The collection of objects which is represented by last in and first out is called a Stack and it is a collection which increases with the addition of elements to the stack as per the need of the program, hence it is a dynamic collection and elements of both same type and different types can be stored in the stack and the process of adding an element to the stack is called pushing the element to the stack and the process of removing an element from the stack is called popping the element from the stack and this stack comes under Systems. Collections namespace.
Syntax:
The syntax of C# Stack is as follows:
Stack stack_name = new Stack();
Where stack_name is the name of the stack.l
Functions of Stack in C#
- Whenever we need access to the elements of the stack in last in and first out order, we the collection of object called Stack.
- The process of adding an element to the Stack is called pushing the elements to the stack and the process of removing an element from the stack is called popping an element from the Stack.
- Stack is a dynamic collection of elements because the size of the stack increases with the addition of elements to the stack.
- The number of elements that a stack can hold is called the capacity of the stack. As the size of the stack increases with the addition of elements to the stack, the capacity of the stack also increases through reallocation.
- There can be duplicate elements allowed in the stack.
- Null is accepted by the stack as a valid value for type, references.
There are several constructors in Stack in C#. They are:
- Stack(): A new instance of the stack class is initialized which is empty whose initial capacity is the default.
- Stack(ICollection): A new instance of the stack class is initialized which consists of elements that are taken from a collection specified as a parameter and the initial capacity is the same as the number of elements taken from the collection specified as a parameter.
- Stack(Int32): A new instance of the stack class is initialized which is empty whose initial capacity is either the initial capacity specified as the parameter or the initial capacity which is default.
Methods in C# Stack
There are several methods in Stack in C#. They are:
- Clear(): The objects of the stack are removed using the Clear() method.
- Push(Object): An object specified as the parameter is inserted at the top of the stack using the Push(Object) method.
- Contains(Object): The Contains(Object) method is used to determine if an element is present in the stack.
- Peek(): The object specified at the top of the stack is returned but is not removed using the Peek() method.
- Pop(): The object specified at the top of the stack is returned and is removed using the Pop() method.
Examples
Following are the examples of c# stack :
Example #1
Consider the example program below to demonstrate Push() method, Pop() method, Peek() method, Contains() method and Clear() method:
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections;
//a class called program is defined
class program
{
//main method is called
public static void Main()
{
//a new stack is created
Stack mystk = new Stack();
//Adding the elements to the newly created stack
mystk.Push("India");
mystk.Push("USA");
mystk.Push("Canada");
mystk.Push("Germany");
//displaying the elements of the stack using foreach loop
Console.Write("The elements in the Stack are : ");
foreach(varele in mystk)
{
Console.WriteLine(ele);
}
//using contains() method to check if an element is present in the stack or not
Console.WriteLine(mystk.Contains("Germany"));
// The count of the elements in the stack is displayed
Console.Write("The count of elements in the Stack are : ");
Console.WriteLine(mystk.Count);
// displaying the top most element of the stack using Peek() method
Console.WriteLine("The topmost element in the stack is? : " + mystk.Peek());
//Using pop() method to remove the top element in the stack
Console.WriteLine("the element of the stack that is going to be removed" + " is: {0}",mystk.Pop());
Console.Write("The elements in the Stack after using pop() method are : ");
foreach(var el in mystk)
{
Console.WriteLine(el);
}
Console.Write("The count of elements in the Stack after using pop() method is : ");
Console.WriteLine(mystk.Count);
//using Clear() method to remove all the elements in the stack
mystk.Clear();
Console.Write("The count of elements in the Stack after using Clear() method is : ");
Console.WriteLine(mystk.Count);
}
}
Output:
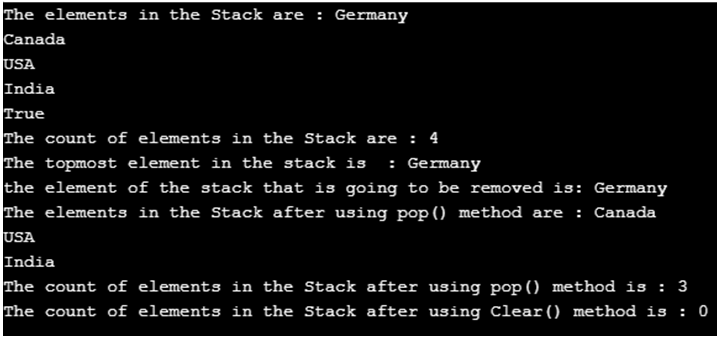
In the above program, a class called program is defined. Then the main method is called. Then a new stack is created. Then the elements are added into the newly created stack using Push() method. Then the elements of the newly created stack are displayed using foreach loop. Then contains() method is used to check if an element is present in the stack or not. Then the count of the elements in the stack is displayed by using count() method. Then the topmost element of the stack is displayed using the Peek() method. Then the topmost element of the stack is removed using the Pop() method. Then again the count of the elements and the elements of the stack are displayed after using Pop() method. Then Clear() method is used to remove all the elements of the stack. Then again the count of the elements and the elements of the stack are displayed after using the Clear() method. The output of the program is shown in the snapshot above.
- Clone(): A shallow copy of the stack is created using the Clone() method.
- Equals(Object): The Equals(Object) method is used to determine if the object specified as the parameter is equal to the current object.
- Synchronized(Stack): A synchronized wrapper for the stack is returned using the Synchronized(Stack) method.
- CopyTo(Array,Int32): The stack is copied into an array which is one dimensional with the index of the array specified as a parameter.
- ToArray(): The stack is copied to a new array using ToArray() method.
- GetType(): The type of the current instance is obtained using GetType() method.
- ToString(): A string representing the current object is returned using ToString() method.
- GetEnumerator(): An IEnumerator for the stack is returned using GetEnumerator() method.
- GetHashCode(): The GetHashCode() method is the hash function by default.
- MemberwiseClone(): A shallow copy of the current object is created using MemberwiseClone() method.
Example #2
Consider the example program below to demonstrate Clone() method, Equals() method, Synchronized() method, CopyTo() method, ToArray() method, GetType() method and GetEnumerator() method:
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections;
//a class called program is defined
class program
{
// Main Method is called
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// creating a new stack
Stack mystk = new Stack();
mystk.Push("India");
mystk.Push("USA");
mystk.Push("Canada");
mystk.Push("Germany");
Console.Write("The elements in the Stack are : ");
foreach(varele in mystk)
{
Console.WriteLine(ele);
}
// a clone of the newly created stack is created
Stack mystk1 = (Stack)mystk.Clone();
// the top most element of the clone of the newly created stack is removed using pop() method
mystk1.Pop();
Console.Write("The elements in the clone of the Stack after using pop() method are : ");
//the elements of the clone of the newly created stack is displayed
foreach(Object ob in mystk1)
Console.WriteLine(ob);
//checking if the elements of the clone of the newly created stack and the newly created stack are equal or not
Console.Write("The elements in the clone of the Stack and the stack are equal or not : ");
Console.WriteLine(mystk.Equals(mystk1));
//Checking if the clone of the newly created stack and the newly created stack is synchronised or not
Console.WriteLine("The Clone of the newly created stack is {0}.", mystk1.IsSynchronized ? "Synchronized" : "Not Synchronized");
Console.WriteLine("The newly created stack is {0}.", mystk.IsSynchronized ? "Synchronized" : "Not Synchronized");
//a new array of strings is created and the newly created stack is assigned to this array
string[] arra = new string[mystk.Count];
// The elements of the newly created stack is copied to the array
mystk.CopyTo(arra, 0);
// the elements of the array are displayed
Console.Write("The elements of the array copied from the newly created stack are : ");
foreach(string st in arra)
{
Console.WriteLine(st);
}
//converting the elements of the newly created stack to array using toarray() method
Object[] ar1 = mystk.ToArray();
Console.Write("The elements of the array copied from the newly created stack by using ToArray() method are :");
//the elements of the array are displayed
foreach(Object st1 in ar1)
{
Console.WriteLine(st1);
}
Console.WriteLine("The type of newly created stack before using "+
"ToStringMethod is: "+mystk.GetType());
Console.WriteLine("The type of newly created stack after using "+
"ToString Method is: "+mystk.ToString().GetType());
Console.Write("The elements of the newly created stack after using GetEnumerator() method are : ");
//Getenumerator() method is used to obtain the enumerator of thestack
IEnumeratorenume = mystk.GetEnumerator();
while (enume.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(enume.Current);
}
}
}
Output:
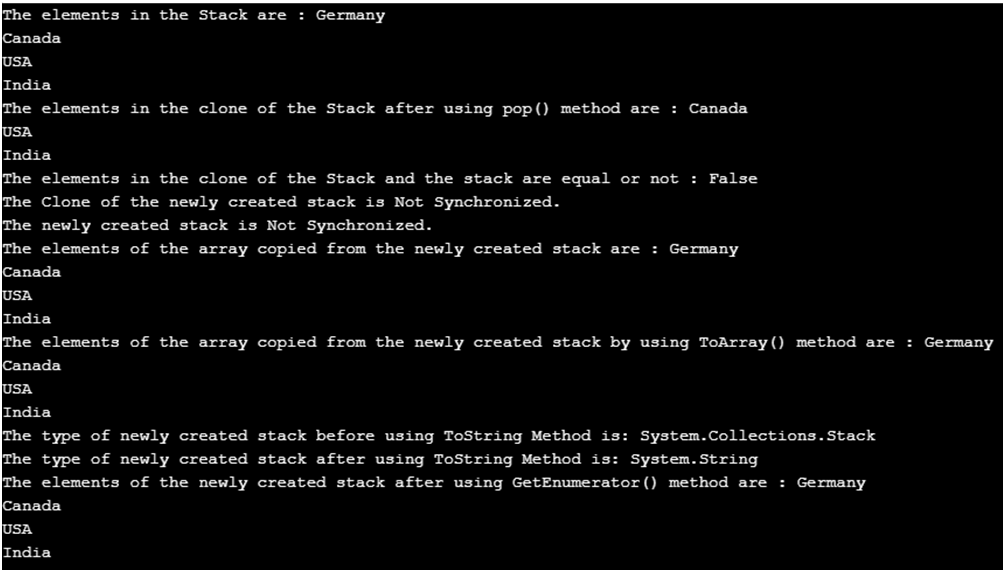
In the above program, a class called program is defined. Then the main method is called. Then a new stack is created. Then the clone of the newly created stack is created by using the clone() method. Then the topmost element of the clone of the newly created stack is removed using the pop() method. Then the elements of the clone of the newly created method are displayed. Then Equals() method is used to check if the newly created stack and the clone of the newly created stack are equal or not. Then the synchronized() method is used to check if the newly created stack and the clone of the newly created stack are synchronized or not. Then Copyto() method is used to copy the newly created stack to an array and the elements of the array are displayed. Then ToArray() method is used to copy the newly created stack to another array and then the elements of the array are displayed. Then GetType() method is used to obtain the type of the newly created stack. Then ToString() method is used to convert the type stack to string. Then GetEnumerator() method is used to obtain the IEnumerator of the stack. The output of the program is shown in the snapshot above.
The above is the detailed content of C# Stack. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Active Directory with C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Active Directory with C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Guide to Active Directory with C#. Here we discuss the introduction and how Active Directory works in C# along with the syntax and example.
 Random Number Generator in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Random Number Generator in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in C#. Here we discuss how?Random Number Generator work, concept of pseudo-random and secure numbers.
 C# Data Grid View
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
C# Data Grid View
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
Guide to C# Data Grid View. Here we discuss the examples of how a data grid view can be loaded and exported from the SQL database or an excel file.
 Factorial in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Factorial in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Guide to Factorial in C#. Here we discuss the introduction to factorial in c# along with different examples and code implementation.
 The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous is that multithreading executes multiple threads at the same time, while asynchronously performs operations without blocking the current thread. Multithreading is used for compute-intensive tasks, while asynchronously is used for user interaction. The advantage of multi-threading is to improve computing performance, while the advantage of asynchronous is to not block UI threads. Choosing multithreading or asynchronous depends on the nature of the task: Computation-intensive tasks use multithreading, tasks that interact with external resources and need to keep UI responsiveness use asynchronous.
 Prime Numbers in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
Prime Numbers in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
Guide to Prime Numbers in C#. Here we discuss the introduction and examples of prime numbers in c# along with code implementation.
 Patterns in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Patterns in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Guide to Patterns in C#. Here we discuss the introduction and top 3 types of Patterns in C# along with its examples and code implementation.
 C# vs. C : History, Evolution, and Future Prospects
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:07 AM
C# vs. C : History, Evolution, and Future Prospects
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The history and evolution of C# and C are unique, and the future prospects are also different. 1.C was invented by BjarneStroustrup in 1983 to introduce object-oriented programming into the C language. Its evolution process includes multiple standardizations, such as C 11 introducing auto keywords and lambda expressions, C 20 introducing concepts and coroutines, and will focus on performance and system-level programming in the future. 2.C# was released by Microsoft in 2000. Combining the advantages of C and Java, its evolution focuses on simplicity and productivity. For example, C#2.0 introduced generics and C#5.0 introduced asynchronous programming, which will focus on developers' productivity and cloud computing in the future.






