 Java
Java
 JavaInterview questions
JavaInterview questions
 Java multithreading and concurrency interview questions (Question 4, with answers)
Java multithreading and concurrency interview questions (Question 4, with answers)
Java multithreading and concurrency interview questions (Question 4, with answers)
Nov 26, 2019 pm 05:17 PM
4. ConcurrentLinkedQueue non-blocking unbounded linked list queue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue is a thread-safe queue, implemented based on the linked list structure, and is an unbounded queue. Theoretically, the length of the queue can be expanded infinitely.
Like other queues, ConcurrentLinkedQueue also uses the first-in-first-out (FIFO) enqueuing rule to sort elements. (Recommended study: java interview questions)
When we add elements to the queue, the newly inserted element will be inserted into the end of the queue; and when we get an element, it will Removed from the head of the queue.
Because ConcurrentLinkedQueue is a linked list structure, when entering the queue, the inserted elements are extended backwards in order to form a linked list; when dequeuing, they are obtained starting from the first element of the linked list and increasing in sequence;
It is worth noting that when using ConcurrentLinkedQueue, if it involves judging whether the queue is empty, remember not to use size()==0, because in the size() method, the entire linked list is traversed. In practice, when there are many queue elements, the size() method consumes a lot of performance and time. You can simply use isEmpty() to determine if the queue is empty.
public class ConcurrentLinkedQueueTest {<br/> public static int threadCount = 10;<br/> public static ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String>();<br/> static class Offer implements Runnable {<br/> public void run() {<br/> //不建議使用 queue.size()==0,影響效率。可以使用!queue.isEmpty()<br/> if (queue.size() == 0) {<br/> String ele = new Random().nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE) + "";<br/> queue.offer(ele);<br/> System.out.println("入隊(duì)元素為" + ele);<br/> }<br/> }<br/> }<br/> static class Poll implements Runnable {<br/> public void run() {<br/> if (!queue.isEmpty()) {<br/> String ele = queue.poll();<br/> System.out.println("出隊(duì)元素為" + ele);<br/> }<br/> }<br/> }<br/> public static void main(String[] agrs) {<br/> ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);<br/> for (int x = 0; x < threadCount; x++) {<br/> executorService.submit(new Offer());<br/> executorService.submit(new Poll());<br/> }<br/> executorService.shutdown();<br/> }<br/>}<br/>One output:
入隊(duì)元素為313732926<br/>出隊(duì)元素為313732926<br/>入隊(duì)元素為812655435<br/>出隊(duì)元素為812655435<br/>入隊(duì)元素為1893079357<br/>出隊(duì)元素為1893079357<br/>入隊(duì)元素為1137820958<br/>出隊(duì)元素為1137820958<br/>入隊(duì)元素為1965962048<br/>出隊(duì)元素為1965962048<br/>出隊(duì)元素為685567162<br/>入隊(duì)元素為685567162<br/>出隊(duì)元素為1441081163<br/>入隊(duì)元素為1441081163<br/>出隊(duì)元素為1627184732<br/>入隊(duì)元素為1627184732<br/>
ConcurrentLinkedQuere class diagram
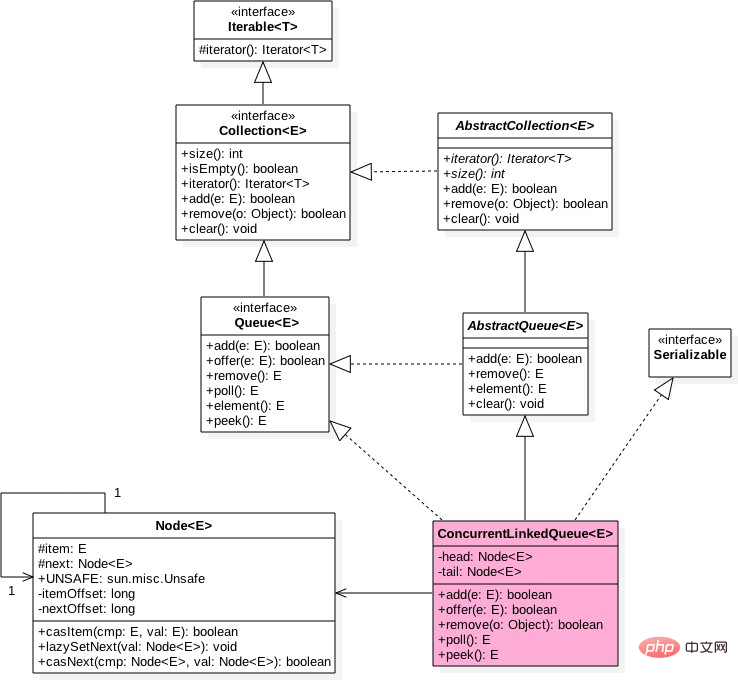
As shown in the figure There are two volatile Node nodes in ConcurrentLinkedQueue, which are used to store the first and last nodes of the list. The head node stores the node whose first item in the linked list is null, and the tail does not always point to the last node.
The Node node maintains a variable item internally to store the value of the node, and next is used to store the next node, thus linking it to a one-way unbounded list.
public ConcurrentLinkedQueue(){<br/> head=tail=new Node<E>(null);<br/>}<br/>When the above code is initialized, an empty node with item NULL will be constructed as the head and tail nodes of the linked list.
Offer operation The offer operation is to add an element at the end of the linked list.
Let’s take a look at the implementation principle.
public boolean offer(E e) {<br/> //e 為 null 則拋出空指針異常<br/> checkNotNull(e);<br/> //構(gòu)造 Node 節(jié)點(diǎn)構(gòu)造函數(shù)內(nèi)部調(diào)用 unsafe.putObject,后面統(tǒng)一講<br/> final Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e);<br/> //從尾節(jié)點(diǎn)插入<br/> for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t; ; ) {<br/> Node<E> q = p.next;<br/> //如果 q=null 說(shuō)明 p 是尾節(jié)點(diǎn)則插入<br/> if (q == null) {<br/> //cas 插入(1)<br/> if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) {<br/> //cas 成功說(shuō)明新增節(jié)點(diǎn)已經(jīng)被放入鏈表,然后設(shè)置當(dāng)前尾節(jié)點(diǎn)(包含 head,1,3,5.。。個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)為尾節(jié)點(diǎn))<br/> if (p != t)// hop two nodes at a time<br/> casTail(t, newNode); // Failure is OK. return true;<br/> }<br/> // Lost CAS race to another thread; re-read next<br/> } else if (p == q)//(2)<br/> //多線(xiàn)程操作時(shí)候,由于 poll 時(shí)候會(huì)把老的 head 變?yōu)樽砸?,然?head 的 next 變?yōu)樾?head,所以這里需要<br/> //重新找新的 head,因?yàn)樾碌?head 后面的節(jié)點(diǎn)才是激活的節(jié)點(diǎn)<br/> p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head;<br/> else<br/> // 尋找尾節(jié)點(diǎn)(3)<br/> p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q;<br/> }<br/>}<br/>From the constructor, we know that there is a sentinel node with null item at the beginning, and both head and tail point to this node.
The above is the detailed content of Java multithreading and concurrency interview questions (Question 4, with answers). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 VSCode settings.json location
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:12 AM
VSCode settings.json location
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:12 AM
The settings.json file is located in the user-level or workspace-level path and is used to customize VSCode settings. 1. User-level path: Windows is C:\Users\\AppData\Roaming\Code\User\settings.json, macOS is /Users//Library/ApplicationSupport/Code/User/settings.json, Linux is /home//.config/Code/User/settings.json; 2. Workspace-level path: .vscode/settings in the project root directory
 How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
To correctly handle JDBC transactions, you must first turn off the automatic commit mode, then perform multiple operations, and finally commit or rollback according to the results; 1. Call conn.setAutoCommit(false) to start the transaction; 2. Execute multiple SQL operations, such as INSERT and UPDATE; 3. Call conn.commit() if all operations are successful, and call conn.rollback() if an exception occurs to ensure data consistency; at the same time, try-with-resources should be used to manage resources, properly handle exceptions and close connections to avoid connection leakage; in addition, it is recommended to use connection pools and set save points to achieve partial rollback, and keep transactions as short as possible to improve performance.
 Mastering Dependency Injection in Java with Spring and Guice
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:53 AM
Mastering Dependency Injection in Java with Spring and Guice
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:53 AM
DependencyInjection(DI)isadesignpatternwhereobjectsreceivedependenciesexternally,promotingloosecouplingandeasiertestingthroughconstructor,setter,orfieldinjection.2.SpringFrameworkusesannotationslike@Component,@Service,and@AutowiredwithJava-basedconfi
 python itertools combinations example
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:53 AM
python itertools combinations example
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:53 AM
itertools.combinations is used to generate all non-repetitive combinations (order irrelevant) that selects a specified number of elements from the iterable object. Its usage includes: 1. Select 2 element combinations from the list, such as ('A','B'), ('A','C'), etc., to avoid repeated order; 2. Take 3 character combinations of strings, such as "abc" and "abd", which are suitable for subsequence generation; 3. Find the combinations where the sum of two numbers is equal to the target value, such as 1 5=6, simplify the double loop logic; the difference between combinations and arrangement lies in whether the order is important, combinations regard AB and BA as the same, while permutations are regarded as different;
 python pytest fixture example
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:35 AM
python pytest fixture example
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:35 AM
fixture is a function used to provide preset environment or data for tests. 1. Use the @pytest.fixture decorator to define fixture; 2. Inject fixture in parameter form in the test function; 3. Execute setup before yield, and then teardown; 4. Control scope through scope parameters, such as function, module, etc.; 5. Place the shared fixture in conftest.py to achieve cross-file sharing, thereby improving the maintainability and reusability of tests.
 Understanding the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Internals
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:31 AM
Understanding the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Internals
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:31 AM
TheJVMenablesJava’s"writeonce,runanywhere"capabilitybyexecutingbytecodethroughfourmaincomponents:1.TheClassLoaderSubsystemloads,links,andinitializes.classfilesusingbootstrap,extension,andapplicationclassloaders,ensuringsecureandlazyclassloa
 How to work with Calendar in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 am 02:38 AM
How to work with Calendar in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 am 02:38 AM
Use classes in the java.time package to replace the old Date and Calendar classes; 2. Get the current date and time through LocalDate, LocalDateTime and LocalTime; 3. Create a specific date and time using the of() method; 4. Use the plus/minus method to immutably increase and decrease the time; 5. Use ZonedDateTime and ZoneId to process the time zone; 6. Format and parse date strings through DateTimeFormatter; 7. Use Instant to be compatible with the old date types when necessary; date processing in modern Java should give priority to using java.timeAPI, which provides clear, immutable and linear
 Google Chrome cannot open local files
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:24 AM
Google Chrome cannot open local files
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:24 AM
ChromecanopenlocalfileslikeHTMLandPDFsbyusing"Openfile"ordraggingthemintothebrowser;ensuretheaddressstartswithfile:///;2.SecurityrestrictionsblockAJAX,localStorage,andcross-folderaccessonfile://;usealocalserverlikepython-mhttp.server8000tor





