The difference between heap and stack java
Nov 13, 2019 pm 02:32 PM
The difference between heap and stack java
Before talking about heap and stack, let’s talk about JVM (virtual Machine) memory division:
Java programs must allocate space when they are running. Any software must allocate space in the memory when they are running. The Java virtual machine also must allocate space when it is running. The JVM opens up a memory area in the memory when it is running, and divides it more carefully in its own memory area when it starts. Because each piece of memory in the virtual machine is processed in a different way, it must be managed separately.
The JVM memory is divided into five parts:
1. Register;
2. Local method area;
3. Method area;
4. Stack memory;
5. Heap memory.
Let’s focus on the heap and stack:
Stack memory: Stack memory is first of all a memory area, which stores local variables, all defined in methods All are local variables (global variables outside the method). Local variables are also defined inside the for loop. The function must be loaded first before local variables can be defined. Therefore, the method first stacks the stack and then defines the variables. The variables have their own scope. , the variable will be released once it leaves the scope. The stack memory is updated very quickly because the life cycle of local variables is very short.
Heap memory: stores arrays and objects (in fact, arrays are objects). Everything created by new is in the heap. Entities (objects) are stored in the heap. Entities are used to encapsulate data, and It encapsulates multiple (multiple attributes of an entity). If one piece of data disappears, the entity does not disappear and can still be used, so the heap will not be released at any time, but the stack is different. The stack stores only a single variable. Once the variable is released, it is gone. Although the entities in the heap will not be released, they will be treated as garbage. Java has a garbage collection mechanism to collect them from time to time.
Let’s talk about the heap and stack in detail through an illustration:
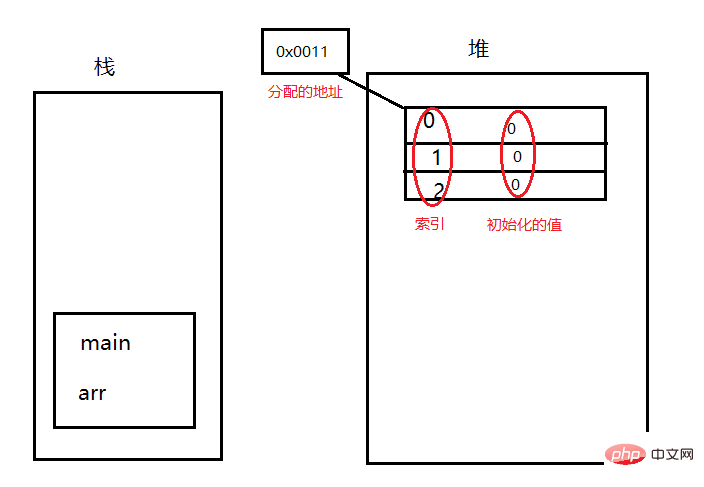
For example, the statement in the main function int [] arr=new int [3]; in memory How it is defined:
The main function goes to the stack first, defines a variable arr in the stack, and then assigns a value to arr, but the right side is not a specific value, but an entity. The entity is created in the heap. First, a space is opened in the heap through the new keyword. When the memory stores data, it is reflected by the address. The address is a continuous binary, and then a memory address is allocated to the entity. Arrays have an index. After the array entity is generated in the heap memory, each space will be initialized by default (this is a characteristic of heap memory. Uninitialized data cannot be used, but it can be used in the heap. Because it has been initialized but not on the stack), different types have different initialized values. So variables and entities are created in the heap and stack:
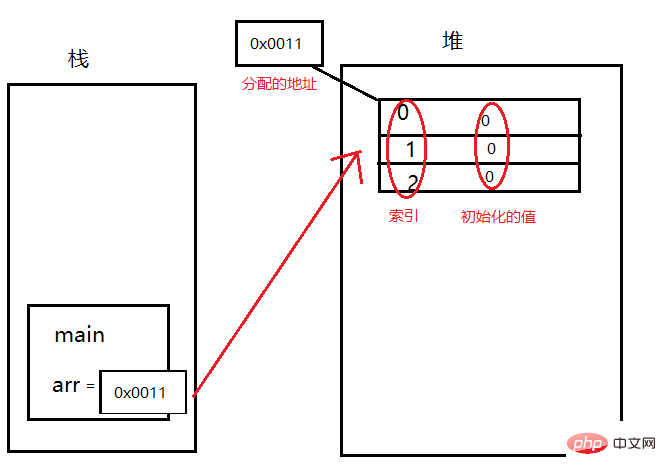
So how are the heap and stack connected?
We just said that we allocate an address to the heap, assign the address of the heap to arr, and arr points to the array through the address. So when arr wants to manipulate the array, it uses the address instead of assigning entities to it directly. We no longer call this a basic data type, but a reference data type. It is called arr and refers to the entity in the heap memory. (Can be understood as a pointer to c or c. Java grew up from c and is very similar to c, optimizing c)
If when int [] arr=null;
arr does not point to anything, and the function of null is to dereference the pointer of the data type.
When an entity is not pointed to by a reference data type, it will not be released in the heap memory, but will be treated as garbage and automatically recycled at an irregular time, because Java has an automatic recycling mechanism. , (while c does not, the programmer needs to manually recycle. If it is not recycled, the heap will grow until it is full and the memory overflows, so Java is better than c in memory management). The automatic recycling mechanism (program) automatically monitors whether there is garbage in the heap. If there is garbage, it will automatically perform garbage collection, but it is not certain when it will be collected.
So the difference between heap and stack is obvious:
1. Stack memory stores local variables while heap memory stores entities;
2. The update speed of stack memory is faster than that of heap memory, because the life cycle of local variables is very short;
3. The variables stored in stack memory will be released once their life cycle ends, while the entities stored in heap memory will be released. It will be collected by the garbage collection mechanism from time to time.
php Chinese website, a large number of free Java introductory tutorials, welcome to learn online!
The above is the detailed content of The difference between heap and stack java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 VSCode settings.json location
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:12 AM
VSCode settings.json location
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:12 AM
The settings.json file is located in the user-level or workspace-level path and is used to customize VSCode settings. 1. User-level path: Windows is C:\Users\\AppData\Roaming\Code\User\settings.json, macOS is /Users//Library/ApplicationSupport/Code/User/settings.json, Linux is /home//.config/Code/User/settings.json; 2. Workspace-level path: .vscode/settings in the project root directory
 How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
To correctly handle JDBC transactions, you must first turn off the automatic commit mode, then perform multiple operations, and finally commit or rollback according to the results; 1. Call conn.setAutoCommit(false) to start the transaction; 2. Execute multiple SQL operations, such as INSERT and UPDATE; 3. Call conn.commit() if all operations are successful, and call conn.rollback() if an exception occurs to ensure data consistency; at the same time, try-with-resources should be used to manage resources, properly handle exceptions and close connections to avoid connection leakage; in addition, it is recommended to use connection pools and set save points to achieve partial rollback, and keep transactions as short as possible to improve performance.
 Mastering Dependency Injection in Java with Spring and Guice
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:53 AM
Mastering Dependency Injection in Java with Spring and Guice
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:53 AM
DependencyInjection(DI)isadesignpatternwhereobjectsreceivedependenciesexternally,promotingloosecouplingandeasiertestingthroughconstructor,setter,orfieldinjection.2.SpringFrameworkusesannotationslike@Component,@Service,and@AutowiredwithJava-basedconfi
 How to obtain digital currency BTC? What are the differences between btc and digital currency?
Aug 01, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
How to obtain digital currency BTC? What are the differences between btc and digital currency?
Aug 01, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
There are four main ways to obtain BTC: 1. Register and exchange it with fiat currency or other digital assets through centralized trading platforms such as Binance, OK, Huobi, and Gate.io; 2. Participate in P2P platforms to directly trade with individuals, and pay attention to the credit risks of the counterparty; 3. Provide goods or services to accept BTC as payment; 4. Participate in airdrops, competitions and other platform reward activities to obtain a small amount of BTC. The core difference between BTC and digital currency is: 1. BTC is a type of digital currency, which belongs to a genus relationship; 2. BTC adopts a proof of work (PoW) mechanism, while other digital currencies may use various technologies such as proof of stake (PoS); 3. BTC emphasizes the value storage function of "digital gold", and other digital currencies may focus on payment efficiency or
 Understanding the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Internals
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:31 AM
Understanding the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Internals
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:31 AM
TheJVMenablesJava’s"writeonce,runanywhere"capabilitybyexecutingbytecodethroughfourmaincomponents:1.TheClassLoaderSubsystemloads,links,andinitializes.classfilesusingbootstrap,extension,andapplicationclassloaders,ensuringsecureandlazyclassloa
 How to work with Calendar in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 am 02:38 AM
How to work with Calendar in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 am 02:38 AM
Use classes in the java.time package to replace the old Date and Calendar classes; 2. Get the current date and time through LocalDate, LocalDateTime and LocalTime; 3. Create a specific date and time using the of() method; 4. Use the plus/minus method to immutably increase and decrease the time; 5. Use ZonedDateTime and ZoneId to process the time zone; 6. Format and parse date strings through DateTimeFormatter; 7. Use Instant to be compatible with the old date types when necessary; date processing in modern Java should give priority to using java.timeAPI, which provides clear, immutable and linear
 Google Chrome cannot open local files
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:24 AM
Google Chrome cannot open local files
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:24 AM
ChromecanopenlocalfileslikeHTMLandPDFsbyusing"Openfile"ordraggingthemintothebrowser;ensuretheaddressstartswithfile:///;2.SecurityrestrictionsblockAJAX,localStorage,andcross-folderaccessonfile://;usealocalserverlikepython-mhttp.server8000tor
 What are the differences between USDT standard, USDC standard and currency standard? Monetary Circle
Jul 31, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
What are the differences between USDT standard, USDC standard and currency standard? Monetary Circle
Jul 31, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
In the digital asset derivatives market, contract trading is one of the core ways to play, and understanding different margin types is the first lesson for beginners. Choosing USDT, USDC, or currency standard contracts is directly related to your income calculation method and risk exposure. Understanding their differences will allow you to make better decisions in market fluctuations. If you have higher requirements for the compliance and transparency of funds, then choosing a USDC-based contract supported by large platforms such as Ouyi OKX and Binance will make you feel more at ease.






