Goal
The goal of this miniproject/tutorial is to make a super simple HR monitor and scrolling ECG display with minimal components.
Requirements:
- python
- audio interface
- 1/4" cable/guitar cable/instrument cable (it just needs to get into the computer via the audio interface)
Quick Background
The muscles in the heart create electrical signals. Some of those signals are detectable on the surface of the skin.
We can pick those signals up using surface electrodes. The problem is, these aren't the only electrical signals on the skin. Thankfully, most of the signals we want to see are confined to around 1-40Hz.
Process
We are going to take our 1/4" cable, which will act as our electrode and poke it into our skin in the vicinity of the heart. Then we use the USB audio interface to amplify and convert the analogue signal to digital. Finally we filter and display in python.
Steps
Step 1: A 1/4" cable has two parts, the sleeve and the tip. Both parts need to make contact with your skin- just hold the sleeve with your hand and mash it against the left side of your chest/upper rib cage (some cables may have more channels, just make sure they all have contact to start). Adjust gain on audio interface (I turn mine all the way up).
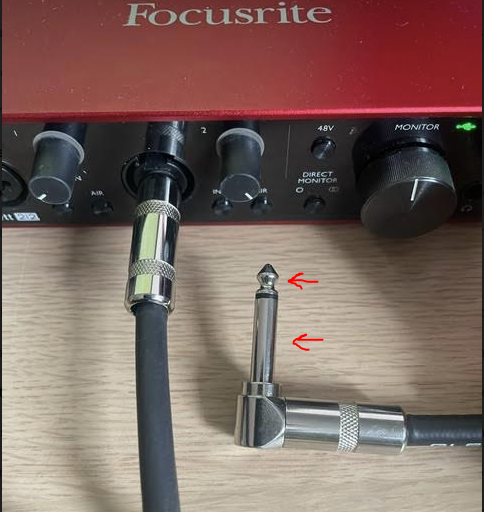

Step 2: Run the below code. Make sure to check that the input_device_index line is pointing to your audio interface. What we are doing is taking chunks of the incoming audio, converting to the frequency domain using fft, setting all unnecessary frequencies to 0, and then converting back to the time domain. Next we find the peaks to calculate the HR then graph in a way that scrolls.
import numpy as np
import pyaudio as pa
import struct
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.signal import decimate, find_peaks
CHUNK = 4410 #.1 second
FORMAT = pa.paInt16
CHANNELS = 1
RATE = 44100 # in Hz
fstep = RATE/CHUNK
p = pa.PyAudio()
values = []
dsf=44 #down sample factor
rds=RATE/dsf #down sampled rate
stream = p.open(
format = FORMAT,
channels = CHANNELS,
rate = RATE,
input_device_index=3, #adjust based on input
input=True,
frames_per_buffer=CHUNK
)
#set up graph
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1)
x = np.arange(0,2*CHUNK,2)
line, = ax.plot(x, np.random.rand(CHUNK))
ax.set_ylim(-100,100)
ax.set_xlim(0,2500)
text = ax.text(0.05, 0.95, str(0), transform=ax.transAxes, fontsize=14,
verticalalignment='top')
fig.show()
def getFiltered(x,hp=1,lp=41): #this sets the unneeded freqs to 0
fft=np.fft.fft(x)
hptrim=len(fft)/RATE*hp
lptrim=len(fft)/RATE*lp
fft[int(lptrim):-int(lptrim)]=0
fft[0:int(hptrim)]=0
return np.real(np.fft.ifft(fft))
def getHR(x):
pdis = int(0.6 * rds) #minimum distance between peaks. stops rapid triggering. also caps max hr, so adjust
peaks, _ = find_peaks(x, distance=pdis, height=0.1)
intervals = np.diff(peaks)/rds # in seconds
hr = 60 / intervals # in BPM
return peaks,round(np.mean(hr),0) #peaks,avg hr
while 1:
data = stream.read(CHUNK)
dataInt = struct.unpack(str(CHUNK) + 'h', data)
filtered=getFiltered(dataInt) #filter (working with full chunk)
dsed=decimate(filtered, 44) #down sample (turns chunk into ds chunk)
values=np.concatenate((values,dsed)) #puts the chunks into an array
peaks,hr = getHR(values*-1) # gets the peaks and determins avg HR.
text.set_text(str(hr))
line.set_xdata(np.arange(len(values)))
line.set_ydata(values*-10) #the negative is bc it comes in upside down with my set up. the *10 is just for fun
ax.set_xlim(max(0,len(values)-2500),len(values)) #keep the graph scrolling
vlines = ax.vlines(peaks,ymin=-100,ymax=100,colors='red', linestyles='dashed') # pop some lines at the peaks
fig.canvas.draw()
fig.canvas.flush_events()
vlines.remove()
if len(values)>10000: #keeps the array managably sized, and graph scrolling pretty
values=values[5000:] #5 seconds @ ~1000 sr.
Notes
Hold the cable still - you may need to wait a few seconds after movement to get an accurate heart rate. I checked it against my garmin watch, and it consistently returned similar values.
Output
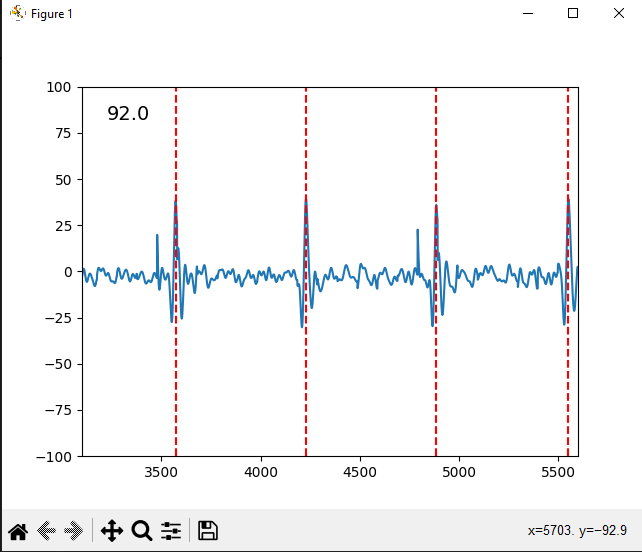
Disclaimer
Keep in mind, you are technically making your body a part of the circuit. The cable is connected to the interface which is connected to the computer which is connected to the wall power outlet... Try this at your own risk. I am no expert- I just enjoy playing around with stuff, and wanted to share.
Next Steps
This method doesn't really work very well for cleanly seeing all of the different parts of an ECG signal. The electrode is super scuffed and I did a bare minimum of filtering.
It also doesn't do well in detecting smaller signals like for EMG.
From here you can dig deeper on the software side and play around with additional filters, or create an actual circuit and use real electrodes. A bag of electrodes for this type of thing is pretty cheap on amazon (heads up, the adhesive is annoying). For a circuit, I've tried a few different configurations- what I found simplest/worked the best for me was a simple instrumentation amplifier circuit using a JFET opamp (put together on a on a breadboard). 3 electrodes, just look up a diagram for where to put them. If you use the audio interface for the ADC, the code here should work with the 3 electrode breadboard set up (might have to adjust the gain)
Why
The inspiration for this miniproject came about while playing around with a EQ plug-in in a DAW while holding a guitar cable.
The above is the detailed content of Simple DIY HR Monitor ECG Display. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Polymorphism in python classes
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:58 AM
Polymorphism in python classes
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:58 AM
Polymorphism is a core concept in Python object-oriented programming, referring to "one interface, multiple implementations", allowing for unified processing of different types of objects. 1. Polymorphism is implemented through method rewriting. Subclasses can redefine parent class methods. For example, the spoke() method of Animal class has different implementations in Dog and Cat subclasses. 2. The practical uses of polymorphism include simplifying the code structure and enhancing scalability, such as calling the draw() method uniformly in the graphical drawing program, or handling the common behavior of different characters in game development. 3. Python implementation polymorphism needs to satisfy: the parent class defines a method, and the child class overrides the method, but does not require inheritance of the same parent class. As long as the object implements the same method, this is called the "duck type". 4. Things to note include the maintenance
 Python Function Arguments and Parameters
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:26 AM
Python Function Arguments and Parameters
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:26 AM
Parameters are placeholders when defining a function, while arguments are specific values ??passed in when calling. 1. Position parameters need to be passed in order, and incorrect order will lead to errors in the result; 2. Keyword parameters are specified by parameter names, which can change the order and improve readability; 3. Default parameter values ??are assigned when defined to avoid duplicate code, but variable objects should be avoided as default values; 4. args and *kwargs can handle uncertain number of parameters and are suitable for general interfaces or decorators, but should be used with caution to maintain readability.
 Explain Python generators and iterators.
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:55 AM
Explain Python generators and iterators.
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:55 AM
Iterators are objects that implement __iter__() and __next__() methods. The generator is a simplified version of iterators, which automatically implement these methods through the yield keyword. 1. The iterator returns an element every time he calls next() and throws a StopIteration exception when there are no more elements. 2. The generator uses function definition to generate data on demand, saving memory and supporting infinite sequences. 3. Use iterators when processing existing sets, use a generator when dynamically generating big data or lazy evaluation, such as loading line by line when reading large files. Note: Iterable objects such as lists are not iterators. They need to be recreated after the iterator reaches its end, and the generator can only traverse it once.
 Python `@classmethod` decorator explained
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:26 AM
Python `@classmethod` decorator explained
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:26 AM
A class method is a method defined in Python through the @classmethod decorator. Its first parameter is the class itself (cls), which is used to access or modify the class state. It can be called through a class or instance, which affects the entire class rather than a specific instance; for example, in the Person class, the show_count() method counts the number of objects created; when defining a class method, you need to use the @classmethod decorator and name the first parameter cls, such as the change_var(new_value) method to modify class variables; the class method is different from the instance method (self parameter) and static method (no automatic parameters), and is suitable for factory methods, alternative constructors, and management of class variables. Common uses include:
 How to handle API authentication in Python
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:22 AM
How to handle API authentication in Python
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:22 AM
The key to dealing with API authentication is to understand and use the authentication method correctly. 1. APIKey is the simplest authentication method, usually placed in the request header or URL parameters; 2. BasicAuth uses username and password for Base64 encoding transmission, which is suitable for internal systems; 3. OAuth2 needs to obtain the token first through client_id and client_secret, and then bring the BearerToken in the request header; 4. In order to deal with the token expiration, the token management class can be encapsulated and automatically refreshed the token; in short, selecting the appropriate method according to the document and safely storing the key information is the key.
 What are Python magic methods or dunder methods?
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:20 AM
What are Python magic methods or dunder methods?
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:20 AM
Python's magicmethods (or dunder methods) are special methods used to define the behavior of objects, which start and end with a double underscore. 1. They enable objects to respond to built-in operations, such as addition, comparison, string representation, etc.; 2. Common use cases include object initialization and representation (__init__, __repr__, __str__), arithmetic operations (__add__, __sub__, __mul__) and comparison operations (__eq__, ___lt__); 3. When using it, make sure that their behavior meets expectations. For example, __repr__ should return expressions of refactorable objects, and arithmetic methods should return new instances; 4. Overuse or confusing things should be avoided.
 How does Python memory management work?
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:26 AM
How does Python memory management work?
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:26 AM
Pythonmanagesmemoryautomaticallyusingreferencecountingandagarbagecollector.Referencecountingtrackshowmanyvariablesrefertoanobject,andwhenthecountreacheszero,thememoryisfreed.However,itcannothandlecircularreferences,wheretwoobjectsrefertoeachotherbuta
 Python `@property` decorator
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:28 AM
Python `@property` decorator
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:28 AM
@property is a decorator in Python used to masquerade methods as properties, allowing logical judgments or dynamic calculation of values ??when accessing properties. 1. It defines the getter method through the @property decorator, so that the outside calls the method like accessing attributes; 2. It can control the assignment behavior with .setter, such as the validity of the check value, if the .setter is not defined, it is read-only attribute; 3. It is suitable for scenes such as property assignment verification, dynamic generation of attribute values, and hiding internal implementation details; 4. When using it, please note that the attribute name is different from the private variable name to avoid dead loops, and is suitable for lightweight operations; 5. In the example, the Circle class restricts radius non-negative, and the Person class dynamically generates full_name attribute






