 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 Popular video tutorials for getting started with Linux systems
Popular video tutorials for getting started with Linux systems
Popular video tutorials for getting started with Linux systems
May 17, 2020 pm 05:03 PMThe following linux basic tutorial column recommends a high-quality video tutorial for getting started with the Linux system. You can learn and watch it online for free!

This high-quality video tutorial is "Linux from Beginner to Master". This video tutorial will teach you how to install linux, understand the linux directory, The use of various Linux commands, the use of vi editor, etc. So if you are interested, follow us to learn Linux! ! !
The content chapters of this video tutorial are as follows:
Chapter 1 Linux Installation
1 Preparation
2 VMware Basic Configuration
3 Linux installation and general configuration
4 Disk partition and directory mounting
Chapter 2 Introduction to Linux
1 What is Linux
2 Linux Main Version
3 Advantages and Disadvantages of Linux
Chapter 3 Linux Desktop System
1 Graphical Interface Login
2 Common Desktop System
3 Remote login
Chapter 4 Linux file and directory management
1 File system architecture
2 Important directory description
3 Directory and file naming rules
4 ls command operation
5 File and directory operation
Chapter 5 Linux users, groups and permissions
1 Linux security model
2 User Overview
3 User Group Overview
4 Types of Permissions
5 Interpretation of Linux File and Directory Permissions
6 Linux Permissions Verification process
7 How to set Linux file and directory permissions
Chapter 6 Advanced Learning of Linux Users and Groups
1 Primary and Secondary Groups of Users Group
2 User management
3 User information check
4 Default permission control
5 User group management
Chapter 7 File Compression and Packaging
1 About File Compression and Packaging
2 Linux File Compression Instructions
3 Linux File Packaging Instructions
Chapter Chapter 8 Use of vi editor
1 Introduction to vi editor
2 Basic use of vi editor
3 Advanced use of vi editor
Chapter 9 Installation of Linux software
1 Introduction to YUM
2 Use of YUM
Chapter 10 Learning of bash shell
1 Bash shell Overview
2 Configuration of bash shell
3 Principles and functions of shell startup scripts
4 Data flow redirection and pipe commands
More high-quality For linux video tutorials, please visit linux tutorial! ! !
The above is the detailed content of Popular video tutorials for getting started with Linux systems. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Understand the four major IO scheduling algorithms of the Linux kernel in one article
Feb 14, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
Understand the four major IO scheduling algorithms of the Linux kernel in one article
Feb 14, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
The Linux kernel contains four types of IO schedulers, namely NoopIOscheduler, AnticipatoryIOscheduler, DeadlineIOscheduler and CFQIOscheduler. Typically, disk read and write latency is caused by the head moving to the cylinder. In order to solve this delay, the kernel mainly adopts two strategies: caching and IO scheduling algorithms. Scheduling Algorithm Concepts When a block of data is written to or read from a device, the request is placed in a queue waiting for completion. Each block device has its own queue. The I/O scheduler is responsible for maintaining the order of these queues to utilize the media more efficiently. The I/O scheduler will unordered I/O
 How to list block devices of Linux system using lsblk command
Feb 15, 2024 am 08:10 AM
How to list block devices of Linux system using lsblk command
Feb 15, 2024 am 08:10 AM
sblk is a command used to list all available block device information in a Linux system. Block devices refer to devices that can transmit data in blocks, such as hard disks, optical drives, USB flash drives, etc. The lsblk command can display the dependencies between block devices, as well as various attributes such as size, type, file system, mount point, etc. The lsblk command obtains information from the /sys virtual file system and udev database. If there is no udev database or lsblk is not compiled with udev support, then it will try to read the label, UUID and file system type from the block device, which requires root privileges. In this article, we will explain how to use the lsblk command to list the block devices of a Linux system to
 Secrets of the Linux root file system
Feb 15, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
Secrets of the Linux root file system
Feb 15, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
Linux is an open source, portable, and customizable operating system that is widely used in various fields, such as servers, desktops, embedded devices, etc. The core of Linux is the kernel, which is responsible for managing hardware resources and providing basic services. However, the kernel is not an independent entity and requires a file system to store and access various data and programs. A file system is a method of organizing and managing files. It defines the file's name, location, attributes, permissions and other information. In Linux, there are many different types of file systems, such as ext4, xfs, btrfs, etc., each of which has its own characteristics and advantages. However, among all file systems, there is a special file system, which is the foundation and core of the Linux system, which is
 What functions of the df command you don't know under Linux
Feb 14, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
What functions of the df command you don't know under Linux
Feb 14, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
Question: I want to use df command on Linux to check disk usage space. Can you give me some specific examples of the df command so I can make better use of it? On Linux, if you want to know how much space a specific file system takes up, or how much space is available for a specific file system, you can use the df command. The df command is a command that displays the available disk space of the file system for each filename parameter. If you do not specify any file names, the output will show the available space for all currently mounted file systems. By default, df displays disk space in 1K blocks. Linux has many command line or graphical interface tools that can tell you detailed information about current disk space usage, such as
 6 ways to configure Linux environment variables, recommended to collect!
Feb 14, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
6 ways to configure Linux environment variables, recommended to collect!
Feb 14, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Linux environment variable configuration When customizing software installation, it is often necessary to configure environment variables. Listed below are various methods of configuring environment variables. The environment description of all the examples below is as follows: System: Ubuntu14.0 User name: uusama Need to configure MySQL environment variables Path: /home/uusama/mysql/binLinux Reading environment variables Method of reading environment variables: The export command displays the current system definition All environment variables echo$PATH command outputs the value of the current PATH environment variable. The effect of executing these two commands is as follows uusama@ubuntu:~exportdeclare-xHOME="/home/uu
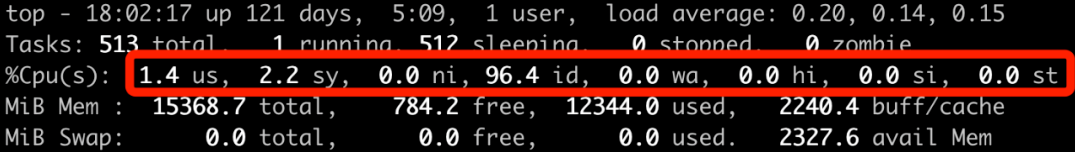 How is CPU utilization calculated in Linux?
Feb 15, 2024 am 11:15 AM
How is CPU utilization calculated in Linux?
Feb 15, 2024 am 11:15 AM
When observing the running status of online services on an online server, most people like to use the top command first to see the overall CPU utilization of the current system. For example, for a random machine, the utilization information displayed by the top command is as follows: This output result is simple to say, but complex, it is not so easy to understand it all. For example: Question 1: How is the utilization information output by top calculated? Is it accurate? Question 2: The ni column is nice. It outputs the CPU overhead when processing? Question 3: wa represents iowait, so is the CPU busy or idle during this period? Today we will conduct an in-depth study of CPU utilization statistics. Through today's study, you will not only understand c
 Overcoming obstacles: Solving GRUB and SHIM problems during Linux system startup
Feb 15, 2024 pm 06:54 PM
Overcoming obstacles: Solving GRUB and SHIM problems during Linux system startup
Feb 15, 2024 pm 06:54 PM
As a Linux user, you will inevitably encounter various problems during the startup process. Among them, the two tools GRUB and SHIM are often the most likely to cause problems. GRUB is the GNU boot loader, and SHIM is a trusted boot (SecureBoot) solution. The two work together in the Linux system startup process, but they also make some users confused and distressed. This article will introduce you how to solve GRUB and SHIM problems during Linux system startup, allowing you to easily overcome these obstacles. When using the efibootmgr-v command to modify the efi startup item, I don’t know whether to choose GRUBX64.EFI or SHIMX64.EFI when specifying the boot program.
 dd, a super powerful Linux command!
Mar 19, 2024 pm 01:52 PM
dd, a super powerful Linux command!
Mar 19, 2024 pm 01:52 PM
In Linux systems, the dd command is a highly respected tool with powerful and diverse functions, mainly used for file copying and conversion. Because it is widely used in disk copy and data copy operations, it is named the "disk copy" or "data copy" command. This article aims to comprehensively introduce the various uses of the dd command and provide rich sample code to help readers fully appreciate its functions and potential. The flexibility and customizability of the dd command make it a powerful tool for processing data conversion between files and devices, showing strong application value in various scenarios. Copy files The dd command can be used to copy files. The following example copies a file to another location: ddif=input.txtof=output.txt This will copy a file from i





