Google Colab Secrets: A Secure Approach to API Key Management
Data scientists, researchers, and developers frequently use APIs within Google Colab. However, managing API keys—essentially passwords granting API access—requires robust security measures. This article highlights the risks of embedding API keys directly in code or using standard environment variables, and provides a comprehensive guide to leveraging Google Colab's "Secrets" feature for secure credential management.
Why Secure API Key Management Matters
API keys are digital access keys. Compromised keys can lead to:
- Unauthorized Access: Malicious actors could exploit your keys, resulting in unexpected costs or exceeding usage limits.
- Data Breaches: Access to sensitive data or unauthorized account modifications are possible.
- Reputational Harm: Security breaches can severely damage your reputation and erode user trust.
The Risks of Traditional Methods
Storing API keys directly in Colab notebooks or as plain environment variables creates vulnerabilities:
- Exposure in Shared Notebooks: Publicly shared notebooks expose your keys.
- Version Control Issues: Committing keys to version control systems (like Git) risks public exposure, even in private repositories with inadequate access control.
- Difficult Key Rotation: Changing keys requires manual updates across your code, increasing error potential.
Google Colab Secrets: A Secure Solution
Colab's Secrets feature offers a secure, centralized solution:
- Encrypted Storage: Keys are encrypted and stored securely on Google's servers.
- Fine-Grained Access Control: You control which notebooks can access specific secrets.
- No Direct Code Exposure: Keys are never directly embedded in your code.
- Easy Key Rotation: Updating a key is straightforward via the Secrets panel; all using notebooks automatically reflect the change.
Step-by-Step Guide
-
Access the Secrets Panel: In your Colab notebook's left sidebar, click the key icon.

-
Create a New Secret: Click "Add a new secret," provide a descriptive name (e.g., "OPENAI_API_KEY"), enter the key value, and click "Save."


-
Grant Notebook Access: Enable the toggle switch next to the secret to grant the current notebook access.

-
Retrieve the Secret: Use this code:
from google.colab import userdata api_key = userdata.get('OPENAI_API_KEY')
-
Using Secrets as Environment Variables: For libraries requiring environment variables:
import os from google.colab import userdata os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = userdata.get('OPENAI_API_KEY') # ... use openai.api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY") ...
Best Practices
- Descriptive Names: Use clear, consistent naming for your secrets.
- Regular Access Review: Periodically review and revoke unnecessary notebook access.
- Careful Updates: Update secrets directly in the panel; avoid deleting and recreating.
- Avoid Printing Secrets: Never display secret values in your output.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant access only to notebooks that require it.
Conclusion
Google Colab's Secrets feature is crucial for secure API key management. By following these best practices, you can significantly enhance the security of your Colab projects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q1: Will sharing a notebook expose my secrets? A1: No. Secrets are securely stored and not included when sharing.
- Q2: Can I rename a secret? A2: No, secret names are permanent. Create a new one if needed.
- Q3: How do I update a secret? A3: Modify the value in the Secrets panel.
- Q4: Is there a limit to the number of secrets? A4: While there's no documented limit, excessive secrets might impact performance.
- Q5: Deleting a notebook—are secrets deleted? A5: No, delete secrets manually from the panel.
(Note: Images remain in their original format and positions as requested.)
The above is the detailed content of Securing Your API Keys in Google Colab. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Remember the flood of open-source Chinese models that disrupted the GenAI industry earlier this year? While DeepSeek took most of the headlines, Kimi K1.5 was one of the prominent names in the list. And the model was quite cool.
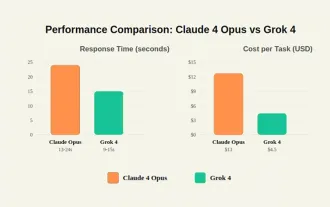 Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
By mid-2025, the AI “arms race” is heating up, and xAI and Anthropic have both released their flagship models, Grok 4 and Claude 4. These two models are at opposite ends of the design philosophy and deployment platform, yet they
 10 Amazing Humanoid Robots Already Walking Among Us Today
Jul 16, 2025 am 11:12 AM
10 Amazing Humanoid Robots Already Walking Among Us Today
Jul 16, 2025 am 11:12 AM
But we probably won’t have to wait even 10 years to see one. In fact, what could be considered the first wave of truly useful, human-like machines is already here. Recent years have seen a number of prototypes and production models stepping out of t
 Context Engineering is the 'New' Prompt Engineering
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:33 AM
Context Engineering is the 'New' Prompt Engineering
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:33 AM
Until the previous year, prompt engineering was regarded a crucial skill for interacting with large language models (LLMs). Recently, however, LLMs have significantly advanced in their reasoning and comprehension abilities. Naturally, our expectation
 6 Tasks Manus AI Can Do in Minutes
Jul 06, 2025 am 09:29 AM
6 Tasks Manus AI Can Do in Minutes
Jul 06, 2025 am 09:29 AM
I am sure you must know about the general AI agent, Manus. It was launched a few months ago, and over the months, they have added several new features to their system. Now, you can generate videos, create websites, and do much mo
 Leia's Immersity Mobile App Brings 3D Depth To Everyday Photos
Jul 09, 2025 am 11:17 AM
Leia's Immersity Mobile App Brings 3D Depth To Everyday Photos
Jul 09, 2025 am 11:17 AM
Built on Leia’s proprietary Neural Depth Engine, the app processes still images and adds natural depth along with simulated motion—such as pans, zooms, and parallax effects—to create short video reels that give the impression of stepping into the sce
 What Are The 7 Types Of AI Agents?
Jul 11, 2025 am 11:08 AM
What Are The 7 Types Of AI Agents?
Jul 11, 2025 am 11:08 AM
Picture something sophisticated, such as an AI engine ready to give detailed feedback on a new clothing collection from Milan, or automatic market analysis for a business operating worldwide, or intelligent systems managing a large vehicle fleet.The
 These AI Models Didn't Learn Language, They Learned Strategy
Jul 09, 2025 am 11:16 AM
These AI Models Didn't Learn Language, They Learned Strategy
Jul 09, 2025 am 11:16 AM
A new study from researchers at King’s College London and the University of Oxford shares results of what happened when OpenAI, Google and Anthropic were thrown together in a cutthroat competition based on the iterated prisoner's dilemma. This was no












