
Introduction: Starting as a personal project in the mid-1990s, PHP has grown into one of the most popular web development languages, serving small and medium-sized developers. Supporting everything from blogs to large enterprise applications.
PHP This language has experienced amazing iterative changes in the past 30 years. Over the past 10 years, PHP has changed in ways we couldn't have imagined.
Every New Year I will write an article about the current situation of PHP, looking back and looking forward to the future. Let's start now!
PHP Foundation
In the past, I usually started with a summary of the latest PHP version. However, this time I want to focus on PHP Foundation first.

It has been more than a year since the PHP Foundation was established. It consists of a team of 10 volunteers plus 6 developers. Get paid to work on the PHP language.
Last year, I wrote this:
Now that Nikita (a kernel developer) has left, I am a little worried. But he's definitely not the only one able to work on core PHP, he's done a lot of work on PHP 8.0 and 8.1 over the past few years.
I hope the PHP Foundation can catch up soon and have enough core developers free to work on PHP within the next year.
PHP 8.2 is already in development, although not many RFCs have been drafted yet.
I wouldn’t be wrong to think that 2022 will not be the most exciting year for PHP, but rather a year of increased stability.
I think it's fair to say that the PHP Foundation is now functioning properly. They recently released their 2022 report, which shows a pretty impressive set of numbers:
$580,000 raised in 2022
Foundation 6 developers will be paid for work on the PHP core
Foundation members completed nearly half of the commits in php-src
They created 8 new RFCs, only one of which failed
I think the PHP Foundation is one of the best things to happen to PHP. I hope they improve the language further in 2023. If you work for a company that uses PHP, I highly recommend you consider donating some.
PHP 8.2
Let’s talk about using PHP 8.2. It's often considered a smaller version by developers, but it actually has a lot of nice features.
Here are a few examples:
ReadOnly class (ReadOnly):
readonly?class?PostData
{
public?function?__construct(
public?string?$title,
public?string?$author,
public?string?$body,
public?DateTimeImmutable?$createdAt,
public?PostState?$state,
????)?{}
}
New random generator:
$rng?=?$is_production
??????new?Random\Engine\Secure()
????:?new?Random\Engine\Mt19937(1234);
$randomizer?=?new?Random\Randomizer($rng);
$randomizer->shuffleString('foobar');True and false independent of null:
function?alwaysFalse():?false
{
????return?false;
}Disjunctive normal form type:
function?generateSlug((HasTitle&HasId)|null?$post)
{?/*?…?*/?}
編輯參數(shù):
function?connect(
????string?$user,
????#[\SensitiveParameter]?string?$password
)?{
//?…
}Of course, there are more, worth exploring.
Consider how crazy PHP has grown over the years. I did some comparisons and the differences are clearly shown below:
Ecosystem
Like every year, I should mention Packagist, which is PHP’s package manager, so far this year it lists 361,000 packages, 60,000 more than last year:
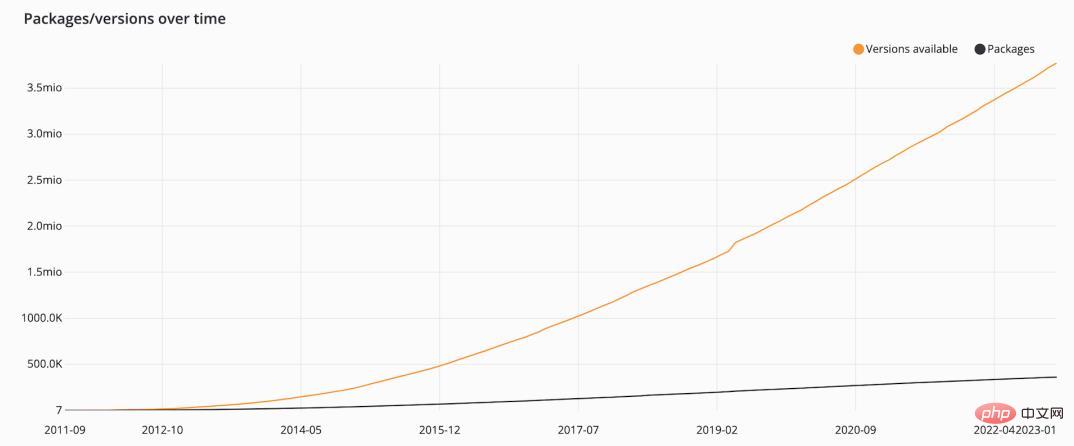
Well, by the way, recently Packagist passed the milestone of processing over 50 billion installations. Congratulations Packagist!I just checked and Packagist’s current installation volume is 74,492,061,634 times. That’s 24 billion installs in a year and 2 billion monthly installs. To sum up: the PHP ecosystem is growing rapidly. Twice a year, I publish version statistics. In these posts, I analyze PHP version usage across the community based on data from Packagist. I'd like to share the chart from that post again: a timeline from 2013 to the present, showing the usage history of each version.
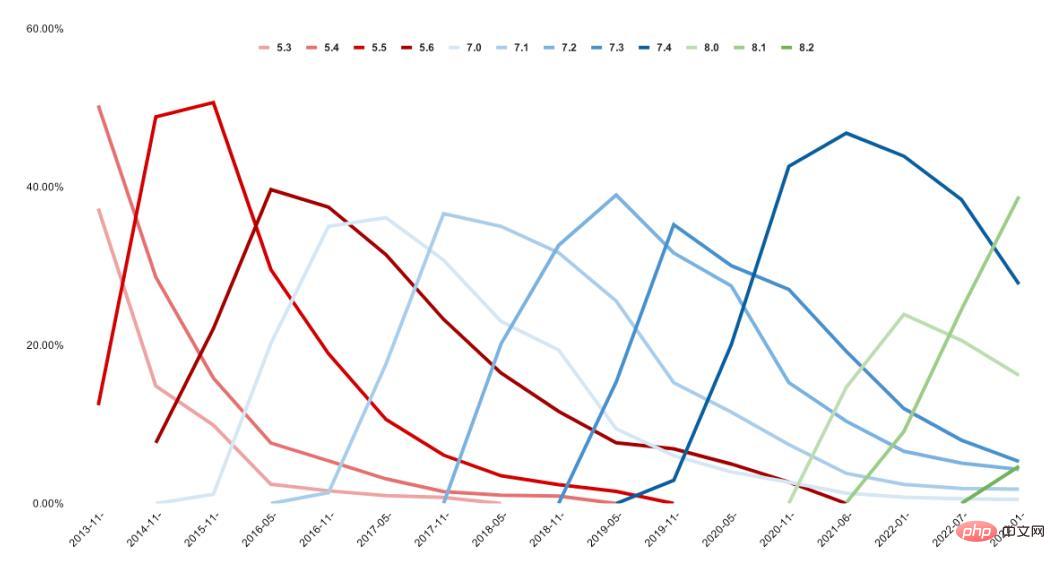
This data beautifully visualizes the division within the PHP community: one part keeps pace with modern PHP, while the other part is helplessly left behind.
When it comes to upgrading, I want to mention one tool in particular: Rector.
Rector is a free automation tool that helps upgrade your PHP code base. All it requires is a small amount of configuration and it does a lot of the work for you.
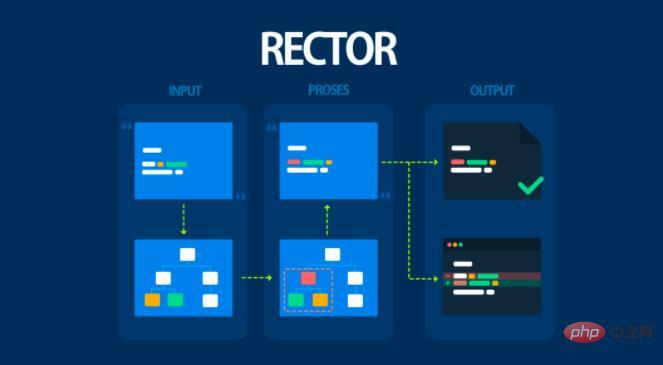
I recently used it to update my community-driven content aggregator, Aggregate to PHP 8.2, and it was really fun and easy to use.
After posting my version stats post, several people told me that they hadn't updated yet and were stuck on PHP 7.*, and I asked them why? They told me it was just too much manual labor. Interestingly, no one has even tried to use tools like Rector to help them...
I firmly believe that a "programming language" is more than just a compiler: it plays an equal role in defining a "programming language" Tools and ecosystem, I really think a lot of people, projects, and businesses would benefit if they looked into using an automation tool like Rector.
Since I’m talking about the ecosystem, I can’t help but mention the two largest frameworks for PHP: Laravel and Symfony.
Laravel has grown tremendously over the past few years. They now employ 8 full-time developers to develop the framework and its ecosystem. On top of that, JetBrains’ Development Survey reports that 67% of PHP developers use Laravel.
While Symfony may be less popular as a framework today compared to Laravel, it is still one of the most mature and stable frameworks in the PHP community. It's more commonly used for enterprise application development, but its standalone components are popular throughout the PHP ecosystem - Laravel also has some dependencies on Symfony components, so it's not surprising that many Symfony packages make it onto Packagist's top packages list No surprise.
I should also mention WordPress. To be honest, I have a love-hate relationship with WordPress. As a user, WordPress is great. It's so simple to install and use, and I think it's earned every ounce of popularity over the years. As a developer, though, WordPress makes me sad. The inability to keep up with modern and secure PHP versions casts a pall over the entire PHP community.
Currently, WordPress only provides beta support for PHP 8.0. Now, to be clear: PHP 8.0 was released in 2020 and reached end of life 3 years later - and WordPress doesn't support it yet... Of course, not properly supporting newer PHP versions is There are reasons, and it should be up to the user to decide whether they are correct. My personal opinion is that the decision to insist on backwards compatibility like WordPress is primarily business driven: a large part of WordPress is the commercial part, and a large part of their customer base runs older PHP versions. It's a vicious cycle, with both sides hindering each other and, to a certain extent, hindering the development of the entire PHP community.
On the other hand, we should recognize the fact that after almost 20 years, not many software projects are as popular and relevant as WordPress, so maybe their strategy regarding backwards compatibility is correct ?
Super EpisodeFinally, I can’t help but mention my long-term dream for PHP.
I'm writing it now, and I hope it will one day become a reality: a superset of PHP, with proper IDE and static analyzer support.
There are many reasons why I hope it happens. You can read and listen to them if you want, but I really hope it becomes a reality. It will be some time before we see a widely accepted and supported superset in 2023, but some small steps have already begun. I'll definitely be keeping an eye on PXP, it will push things in a more right direction.
To sum up, I feel that all developers will love 2023! One final note, just in case you're new here, I'm Brent, a developer evangelist at JetBrains.
Note: The original English address is: https://stitcher.io/blog/php-in-2023

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use PHP to build social sharing functions PHP sharing interface integration practice
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
How to use PHP to build social sharing functions PHP sharing interface integration practice
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
The core method of building social sharing functions in PHP is to dynamically generate sharing links that meet the requirements of each platform. 1. First get the current page or specified URL and article information; 2. Use urlencode to encode the parameters; 3. Splice and generate sharing links according to the protocols of each platform; 4. Display links on the front end for users to click and share; 5. Dynamically generate OG tags on the page to optimize sharing content display; 6. Be sure to escape user input to prevent XSS attacks. This method does not require complex authentication, has low maintenance costs, and is suitable for most content sharing needs.
 How to use PHP combined with AI to achieve text error correction PHP syntax detection and optimization
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:57 PM
How to use PHP combined with AI to achieve text error correction PHP syntax detection and optimization
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:57 PM
To realize text error correction and syntax optimization with AI, you need to follow the following steps: 1. Select a suitable AI model or API, such as Baidu, Tencent API or open source NLP library; 2. Call the API through PHP's curl or Guzzle and process the return results; 3. Display error correction information in the application and allow users to choose whether to adopt it; 4. Use php-l and PHP_CodeSniffer for syntax detection and code optimization; 5. Continuously collect feedback and update the model or rules to improve the effect. When choosing AIAPI, focus on evaluating accuracy, response speed, price and support for PHP. Code optimization should follow PSR specifications, use cache reasonably, avoid circular queries, review code regularly, and use X
 PHP creates a blog comment system to monetize PHP comment review and anti-brush strategy
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
PHP creates a blog comment system to monetize PHP comment review and anti-brush strategy
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
1. Maximizing the commercial value of the comment system requires combining native advertising precise delivery, user paid value-added services (such as uploading pictures, top-up comments), influence incentive mechanism based on comment quality, and compliance anonymous data insight monetization; 2. The audit strategy should adopt a combination of pre-audit dynamic keyword filtering and user reporting mechanisms, supplemented by comment quality rating to achieve content hierarchical exposure; 3. Anti-brushing requires the construction of multi-layer defense: reCAPTCHAv3 sensorless verification, Honeypot honeypot field recognition robot, IP and timestamp frequency limit prevents watering, and content pattern recognition marks suspicious comments, and continuously iterate to deal with attacks.
 PHP calls AI intelligent voice assistant PHP voice interaction system construction
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
PHP calls AI intelligent voice assistant PHP voice interaction system construction
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
User voice input is captured and sent to the PHP backend through the MediaRecorder API of the front-end JavaScript; 2. PHP saves the audio as a temporary file and calls STTAPI (such as Google or Baidu voice recognition) to convert it into text; 3. PHP sends the text to an AI service (such as OpenAIGPT) to obtain intelligent reply; 4. PHP then calls TTSAPI (such as Baidu or Google voice synthesis) to convert the reply to a voice file; 5. PHP streams the voice file back to the front-end to play, completing interaction. The entire process is dominated by PHP to ensure seamless connection between all links.
 How to use PHP to combine AI to generate image. PHP automatically generates art works
Jul 25, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to use PHP to combine AI to generate image. PHP automatically generates art works
Jul 25, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
PHP does not directly perform AI image processing, but integrates through APIs, because it is good at web development rather than computing-intensive tasks. API integration can achieve professional division of labor, reduce costs, and improve efficiency; 2. Integrating key technologies include using Guzzle or cURL to send HTTP requests, JSON data encoding and decoding, API key security authentication, asynchronous queue processing time-consuming tasks, robust error handling and retry mechanism, image storage and display; 3. Common challenges include API cost out of control, uncontrollable generation results, poor user experience, security risks and difficult data management. The response strategies are setting user quotas and caches, providing propt guidance and multi-picture selection, asynchronous notifications and progress prompts, key environment variable storage and content audit, and cloud storage.
 PHP realizes commodity inventory management and monetization PHP inventory synchronization and alarm mechanism
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
PHP realizes commodity inventory management and monetization PHP inventory synchronization and alarm mechanism
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
PHP ensures inventory deduction atomicity through database transactions and FORUPDATE row locks to prevent high concurrent overselling; 2. Multi-platform inventory consistency depends on centralized management and event-driven synchronization, combining API/Webhook notifications and message queues to ensure reliable data transmission; 3. The alarm mechanism should set low inventory, zero/negative inventory, unsalable sales, replenishment cycles and abnormal fluctuations strategies in different scenarios, and select DingTalk, SMS or Email Responsible Persons according to the urgency, and the alarm information must be complete and clear to achieve business adaptation and rapid response.
 Beyond the LAMP Stack: PHP's Role in Modern Enterprise Architecture
Jul 27, 2025 am 04:31 AM
Beyond the LAMP Stack: PHP's Role in Modern Enterprise Architecture
Jul 27, 2025 am 04:31 AM
PHPisstillrelevantinmodernenterpriseenvironments.1.ModernPHP(7.xand8.x)offersperformancegains,stricttyping,JITcompilation,andmodernsyntax,makingitsuitableforlarge-scaleapplications.2.PHPintegrateseffectivelyinhybridarchitectures,servingasanAPIgateway
 PHP integrated AI speech recognition and translator PHP meeting record automatic generation solution
Jul 25, 2025 pm 07:06 PM
PHP integrated AI speech recognition and translator PHP meeting record automatic generation solution
Jul 25, 2025 pm 07:06 PM
Select the appropriate AI voice recognition service and integrate PHPSDK; 2. Use PHP to call ffmpeg to convert recordings into API-required formats (such as wav); 3. Upload files to cloud storage and call API asynchronous recognition; 4. Analyze JSON results and organize text using NLP technology; 5. Generate Word or Markdown documents to complete the automation of meeting records. The entire process needs to ensure data encryption, access control and compliance to ensure privacy and security.





