Artificial Intelligence: A Comprehensive Guide
Technology has enabled us to envision a world where machines understand our preferences, anticipate our needs, and learn from past interactions to provide better results. This isn't science fiction; it's the present, powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI). From smartphone virtual assistants to business algorithms and stock market prediction models, AI is transforming our world. This article explores the fundamentals of AI, its core technologies, and its diverse applications. By the end, you'll understand how AI mimics human intelligence and its widespread use across various industries.

Key Takeaways:
- Grasp the fundamental concepts of AI systems.
- Learn about the different categories of AI and their characteristics.
- Discover the tools and techniques used in AI development.
- Explore the diverse real-world applications of AI.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Types of Artificial Intelligence
- Core Components of AI
- How AI Functions
- Applications of Artificial Intelligence
- AI Challenges
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding Artificial Intelligence:
Artificial Intelligence simulates human intelligence in machines, enabling them to think, learn, and act like humans. These systems handle tasks requiring human cognitive abilities, such as problem-solving, language comprehension, and pattern recognition. AI excels at processing vast datasets, identifying trends, and making data-driven decisions. At its heart, AI aims to create autonomous machines that learn and improve from their experiences.
Categorizing Artificial Intelligence:
AI is broadly classified into three types based on its capabilities:
- Narrow AI (Weak AI): Designed for a specific task, such as virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa.
- General AI (Strong AI): A hypothetical AI with human-level intelligence across diverse domains, capable of performing any intellectual task a human can.
- Superintelligent AI: A theoretical AI surpassing human intelligence in all aspects, raising significant ethical and philosophical questions.
Essential Elements of AI:
- Data: The lifeblood of AI. The quality and quantity of data significantly impact an AI system's performance.
- Algorithms: Precise procedures or equations used to solve problems. AI uses knowledge-based, computational, and reasoning models to process data and make decisions.
- Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI where systems learn from data without explicit programming.
- Deep Learning: A specialized type of ML using multiple layers of neural networks to process data.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Focuses on enabling computers to understand and interact with human language.
The Inner Workings of AI:
AI functions through a complex process, which can be broken down into stages for analysis:
1. Data Collection and Preparation: AI systems begin by gathering large datasets from various sources (structured and unstructured data, real-time sensor data). This raw data often requires cleaning and pre-processing to handle missing values and inconsistencies.
2. Algorithm Selection: The appropriate algorithm is chosen based on the problem and desired solution. Examples include supervised learning (for tasks with defined inputs and outputs), unsupervised learning (for pattern discovery), and reinforcement learning (for sequential decision-making).
3. Model Training: The chosen algorithm processes the training data, identifying patterns and relationships. The model adjusts its parameters to minimize errors between predictions and actual results.
4. Testing and Validation: The trained model is tested on separate data to evaluate its performance and prevent overfitting. Metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall are used for evaluation.
5. Deployment: The validated model is integrated into an application or system for real-world use.
6. Continuous Improvement: AI models are continuously retrained and updated with new data to improve accuracy and adapt to changing conditions.
7. Feedback Loops and Optimization: Many AI systems incorporate feedback mechanisms to evaluate the consequences of decisions and refine the model's performance.
8. Ethical Considerations and Bias Mitigation: Addressing ethical concerns, such as bias, fairness, and accountability, is crucial in AI development.
AI's Impact Across Industries:
AI is revolutionizing numerous sectors:
- Healthcare: Disease diagnosis, treatment planning, robotic surgery.
- Finance: Fraud detection, risk assessment, algorithmic trading.
- Retail: Personalized recommendations, inventory optimization.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving capabilities.
- Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Entertainment: Music recommendation, content creation.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in AI:
- Data Privacy and Security: Protecting sensitive data.
- Algorithmic Bias: Ensuring fairness and equity in AI models.
- Transparency and Explainability: Making AI decisions understandable.
- Job Displacement: Addressing potential job losses due to automation.
- Ethical Use in Warfare: Responsible development and deployment of AI in military applications.
- Long-Term Risks: Managing potential risks associated with advanced AI.
Conclusion:
AI is no longer a futuristic concept; it's a powerful technology reshaping our world. Understanding its functionality and applications provides valuable insights into its transformative impact. However, it's crucial to address the ethical and societal implications to ensure AI benefits humanity as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1. What is the primary goal of AI?
A1. To create systems capable of performing tasks requiring human intelligence, such as decision-making and problem-solving.
Q2. How does AI learn?
A2. Through machine learning, where algorithms analyze large datasets to identify patterns and make predictions.
Q3. What are some common AI applications?
A3. Virtual assistants, fraud detection, personalized recommendations, autonomous vehicles, and medical diagnostics.
Q4. What are the different types of AI?
A4. Narrow AI, general AI, and superintelligent AI.
Q5. What are the ethical concerns surrounding AI?
A5. Bias, privacy violations, job displacement, and the ethical implications of autonomous decision-making.
The above is the detailed content of How Does AI Work? - Analytics Vidhya. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). Heading Toward AGI And
 Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Remember the flood of open-source Chinese models that disrupted the GenAI industry earlier this year? While DeepSeek took most of the headlines, Kimi K1.5 was one of the prominent names in the list. And the model was quite cool.
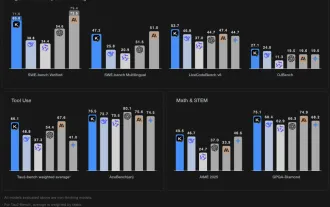
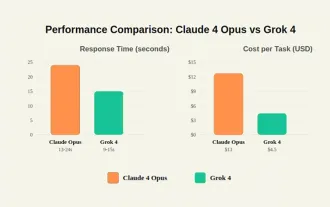 Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
By mid-2025, the AI “arms race” is heating up, and xAI and Anthropic have both released their flagship models, Grok 4 and Claude 4. These two models are at opposite ends of the design philosophy and deployment platform, yet they
 In-depth discussion on how artificial intelligence can help and harm all walks of life
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:11 AM
In-depth discussion on how artificial intelligence can help and harm all walks of life
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:11 AM
We will discuss: companies begin delegating job functions for AI, and how AI reshapes industries and jobs, and how businesses and workers work.
 Premier League Makes An AI Play To Enhance The Fan Experience
Jul 03, 2025 am 11:16 AM
Premier League Makes An AI Play To Enhance The Fan Experience
Jul 03, 2025 am 11:16 AM
On July 1, England’s top football league revealed a five-year collaboration with a major tech company to create something far more advanced than simple highlight reels: a live AI-powered tool that delivers personalized updates and interactions for ev
 10 Amazing Humanoid Robots Already Walking Among Us Today
Jul 16, 2025 am 11:12 AM
10 Amazing Humanoid Robots Already Walking Among Us Today
Jul 16, 2025 am 11:12 AM
But we probably won’t have to wait even 10 years to see one. In fact, what could be considered the first wave of truly useful, human-like machines is already here. Recent years have seen a number of prototypes and production models stepping out of t
 Context Engineering is the 'New' Prompt Engineering
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:33 AM
Context Engineering is the 'New' Prompt Engineering
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:33 AM
Until the previous year, prompt engineering was regarded a crucial skill for interacting with large language models (LLMs). Recently, however, LLMs have significantly advanced in their reasoning and comprehension abilities. Naturally, our expectation
 Chip Ganassi Racing Announces OpenAI As Mid-Ohio IndyCar Sponsor
Jul 03, 2025 am 11:17 AM
Chip Ganassi Racing Announces OpenAI As Mid-Ohio IndyCar Sponsor
Jul 03, 2025 am 11:17 AM
OpenAI, one of the world’s most prominent artificial intelligence organizations, will serve as the primary partner on the No. 10 Chip Ganassi Racing (CGR) Honda driven by three-time NTT IndyCar Series champion and 2025 Indianapolis 500 winner Alex Pa






