In Yii, widgets are used to implement component multiplexing by encapsulating complex view logic. 1. Use the widget() method to call built-in widgets, such as LinkPager for pagination, and ActiveForm for creating model binding forms; 2. Common widgets include GridView to display table data, DetailView to display model details, Menu build navigation menu; 3. You can create custom widgets by inheriting yii\base\Widget, implement the run() method and define properties to enhance reusability, as shown in the HelloWidget example. Mastering these core methods can improve view development efficiency.

In Yii, widgets are reusable components that help you encapsulate complex view logic into self-contained units. Using them in views is straightforward once you understand the basic structure and how to call them.
Basic Widget Usage
Widgets in Yii are typically called using the widget() method inside a view file. The general syntax looks like this:
<?= \yii\widgets\WidgetName::widget([
'option1' => 'value1',
'option2' => 'value2',
]) ?> Each widget has its own set of configuration options. For example, if you're using the built-in LinkPager widget for pagination, it might look like:
<?= \yii\widgets\LinkPager::widget([
'pagination' => $pagination,
]) ?> Make sure to pass the correct parameters — in this case, a Pagination object prepared in your controller.
Commonly Used Widgets and What They Do
Yii comes with several useful widgets out of the box. Here are a few commonly used ones and their purposes:
- ActiveForm : Helps build forms tied to models.
- GridView : Displays tabular data with sorting, filtering, and pagination.
- DetailView : Shows details of a single model record.
- Menu : Renders multi-level navigation menus.
- LinkPager / Pagination : Handles page navigation for paginated content.
For example, using ActiveForm to create a login form:
<?php $form = \yii\widgets\ActiveForm::begin(); ?> <?= $form->field($model, 'username') ?> <?= $form->field($model, 'password')->passwordInput() ?> <button type="submit">Login</button> <?php \yii\widgets\ActiveForm::end(); ?>
This automatically handles form submission, model binding, and error display based on validation rules.
Creating Your Own Widget (Optional but Useful)
If you find yourself repeating certain UI elements or logic across multiple views, consider creating a custom widget.
Here's a quick outline of what to do:
- Create a new class extending
yii\base\Widget. - Override the
run()method to return the HTML/output. - Optionally, add configurable properties via public variables or constructor/configurable options.
Example:
namespace app\widgets;
use yii\base\Widget;
class HelloWidget extends Widget
{
public $message = 'Hello there';
public function run()
{
return "<div class=\"hello\">{$this->message}</div>";
}
}Then in your view:
<?= \app\widgets\HelloWidget::widget(['message' => 'Welcome back!']) ?>
It's a clean way to reuse components without duplicating code.
That's the core of working with widgets in Yii views. You don't always need to build your own — using built-in widgets effectively can save a lot of time. But knowing how to create one gives you more flexibility when needed.
The above is the detailed content of How do I use widgets in Yii views?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Yii2 vs Phalcon: Which framework is better for developing graphics rendering applications?
Jun 19, 2023 am 08:09 AM
Yii2 vs Phalcon: Which framework is better for developing graphics rendering applications?
Jun 19, 2023 am 08:09 AM
In the current information age, big data, artificial intelligence, cloud computing and other technologies have become the focus of major enterprises. Among these technologies, graphics card rendering technology, as a high-performance graphics processing technology, has received more and more attention. Graphics card rendering technology is widely used in game development, film and television special effects, engineering modeling and other fields. For developers, choosing a framework that suits their projects is a very important decision. Among current languages, PHP is a very dynamic language. Some excellent PHP frameworks such as Yii2, Ph
 Data query in Yii framework: access data efficiently
Jun 21, 2023 am 11:22 AM
Data query in Yii framework: access data efficiently
Jun 21, 2023 am 11:22 AM
The Yii framework is an open source PHP Web application framework that provides numerous tools and components to simplify the process of Web application development, of which data query is one of the important components. In the Yii framework, we can use SQL-like syntax to access the database to query and manipulate data efficiently. The query builder of the Yii framework mainly includes the following types: ActiveRecord query, QueryBuilder query, command query and original SQL query
 Symfony vs Yii2: Which framework is better for developing large-scale web applications?
Jun 19, 2023 am 10:57 AM
Symfony vs Yii2: Which framework is better for developing large-scale web applications?
Jun 19, 2023 am 10:57 AM
As the demand for web applications continues to grow, developers have more and more choices in choosing development frameworks. Symfony and Yii2 are two popular PHP frameworks. They both have powerful functions and performance, but when faced with the need to develop large-scale web applications, which framework is more suitable? Next we will conduct a comparative analysis of Symphony and Yii2 to help you make a better choice. Basic Overview Symphony is an open source web application framework written in PHP and is built on
 How to use PHP framework Yii to develop a highly available cloud backup system
Jun 27, 2023 am 09:04 AM
How to use PHP framework Yii to develop a highly available cloud backup system
Jun 27, 2023 am 09:04 AM
With the continuous development of cloud computing technology, data backup has become something that every enterprise must do. In this context, it is particularly important to develop a highly available cloud backup system. The PHP framework Yii is a powerful framework that can help developers quickly build high-performance web applications. The following will introduce how to use the Yii framework to develop a highly available cloud backup system. Designing the database model In the Yii framework, the database model is a very important part. Because the data backup system requires a lot of tables and relationships
 What is the difference between php framework laravel and yii
Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:24 PM
What is the difference between php framework laravel and yii
Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:24 PM
The main differences between Laravel and Yii are design concepts, functional characteristics and usage scenarios. 1.Laravel focuses on the simplicity and pleasure of development, and provides rich functions such as EloquentORM and Artisan tools, suitable for rapid development and beginners. 2.Yii emphasizes performance and efficiency, is suitable for high-load applications, and provides efficient ActiveRecord and cache systems, but has a steep learning curve.
 Yii with Docker: Containerizing and Deploying Your Applications
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:13 PM
Yii with Docker: Containerizing and Deploying Your Applications
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:13 PM
The steps to containerize and deploy Yii applications using Docker include: 1. Create a Dockerfile and define the image building process; 2. Use DockerCompose to launch Yii applications and MySQL database; 3. Optimize image size and performance. This involves not only specific technical operations, but also understanding the working principles and best practices of Dockerfile to ensure efficient and reliable deployment.
 Yii2 vs Symfony: Which framework is better for API development?
Jun 18, 2023 pm 11:00 PM
Yii2 vs Symfony: Which framework is better for API development?
Jun 18, 2023 pm 11:00 PM
With the rapid development of the Internet, APIs have become an important way to exchange data between various applications. Therefore, it has become increasingly important to develop an API framework that is easy to maintain, efficient, and stable. When choosing an API framework, Yii2 and Symfony are two popular choices among developers. So, which one is more suitable for API development? This article will compare these two frameworks and give some conclusions. 1. Basic introduction Yii2 and Symfony are mature PHP frameworks with corresponding extensions that can be used to develop
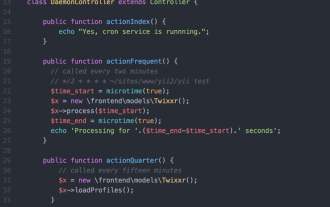 Yii2 Programming Guide: How to run Cron service
Sep 01, 2023 pm 11:21 PM
Yii2 Programming Guide: How to run Cron service
Sep 01, 2023 pm 11:21 PM
If you're asking "What is Yii?" check out my previous tutorial: Introduction to the Yii Framework, which reviews the benefits of Yii and outlines what's new in Yii 2.0, released in October 2014. Hmm> In this Programming with Yii2 series, I will guide readers in using the Yii2PHP framework. In today's tutorial, I will share with you how to leverage Yii's console functionality to run cron jobs. In the past, I've used wget - a web-accessible URL - in a cron job to run my background tasks. This raises security concerns and has some performance issues. While I discussed some ways to mitigate the risk in our Security for Startup series, I had hoped to transition to console-driven commands






