 PHP Framework
PHP Framework
 Workerman
Workerman
 Detailed explanation of the startup process of workerman source code analysis
Detailed explanation of the startup process of workerman source code analysis
Detailed explanation of the startup process of workerman source code analysis
Nov 25, 2019 pm 01:57 PMThe following column workerman tutorial will introduce you to the startup process of workerman source code analysis. I hope it will be helpful to friends in need!

#workerman
Version: 3.1.8 (linux) Model: GatewayWorker (the Worker model can be compared with it)Note: Only part of the code to explain is posted, and the source is given in the form of a file name. You can check it out by yourselfworkerman initially only developed the Linux version, win was added later, and is run based on the command line mode (cli).Multi-process model
Worker process, Master, Gateway and Worker, Gateway is mainly used to process IO events and save client connection status. Send data processing requests to Worker and other tasks. Worker is a complete business logic processing. The former is IO-intensive and the latter is computing-intensive. They communicate through the network. Gateway and Worker register communication addresses in pairs, so It is very convenient for distributed deployment. If the business processing volume is large, you can simply add Worker services.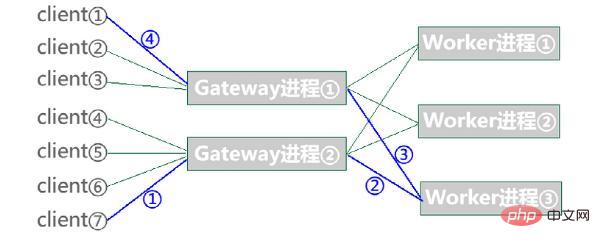
Start command parsing
Since it is running in command mode (cli) (note the difference with fpm, which handles requests from the web page) , there must be a startup script parsing command. For example, version 3.x (previously the default was daemon) adds a -d parameter to indicate that the daemon process is running. When parsed to this parameter, set self::$daemon = true, and then fork The child process can leave the current process group, set the process group leader, etc. There are two very important parameters $argc and $argc. The former represents the number of parameters, and the latter is an array that saves all the parameters of the command, such as: sudo php start.php start -d, $argv is array([0]=>start.php, [1]=>start, [2]=>-d), and $argv is mainly used for parsing. Startup mainly performs the following steps: 1. Include the automatic loader Autoloader and load the startup files under each Application; 2. Set the _appInitPath root directory; 3. Parse, initialize parameters, and execute corresponding commands. The following is the specific implementation (workerman/worker.php):public static function parseCommand()
{
// 檢查運(yùn)行命令的參數(shù)
global $argv;
$start_file = $argv[0];
// 命令
$command = trim($argv[1]);
// 子命令,目前只支持-d
$command2 = isset($argv[2]) ? $argv[2] : '';
// 檢查主進(jìn)程是否在運(yùn)行
$master_pid = @file_get_contents(self::$pidFile);
$master_is_alive = $master_pid && @posix_kill($master_pid, 0);
if($master_is_alive)
{
if($command === 'start')
{
self::log("Workerman[$start_file] is running");
}
}
elseif($command !== 'start' && $command !== 'restart')
{
self::log("Workerman[$start_file] not run");
}
// 根據(jù)命令做相應(yīng)處理
switch($command)
{
// 啟動(dòng) workerman
case 'start':
if($command2 === '-d')
{
Worker::$daemonize = true;
}
break;
// 顯示 workerman 運(yùn)行狀態(tài)
case 'status':
exit(0);
// 重啟 workerman
case 'restart':
// 停止 workeran
case 'stop':
// 想主進(jìn)程發(fā)送SIGINT信號(hào),主進(jìn)程會(huì)向所有子進(jìn)程發(fā)送SIGINT信號(hào)
$master_pid && posix_kill($master_pid, SIGINT);
// 如果 $timeout 秒后主進(jìn)程沒有退出則展示失敗界面
$timeout = 5;
$start_time = time();
while(1)
{
// 檢查主進(jìn)程是否存活
$master_is_alive = $master_pid && posix_kill($master_pid, 0);
if($master_is_alive)
{
// 檢查是否超過$timeout時(shí)間
if(time() - $start_time >= $timeout)
{
self::log("Workerman[$start_file] stop fail");
exit;
}
usleep(10000);
continue;
}
self::log("Workerman[$start_file] stop success");
// 是restart命令
if($command === 'stop')
{
exit(0);
}
// -d 說明是以守護(hù)進(jìn)程的方式啟動(dòng)
if($command2 === '-d')
{
Worker::$daemonize = true;
}
break;
}
break;
// 平滑重啟 workerman
case 'reload':
exit;
}
}The walker code comments are very detailed. Here are some details: 1. Check the main process Survival: Logical AND operation in line 17. If the main process PID exists, signal 0 is sent to the process. In fact, no information is sent. It only detects whether the process (or process group) is alive, and also detects the current user. Do you have permission to send system signals? 2. Why is the main process PID saved? After the system starts, it runs away from the current terminal. If you want to execute shutdown or other commands, the command will be executed in another process. If we don't even know the process PID, then who should we send the signal to? So the main process PID must be saved, and the main process is responsible for monitoring other child processes, so it is the entrance for us to continue operations. Worker::runAll()
#php’s socket programming is actually similar to C. The latter re-wraps the socket and provides The interface is provided to PHP, and the steps of network programming under PHP are greatly reduced. For example: stream_socket_server and stream_socket_client directly create server/client socket (php has two sets of socket operation functions). wm makes extensive use of the former. The startup process is as follows (the comments are very detailed):public static function runAll()
{
// 初始化環(huán)境變量
self::init();
// 解析命令
self::parseCommand();
// 嘗試以守護(hù)進(jìn)程模式運(yùn)行
self::daemonize();
// 初始化所有worker實(shí)例,主要是監(jiān)聽端口
self::initWorkers();
// 初始化所有信號(hào)處理函數(shù)
self::installSignal();
// 保存主進(jìn)程pid
self::saveMasterPid();
// 創(chuàng)建子進(jìn)程(worker進(jìn)程)并運(yùn)行
self::forkWorkers();
// 展示啟動(dòng)界面
self::displayUI();
// 嘗試重定向標(biāo)準(zhǔn)輸入輸出
self::resetStd();
// 監(jiān)控所有子進(jìn)程(worker進(jìn)程)
self::monitorWorkers();
} Let’s just talk about the key points of the process: 1. Initialize environment variables, such as setting the main Process name, log path, initialization timer, etc.; 2. Parse command line parameters, mainly using $argc and $argc. The usage is the same as C language; 3. Generate daemon process, In order to break away from the current terminal (two years ago, most people thought that PHP could not be used as a daemon. In fact, this is a misunderstanding! In fact, the process model of PHP in Linux is very stable. Now the application of wm in business has been very mature. A domestic company handles hundreds of millions of connections every day. , used for order and payment calls, you can put away your worries); 4. Initialize all worker instances (note that this is done in the main process, it just generates a bunch of servers and does not set up monitors. More The process model is monitoring in the child process, that is, IO multiplexing); 5. Register the signal processing function for the main process;
6. Save the main process PID. When the system is running, we can check the system status in the terminal or execute shutdown or restart commands. Communication is through the main process, so we need to know the main process PID. We know to type one in the terminal. The executable command actually creates a new sub-process under the current terminal for execution, so we need to know the main process PID to send SIGNAL to the WM main process. At this time, the signal processing function captures the signal and executes it through a callback.
7. Create a child process and set the current process user (root). In the multi-process model, two types of sub-processes listen to different server addresses respectively. In the main process, we only create servers and do not set up listening, nor do we generate a specified number of servers.
The reason is that if we create the same socket multiple times in a process, an error will be reported. The number of workers is actually the number of sockets, that is, the number of child processes of the socket. The child process inherits the parent process context, but only listens Specific socket events;
8. In the child process, register the server socket to listen for events, and use an extended Event to achieve IO reuse, register data reading callbacks, and also register socket connections. Event callback;
9. Input and output redirection;
10. The main process monitors the status of the sub-process and calls the pcntl_signal_dispatch() function in an infinite loop to capture the exit status of the sub-process. This function will block until a child process exits;
For more workerman related knowledge, please pay attention to the workerman tutorial column.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the startup process of workerman source code analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Implement file upload and download in Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
Implement file upload and download in Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
To implement file upload and download in Workerman documents, specific code examples are required. Introduction: Workerman is a high-performance PHP asynchronous network communication framework that is simple, efficient, and easy to use. In actual development, file uploading and downloading are common functional requirements. This article will introduce how to use the Workerman framework to implement file uploading and downloading, and give specific code examples. 1. File upload: File upload refers to the operation of transferring files on the local computer to the server. The following is used
 Which one is better, swoole or workerman?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 07:00 PM
Which one is better, swoole or workerman?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 07:00 PM
Swoole and Workerman are both high-performance PHP server frameworks. Known for its asynchronous processing, excellent performance, and scalability, Swoole is suitable for projects that need to handle a large number of concurrent requests and high throughput. Workerman offers the flexibility of both asynchronous and synchronous modes, with an intuitive API that is better suited for ease of use and projects that handle lower concurrency volumes.
 How to implement the basic usage of Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 am 11:46 AM
How to implement the basic usage of Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 am 11:46 AM
Introduction to how to implement the basic usage of Workerman documents: Workerman is a high-performance PHP development framework that can help developers easily build high-concurrency network applications. This article will introduce the basic usage of Workerman, including installation and configuration, creating services and listening ports, handling client requests, etc. And give corresponding code examples. 1. Install and configure Workerman. Enter the following command on the command line to install Workerman: c
 How to implement the timer function in the Workerman document
Nov 08, 2023 pm 05:06 PM
How to implement the timer function in the Workerman document
Nov 08, 2023 pm 05:06 PM
How to implement the timer function in the Workerman document Workerman is a powerful PHP asynchronous network communication framework that provides a wealth of functions, including the timer function. Use timers to execute code within specified time intervals, which is very suitable for application scenarios such as scheduled tasks and polling. Next, I will introduce in detail how to implement the timer function in Workerman and provide specific code examples. Step 1: Install Workerman First, we need to install Worker
 How to implement the reverse proxy function in the Workerman document
Nov 08, 2023 pm 03:46 PM
How to implement the reverse proxy function in the Workerman document
Nov 08, 2023 pm 03:46 PM
How to implement the reverse proxy function in the Workerman document requires specific code examples. Introduction: Workerman is a high-performance PHP multi-process network communication framework that provides rich functions and powerful performance and is widely used in Web real-time communication and long connections. Service scenarios. Among them, Workerman also supports the reverse proxy function, which can realize load balancing and static resource caching when the server provides external services. This article will introduce how to use Workerman to implement the reverse proxy function.
 Workerman development: How to implement real-time video calls based on UDP protocol
Nov 08, 2023 am 08:03 AM
Workerman development: How to implement real-time video calls based on UDP protocol
Nov 08, 2023 am 08:03 AM
Workerman development: real-time video call based on UDP protocol Summary: This article will introduce how to use the Workerman framework to implement real-time video call function based on UDP protocol. We will have an in-depth understanding of the characteristics of the UDP protocol and show how to build a simple but complete real-time video call application through code examples. Introduction: In network communication, real-time video calling is a very important function. The traditional TCP protocol may have problems such as transmission delays when implementing high-real-time video calls. And UDP
 How to use Workerman to build a high-availability load balancing system
Nov 07, 2023 pm 01:16 PM
How to use Workerman to build a high-availability load balancing system
Nov 07, 2023 pm 01:16 PM
How to use Workerman to build a high-availability load balancing system requires specific code examples. In the field of modern technology, with the rapid development of the Internet, more and more websites and applications need to handle a large number of concurrent requests. In order to achieve high availability and high performance, the load balancing system has become one of the essential components. This article will introduce how to use the PHP open source framework Workerman to build a high-availability load balancing system and provide specific code examples. 1. Introduction to Workerman Worke
 Implement the file transfer function in Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 pm 03:39 PM
Implement the file transfer function in Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 pm 03:39 PM
Workerman is a high-performance asynchronous event-driven framework developed based on PHP. It can easily realize the development of long connections under the TCP/UDP protocol. In addition, Workerman also provides the function of realizing file transfer, which can be used in scenarios such as large file transfer and data backup. This article will introduce how to implement the file transfer function in Workerman and provide specific code examples. 1. File upload function To implement the file upload function, the client needs to send the file to be uploaded to the server, and the server verifies





