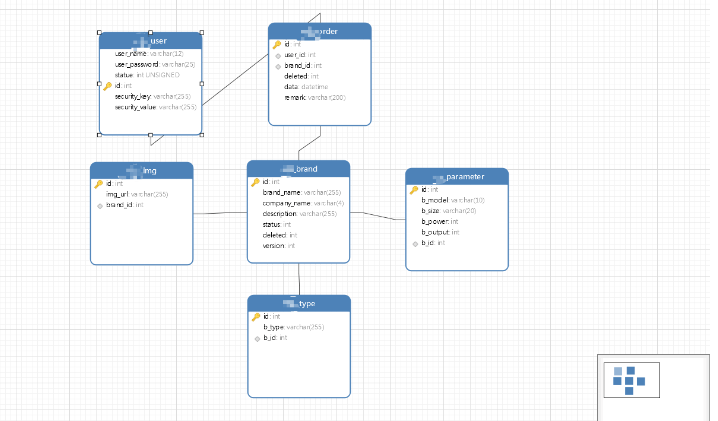
Preparation work
Because I have used mybatis before this operation -plus-join multi-table query operation, so I have generated a DTO entity class
@Data
public class BrandDTO {
private Integer id;
//類型表
private String type;
//商品表
private String brandName;
private String companyName;
private String description;
//圖片鏈接表
private List<Img> imgUrlList;
//參數(shù)表
private List<Parameter> parameterList;
}In this class you will wonder: Why don’t I directly encapsulate a Brand entity object?
Because I have used this class to perform join table queries before, and put the parameters of each entity class separately (there is no duplicate name hhhh), and this class needs to be displayed, so I added the attributes of the Brand class as they are, and The tpye corresponding to Brand should be many (type) to one (Brand), so I only encapsulated one here, but since Brand has a one-to-many relationship with Img and Parameter, I encapsulated them into a list< object >, In this way we got something similar to an intermediate class
Simulated in the test environment
We might as well think about it, with such a class, we only need to separate the parameters To add to each table, we need to imagine that we get a BrandDTO object encapsulating data, and then disassemble it and use the methods of the respective mapper interfaces to insert the table behavior
(First the interface must inherit the corresponding BaseMapper<> ;, you can perform quick operations. Of course, if you have a corresponding adding method in the interface, you can also do it, but since we use mybatis-plus, why do we have to go back and write the adding method ourselves?)
So, after After several repeated experiments, I got the following test method:
@Test
public void addBrand(){
Brand brand = new Brand();
Type type = new Type();
Img img = new Img();
Parameter parameter = new Parameter();
BrandDTO brandDTO = new BrandDTO();
brandDTO.setBrandName("測試商品3");
brandDTO.setCompanyName("廠家3");
brandDTO.setDescription("這是第二個(gè)個(gè)測試");
brandDTO.setType("第Ⅱ型");
List<Img> imgs =new ArrayList<>();
imgs.add(new Img("w/daw/daw/daww"));
imgs.add(new Img("xxwdAWd/dawd/wx"));
brandDTO.setImgUrlList(imgs);
List<Parameter> parameters = new ArrayList<>();
parameters.add(new Parameter("110","270*860*270",30,450));
parameters.add(new Parameter("120","170*4350*720",990,5530));
brandDTO.setParameterList(parameters);
List<Img> imgUrlList = brandDTO.getImgUrlList();
List<Parameter> parameterList = brandDTO.getParameterList();
brand.setBrandName(brandDTO.getBrandName());
brand.setCompanyName(brandDTO.getCompanyName());
brand.setDescription(brandDTO.getDescription());
brandMapper.insert(brand);
Integer id = brand.getId();
type.setBType(brandDTO.getType());
type.setBId(id);
typeMapper.insert(type);
for (Parameter parameterl : parameterList) {
parameter.setBModel(parameterl.getBModel());
parameter.setBOutput(parameterl.getBOutput());
parameter.setBSize(parameterl.getBSize());
parameter.setBId(id);
parameterMapper.insert(parameter);
}
for (Img imgl : imgUrlList) {
img.setImgUrl(imgl.getImgUrl());
img.setBrandId(id);
imgMapper.insert(img);
}
System.out.println(id);
}Thinking breakdown:
Next, I will decompose and express each part of the method body
Create A BrandDTO object with parameters
First we simulated a BrandDTO object encapsulating various parameters:
Type type = new Type();
Img img = new Img();
Parameter parameter = new Parameter();
BrandDTO brandDTO = new BrandDTO();
brandDTO.setBrandName("測試商品3");
brandDTO.setCompanyName("廠家3");
brandDTO.setDescription("這是第二個(gè)個(gè)測試");
brandDTO.setType("第Ⅱ型");
List<Img> imgs =new ArrayList<>();
//此操作能成功是因?yàn)槲以趯?yīng)的對象中生成了除了id屬性和外鍵屬性的有參構(gòu)造
imgs.add(new Img("w/daw/daw/daww"));
imgs.add(new Img("xxwdAWd/dawd/wx"));
brandDTO.setImgUrlList(imgs);
List<Parameter> parameters = new ArrayList<>();
//此操作能成功是因?yàn)槲以趯?yīng)的對象中生成了除了id屬性和外鍵屬性的有參構(gòu)造
parameters.add(new Parameter("110","270*860*270",30,450));
parameters.add(new Parameter("120","170*4350*720",990,5530));
brandDTO.setParameterList(parameters);This part is mainly the encapsulation of parameters, which is the work of the front end. Let us do the background work The server receives a BrandDTO object with parameters
Simulates passing parameters to the background
Takes out the corresponding parameters in each table
//取出ImgUrlList和ParameterList()
List<Img> imgUrlList = brandDTO.getImgUrlList();
List<Parameter> parameterList = brandDTO.getParameterList();
//單獨(dú)封裝brand對象
brand.setBrandName(brandDTO.getBrandName());
brand.setCompanyName(brandDTO.getCompanyName());
brand.setDescription(brandDTO.getDescription());
//調(diào)用對應(yīng)Mapper接口的insert方法(或者你自己寫的添加方法)
brandMapper.insert(brand);
//使用主鍵返回(要確保mybatis中設(shè)置了主鍵自增并且在各個(gè)實(shí)體類中聲明了主鍵屬性)
Integer id = brand.getId();After the above operations, we report to Brand A row of information is added to the table, and the primary key is returned.
So our other tables know the ID of the corresponding product, and can use this ID to define the foreign key ID in the table:
(Please note that in this test class, I injected the Mapper interface of each entity class that I need to use, so I can call the insert method)
//向Type表中添加數(shù)據(jù)并指定外鍵(BrandID)的id
type.setBType(brandDTO.getType());
type.setBId(id);
typeMapper.insert(type);
//向Paramater表中添加數(shù)據(jù)并指定外鍵(BrandID)的id
for (Parameter parameterl : parameterList) {
parameter.setBModel(parameterl.getBModel());
parameter.setBOutput(parameterl.getBOutput());
parameter.setBSize(parameterl.getBSize());
parameter.setBId(id);
parameterMapper.insert(parameter);
}
//向Img表中添加數(shù)據(jù)并指定外鍵(BrandID)的id
for (Img imgl : imgUrlList) {
img.setImgUrl(imgl.getImgUrl());
img.setBrandId(id);
imgMapper.insert(img);
}Use a loop Add, we can add the data in the object to each table one by one. Next, we need to use the console to get the primary key id corresponding to the product we added:
System.out.println(id);
After that we run, what I got here The data is 3, and then we call the method of querying products by ID:
I am using Apifox here:
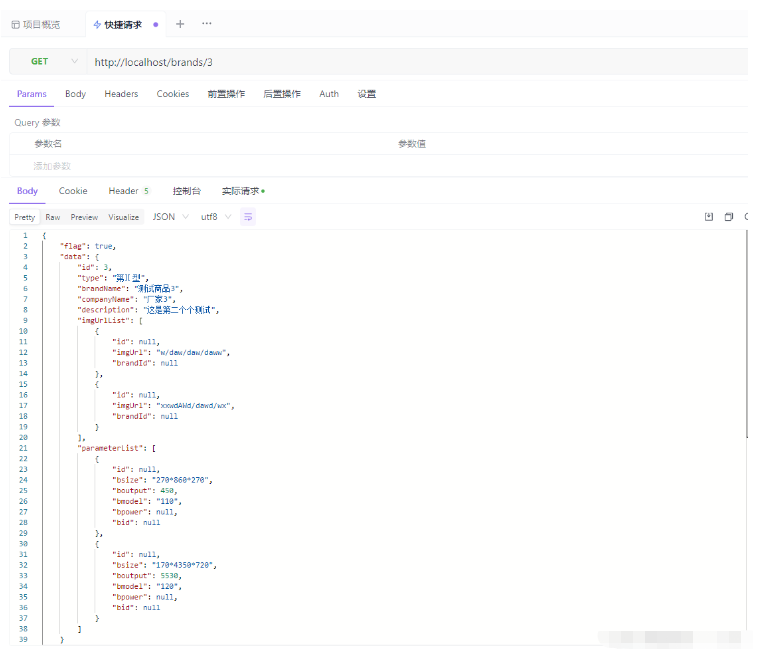
It can be seen that our information has been inserted into the table The return value part is null because the multi-table query I wrote has some small bugs, but there is still data in the database. It can be seen that this test is successful. Next, just CV the code to the corresponding service. The controller layer can simulate passing in a Json object to check whether it is feasible!
The above is the detailed content of How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 The Purpose of SQL: Interacting with MySQL Databases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:12 AM
The Purpose of SQL: Interacting with MySQL Databases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:12 AM
SQL is used to interact with MySQL database to realize data addition, deletion, modification, inspection and database design. 1) SQL performs data operations through SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE statements; 2) Use CREATE, ALTER, DROP statements for database design and management; 3) Complex queries and data analysis are implemented through SQL to improve business decision-making efficiency.
 SQL: The Language, MySQL: The Database Management System
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AM
SQL: The Language, MySQL: The Database Management System
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The relationship between SQL and MySQL is: SQL is a language used to manage and operate databases, while MySQL is a database management system that supports SQL. 1.SQL allows CRUD operations and advanced queries of data. 2.MySQL provides indexing, transactions and locking mechanisms to improve performance and security. 3. Optimizing MySQL performance requires attention to query optimization, database design and monitoring and maintenance.
 MySQL: A Practical Application of SQL
May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL: A Practical Application of SQL
May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL is popular because of its excellent performance and ease of use and maintenance. 1. Create database and tables: Use the CREATEDATABASE and CREATETABLE commands. 2. Insert and query data: operate data through INSERTINTO and SELECT statements. 3. Optimize query: Use indexes and EXPLAIN statements to improve performance.
 SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL is a standard language for managing relational databases, while MySQL is a database management system that uses SQL. SQL defines ways to interact with a database, including CRUD operations, while MySQL implements the SQL standard and provides additional features such as stored procedures and triggers.
 SQL and MySQL: Understanding the Relationship
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
SQL and MySQL: Understanding the Relationship
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
The relationship between SQL and MySQL is the relationship between standard languages ??and specific implementations. 1.SQL is a standard language used to manage and operate relational databases, allowing data addition, deletion, modification and query. 2.MySQL is a specific database management system that uses SQL as its operating language and provides efficient data storage and management.
 SQL and phpMyAdmin: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL and phpMyAdmin: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Beginners can learn SQL and phpMyAdmin from scratch. 1) Create database and tables: Create a new database in phpMyAdmin and create tables using SQL commands. 2) Execute basic query: Use SELECT statement to query data from the table. 3) Optimization and best practices: Create indexes, avoid SELECT*, use transactions, and regularly back up databases.
 phpMyAdmin: Unveiling Its Relationship to SQL
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:11 AM
phpMyAdmin: Unveiling Its Relationship to SQL
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:11 AM
phpMyAdmin implements the operation of the database through SQL commands. 1) phpMyAdmin communicates with the database server through PHP scripts, generates and executes SQL commands. 2) Users can enter SQL commands in the SQL editor for query and complex operations. 3) Performance optimization suggestions include optimizing SQL queries, creating indexes and using pagination. 4) Best practices include regular backups, ensuring security and using version control.
 Comparing SQL and MySQL: Syntax and Features
May 07, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Comparing SQL and MySQL: Syntax and Features
May 07, 2025 am 12:11 AM
The difference and connection between SQL and MySQL are as follows: 1.SQL is a standard language used to manage relational databases, and MySQL is a database management system based on SQL. 2.SQL provides basic CRUD operations, and MySQL adds stored procedures, triggers and other functions on this basis. 3. SQL syntax standardization, MySQL has been improved in some places, such as LIMIT used to limit the number of returned rows. 4. In the usage example, the query syntax of SQL and MySQL is slightly different, and the JOIN and GROUPBY of MySQL are more intuitive. 5. Common errors include syntax errors and performance issues. MySQL's EXPLAIN command can be used for debugging and optimizing queries.





