
GitLab is an open-source, powerful, resilient, extendable, protected, and effective software development and teamwork environment for the entire DevOps lifecycle.
It enables you to structure your development workflow; write code, and validate; package applications, and deploy them with its built-in continuous delivery capability; manage configurations automatically, and keep track of software performance.
You might also find these interesting:
- 10 Top GitHub Alternatives for Hosting Open Source Projects
- Master the Fundamentals of Git to Handle Projects Smoothly {Beginner’s Guide}
- How to Utilize Git Version Control System in Linux [Complete Guide]
- 11 Best Graphical Git Clients and Git Repository Viewers for Linux
- Set Up GIT to Build and Share Your Own Projects on GITHub Repository
It offers features including an issue tracker, shifting issues among projects, time monitoring, highly capable branching utilities, file locking, merge requests, personalized alerts, project roadmaps, burndown charts for project and group milestones, and much more.
GitLab is one of the finest alternatives to GitHub for hosting your open-source projects available.
In this tutorial, we will walk you through the steps to install and set up GitLab (Git-repository manager) on RHEL-based and Debian-based systems.
Step 1: Install and Configure Necessary Dependencies
1. Begin by installing the essential dependencies using the yum or apt package manager as indicated.
<code>sudo yum install curl policycoreutils-python-utils [For RHEL-based] sudo apt install curl policycoreutils-python-utils [For Debian-based]</code>
2. Then, install the Postfix service to send notification emails, activate it to launch at boot, and confirm its operational status with these commands.
<code>sudo yum install postfix [For RHEL-based] sudo apt install postfix [For Debian-based] <p>sudo systemctl start postfix sudo systemctl enable postfix sudo systemctl status postfix</p></code>
Throughout the Postfix setup, a configuration window may pop up. Choose ‘Internet Site’ and specify your server’s external DNS for ‘mail name’, then hit enter. Should additional prompts appear, proceed by pressing enter to accept the defaults.

Step 2: Add GitLab Repository and Install Package
3. Proceed by adding the GitLab package repository to your system via the following script.
On RHEL-based systems:
<code>curl <a href="http://ipnx.cn/link/c0b3cb0842f9f8148f618c587b48d5ba">http://ipnx.cn/link/c0b3cb0842f9f8148f618c587b48d5ba</a> | sudo bash</code>
On Debian-based systems:
<code>curl <a href="http://ipnx.cn/link/9e18189975e5454f9335f3f1a17e0aa9">http://ipnx.cn/link/9e18189975e5454f9335f3f1a17e0aa9</a> | sudo bash</code>
4. Subsequently, install the GitLab Community Edition package using the given command, ensuring to replace ‘http://ipnx.cn/link/1d5988d346d89a4e49e0b43c0f0d28d0‘ with the desired URL to access your GitLab instance from a web browser.
On RHEL-based systems:
<code>sudo EXTERNAL_URL="<a href="http://ipnx.cn/link/1d5988d346d89a4e49e0b43c0f0d28d0">http://ipnx.cn/link/1d5988d346d89a4e49e0b43c0f0d28d0</a>" yum install -y gitlab-ce</code>
On Debian-based systems:
<code>sudo EXTERNAL_URL="<a href="http://ipnx.cn/link/1d5988d346d89a4e49e0b43c0f0d28d0">http://ipnx.cn/link/1d5988d346d89a4e49e0b43c0f0d28d0</a>" apt install -y gitlab-ee</code>
Note: To modify your primary URL, adjust it within the GitLab main configuration file /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb under the external_url segment. After making changes, remember to reconfigure GitLab to implement the updates in the configuration file using this command:
<code>sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure</code>
5. If your system firewall is active, open ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS) to permit connections in the system firewall.
On RHEL-based systems:
<code>sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=80/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=443/tcp sudo# systemctl reload firewalld</code>
On Debian-based systems:
<code>sudo ufw allow http sudo ufw allow https sydo ufw reload</code>
Step 3: Perform Initial GitLab Setup
6. Access your GitLab instance in a web browser using the URL defined during installation.
<code><a href="http://ipnx.cn/link/1d5988d346d89a4e49e0b43c0f0d28d0">http://ipnx.cn/link/1d5988d346d89a4e49e0b43c0f0d28d0</a></code>
7. Upon your initial visit, you'll be directed to a password reset page; establish a new password for your new admin account and click “Change your password”. Following this, you'll be redirected to the login page where you can log in with the username root and the password you just set.

8. A successful login will bring you to the admin user account interface as depicted. Here, you can create entities, form groups, invite members, or customize your GitLab setup according to your needs. Additionally, you can modify your user profile, set up your email, link SSH keys to your GitLab instance, and other actions.

For further details, visit the GitLab About Page: http://ipnx.cn/link/feddfedc98490ed7e123db392f076fa1
That concludes our discussion! In this guide, we've outlined the procedure for installing and configuring GitLab (Git-repository manager) on RHEL-based and Debian-based Linux distributions. Feel free to leave any queries or contributions in the comments section below.
The above is the detailed content of How to Install and Configure GitLab on Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Install LXC (Linux Containers) in RHEL, Rocky & AlmaLinux
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:25 AM
Install LXC (Linux Containers) in RHEL, Rocky & AlmaLinux
Jul 05, 2025 am 09:25 AM
LXD is described as the next-generation container and virtual machine manager that offers an immersive for Linux systems running inside containers or as virtual machines. It provides images for an inordinate number of Linux distributions with support
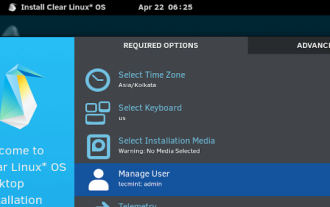 Clear Linux Distro - Optimized for Performance and Security
Jul 02, 2025 am 09:49 AM
Clear Linux Distro - Optimized for Performance and Security
Jul 02, 2025 am 09:49 AM
Clear Linux OS is the ideal operating system for people – ahem system admins – who want to have a minimal, secure, and reliable Linux distribution. It is optimized for the Intel architecture, which means that running Clear Linux OS on AMD sys
 How to create a self-signed SSL certificate using OpenSSL?
Jul 03, 2025 am 12:30 AM
How to create a self-signed SSL certificate using OpenSSL?
Jul 03, 2025 am 12:30 AM
The key steps for creating a self-signed SSL certificate are as follows: 1. Generate the private key, use the command opensslgenrsa-outselfsigned.key2048 to generate a 2048-bit RSA private key file, optional parameter -aes256 to achieve password protection; 2. Create a certificate request (CSR), run opensslreq-new-keyselfsigned.key-outselfsigned.csr and fill in the relevant information, especially the "CommonName" field; 3. Generate the certificate by self-signed, and use opensslx509-req-days365-inselfsigned.csr-signk
 7 Ways to Speed Up Firefox Browser in Linux Desktop
Jul 04, 2025 am 09:18 AM
7 Ways to Speed Up Firefox Browser in Linux Desktop
Jul 04, 2025 am 09:18 AM
Firefox browser is the default browser for most modern Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, Mint, and Fedora. Initially, its performance might be impressive, however, with the passage of time, you might notice that your browser is not as fast and resp
 How to extract a .tar.gz or .zip file?
Jul 02, 2025 am 12:52 AM
How to extract a .tar.gz or .zip file?
Jul 02, 2025 am 12:52 AM
Decompress the .zip file on Windows, you can right-click to select "Extract All", while the .tar.gz file needs to use tools such as 7-Zip or WinRAR; on macOS and Linux, the .zip file can be double-clicked or unzip commanded, and the .tar.gz file can be decompressed by tar command or double-clicked directly. The specific steps are: 1. Windows processing.zip file: right-click → "Extract All"; 2. Windows processing.tar.gz file: Install third-party tools → right-click to decompress; 3. macOS/Linux processing.zip file: double-click or run unzipfilename.zip; 4. macOS/Linux processing.tar
 How to troubleshoot DNS issues on a Linux machine?
Jul 07, 2025 am 12:35 AM
How to troubleshoot DNS issues on a Linux machine?
Jul 07, 2025 am 12:35 AM
When encountering DNS problems, first check the /etc/resolv.conf file to see if the correct nameserver is configured; secondly, you can manually add public DNS such as 8.8.8.8 for testing; then use nslookup and dig commands to verify whether DNS resolution is normal. If these tools are not installed, you can first install the dnsutils or bind-utils package; then check the systemd-resolved service status and configuration file /etc/systemd/resolved.conf, and set DNS and FallbackDNS as needed and restart the service; finally check the network interface status and firewall rules, confirm that port 53 is not
 Install Guacamole for Remote Linux/Windows Access in Ubuntu
Jul 08, 2025 am 09:58 AM
Install Guacamole for Remote Linux/Windows Access in Ubuntu
Jul 08, 2025 am 09:58 AM
As a system administrator, you may find yourself (today or in the future) working in an environment where Windows and Linux coexist. It is no secret that some big companies prefer (or have to) run some of their production services in Windows boxes an
 How would you debug a server that is slow or has high memory usage?
Jul 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
How would you debug a server that is slow or has high memory usage?
Jul 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
If you find that the server is running slowly or the memory usage is too high, you should check the cause before operating. First, you need to check the system resource usage, use top, htop, free-h, iostat, ss-antp and other commands to check CPU, memory, disk I/O and network connections; secondly, analyze specific process problems, and track the behavior of high-occupancy processes through tools such as ps, jstack, strace; then check logs and monitoring data, view OOM records, exception requests, slow queries and other clues; finally, targeted processing is carried out based on common reasons such as memory leaks, connection pool exhaustion, cache failure storms, and timing task conflicts, optimize code logic, set up a timeout retry mechanism, add current limit fuses, and regularly pressure measurement and evaluation resources.






