Writing a custom SQL query in Yii can be implemented through Yii::$app->db. The steps are as follows: 1. Create a query command using createCommand(); 2. Binding parameters through bindValue() or bindParam() to prevent SQL injection; 3. Call queryAll(), queryOne() and other methods to execute queries; 4. For insert and update operations, you can chain call insert() and update() methods; 5. It is recommended to write SQL directly and bind parameters for complex multi-table queries; 6. If the result needs to be converted into a model, you can instantiate and set properties manually; 7. Use Query Builder to build secure queries first, and use native SQL for complex logic.

In Yii, writing custom SQL queries is straightforward and gives you more control when dealing with complex database operations that aren't easily handled by Active Record. The key is knowing how to use Yii's database components properly.
Using Yii::$app->db for Custom Queries
The main entry point for executing raw SQL in Yii is through the yii\db\Connection object, which you can access using Yii::$app->db . This allows you to create commands and execute queries safely.
To run a simple SELECT query:
$command = Yii::$app->db->createCommand('SELECT * FROM user WHERE status=:status'); $command->bindValue(':status', 1); $results = $command->queryAll();
Here's what's happening:
- You create a command using
createCommand() - Use
bindValue()orbindParam()to prevent SQL injection - Call
queryAll()to fetch multiple rows (orqueryOne()for a single row)
You can also perform INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE like this:
Yii::$app->db->createCommand()->insert('user', [
'name' => 'John',
'email' => 'john@example.com',
])->execute();Or update:
Yii::$app->db->createCommand()->update('user', ['status' => 0], 'id = 100')->execute();
These methods are clean and readable, especially for basic data manipulation.
Handling Complex Queries with Multiple Tables
When you're joining tables or pulling data from multiple sources, raw SQL becomes even more useful. For example:
$sql = '
SELECT u.name, p.title
FROM user u
JOIN post p ON u.id = p.user_id
WHERE u.status = :status
';
$posts = Yii::$app->db->createCommand($sql)
->bindValue(':status', 1)
->queryAll();This kind of query would be messy with Active Record, but with raw SQL it stays clear and efficient. Just remember to:
- Always use parameter binding (
:status,:id, etc.) - Avoid concatenating user input directly into SQL strings
Also, if your query returns model-like data, consider hydrating models manually:
foreach ($results as $row) {
$model = new User();
$model->setAttributes($row, false);
// do something with $model
}This keeps your code structured even when not using AR directly.
When to Use Query Builder vs Raw SQL
Yii also provides a query builder ( yii\db\Query ) that helps generate SQL safely without writing everything manually. For example:
$rows = (new \yii\db\Query())
->select(['id', 'name'])
->from('user')
->where(['status' => 1])
->all();This builds the SQL under the hood, still uses parameter binding, and is safer than raw SQL. But sometimes, especially with advanced joins or subqueries, raw SQL ends up being simpler and clearer.
So here's a quick guide:
- ? Use Query Builder for dynamic conditions and simple joins
- ? Don't force complicated logic into Query Builder if it gets too messy
- ? Go with raw SQL when performance matters or query complexity is high
If you're unsure, start with Query Builder—it often leads to cleaner, safer code.
That's the basics of working with custom SQL in Yii. It's flexible but requires attention to security and readability. Stick to parameterized queries, organize your SQL logically, and you'll have solid, maintainable code.
The above is the detailed content of How do I write custom SQL queries in Yii?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Data query in Yii framework: access data efficiently
Jun 21, 2023 am 11:22 AM
Data query in Yii framework: access data efficiently
Jun 21, 2023 am 11:22 AM
The Yii framework is an open source PHP Web application framework that provides numerous tools and components to simplify the process of Web application development, of which data query is one of the important components. In the Yii framework, we can use SQL-like syntax to access the database to query and manipulate data efficiently. The query builder of the Yii framework mainly includes the following types: ActiveRecord query, QueryBuilder query, command query and original SQL query
 Symfony vs Yii2: Which framework is better for developing large-scale web applications?
Jun 19, 2023 am 10:57 AM
Symfony vs Yii2: Which framework is better for developing large-scale web applications?
Jun 19, 2023 am 10:57 AM
As the demand for web applications continues to grow, developers have more and more choices in choosing development frameworks. Symfony and Yii2 are two popular PHP frameworks. They both have powerful functions and performance, but when faced with the need to develop large-scale web applications, which framework is more suitable? Next we will conduct a comparative analysis of Symphony and Yii2 to help you make a better choice. Basic Overview Symphony is an open source web application framework written in PHP and is built on
 How to use PHP framework Yii to develop a highly available cloud backup system
Jun 27, 2023 am 09:04 AM
How to use PHP framework Yii to develop a highly available cloud backup system
Jun 27, 2023 am 09:04 AM
With the continuous development of cloud computing technology, data backup has become something that every enterprise must do. In this context, it is particularly important to develop a highly available cloud backup system. The PHP framework Yii is a powerful framework that can help developers quickly build high-performance web applications. The following will introduce how to use the Yii framework to develop a highly available cloud backup system. Designing the database model In the Yii framework, the database model is a very important part. Because the data backup system requires a lot of tables and relationships
 What is the difference between php framework laravel and yii
Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:24 PM
What is the difference between php framework laravel and yii
Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:24 PM
The main differences between Laravel and Yii are design concepts, functional characteristics and usage scenarios. 1.Laravel focuses on the simplicity and pleasure of development, and provides rich functions such as EloquentORM and Artisan tools, suitable for rapid development and beginners. 2.Yii emphasizes performance and efficiency, is suitable for high-load applications, and provides efficient ActiveRecord and cache systems, but has a steep learning curve.
 Yii with Docker: Containerizing and Deploying Your Applications
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:13 PM
Yii with Docker: Containerizing and Deploying Your Applications
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:13 PM
The steps to containerize and deploy Yii applications using Docker include: 1. Create a Dockerfile and define the image building process; 2. Use DockerCompose to launch Yii applications and MySQL database; 3. Optimize image size and performance. This involves not only specific technical operations, but also understanding the working principles and best practices of Dockerfile to ensure efficient and reliable deployment.
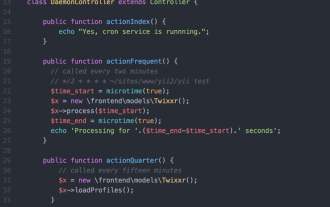 Yii2 Programming Guide: How to run Cron service
Sep 01, 2023 pm 11:21 PM
Yii2 Programming Guide: How to run Cron service
Sep 01, 2023 pm 11:21 PM
If you're asking "What is Yii?" check out my previous tutorial: Introduction to the Yii Framework, which reviews the benefits of Yii and outlines what's new in Yii 2.0, released in October 2014. Hmm> In this Programming with Yii2 series, I will guide readers in using the Yii2PHP framework. In today's tutorial, I will share with you how to leverage Yii's console functionality to run cron jobs. In the past, I've used wget - a web-accessible URL - in a cron job to run my background tasks. This raises security concerns and has some performance issues. While I discussed some ways to mitigate the risk in our Security for Startup series, I had hoped to transition to console-driven commands
 Meituan interview question: Have you ever encountered slow SQL? How was it solved?
Aug 24, 2023 pm 03:41 PM
Meituan interview question: Have you ever encountered slow SQL? How was it solved?
Aug 24, 2023 pm 03:41 PM
MySQL's slow query log is a log record provided by MySQL. It is used to record statements in MySQL whose query time exceeds (greater than) the set threshold (long_query_time) and records them in the slow query log.
 PHP and PDO: How to execute complex SQL queries
Jul 28, 2023 pm 03:43 PM
PHP and PDO: How to execute complex SQL queries
Jul 28, 2023 pm 03:43 PM
PHP and PDO: How to execute complex SQL query statements When processing database operations, PHP provides a powerful extension library PDO (PHPDataObjects) to simplify interaction with the database. PDO supports a variety of databases, such as MySQL, SQLite, etc., and also provides a wealth of functions and methods to facilitate developers to perform various database operations. This article will introduce how to use PDO to execute complex SQL query statements, and attach corresponding code examples. Connect to the database






