In this article, we will learn about various ways of writing code in Java Programming Language?for the purpose of Factorial Calculations. Being one of the Easy to Use, Object-Oriented Language, Java, is Platform Independent and a Simple Programming Language. Java’s Compiler and Interpreter were developed with Security as a major aspect. Java has various range of applications.
ADVERTISEMENT Popular Course in this category JAVA MASTERY - Specialization | 78 Course Series | 15 Mock TestsStart Your Free Software Development Course
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
Factorial, symbolized as “!” (exclamation mark), is a Mathematical operation of Multiplying a number with all the smaller numbers. For example, if the number is 5, output for factorial will be 5! = 5*4*3*2*1 = 120.
How to Execute a Java Program?
1. Complete your code and save it as (filename).java
2. Open Terminal and run the following java command.
- a. javac (filename).java
3. The above command will generate a class file.
4. Now, execute the class file.
- a. java (filename)
Examples of Factorial using various Methods
Below are the different examples using various methods:
Example 1 – Using Basic Method
Moving forward, we will now write a simple Java Program for Factorial Calculation.
public class Factorial
{
public static void main(String args[])
{int i, fact=1;
int number=5;
for(i=1;i<=number;i++)
{
fact=fact*i;
}
System.out.println("Factorial of "+number+" is: "+fact);
}
}
Save the above code with any filename and .java extension.
Code Explanation:
It started with two variables, “i” and “fact,” with value of 1, then “number” with 5, which is our number to calculate the factorial. I went into For Loop, kept increasing the value of i until we matched it with a number, i.e. 5. While incrementing, every time value of fact increases, it is multiplied, and the fact is assigned a new value.
Output:
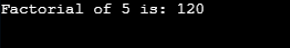
Example 2 – Using User Input
Another commonly used method is where we ask for a user input number for calculation instead of pre-defining it.
Refer to the below code for User Input Based Calculation:
import java.util.Scanner;
class Facto{
public static void main(String args[]) {
int q, a, fact = 1;
System.out.println("Please Enter a number:");
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
q = in.nextInt();
if ( q < 0 )
System.out.println("Please enter a number greater than 0:");
else {
for ( a = 1 ; a <= q ; a++ )
fact = fact*a;
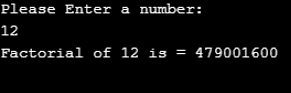
System.out.println("Factorial of "+q+" is = "+fact);
}
}
}
Save the above code as we did for the earlier example.
Code Explanation:
A major difference between the earlier and above example is the user input; Rest is the same. Code will ask for a number to be calculated, then if the number entered by the user is Negative that is in “-”, minus, it will prompt “Please enter a number greater than 0:”, which is obvious as Factorial cannot be calculated for Negative number. Now, it will accept a positive number and proceed with Calculating Factorial and then print the output as shown in the below image.
Output:
Example 3 – Using Recursion Method
Recursion is one of the most useful tools in the world of programming. Recursion basically means reusing the function. So to say, we won’t have to define an extra number of variables here, which means we’ll have only two variables or less.
A major reason to implement Recursion is the power to reduce the code length and elegantly reduce the time complexity of a program. The recursion method, with its advantages, has a few disadvantages that could have a major impact in the long run.
Disadvantages
Disadvantages with recursion:
- Basically, it is quite difficult to debug the recursion code and trace it for any step with an error.
- Other than that, recursion uses more memory, as it uses Stack to accomplish the task, where it keeps adding up the stack with a newer recursive call.
- And, if not implemented wisely, Recursion can slow down the function.
- StackOverflowException: Recursive methods often throw this Exception due to the overuse of stack.
Refer to the below code:
public class FactorialExample2 {
static int factorial(int n){
if (n == 1)
return 1;
else
return(n * factorial(n-1));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
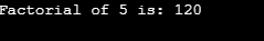
System.out.println("Factorial of 5 is: "+factorial(5));
}
}
Save and compile the program as we did earlier.
Code Explanation:
The above code starts with a single int variable and checks if it is equal to 1; if yes, it returns one, as factorial for 1 is 1. If not equal to 1, it proceeds with the recursion function. Our int value, for example, is 5, so it’ll be like “5 * factorial(5-1)”, factorial is called here for the second time, which is another call. Then it returns again with a newer int value, which is 4, “4 * factorial(4-1)”, now it’ll be the third call to the recursion method. Now, the newer int value is 3, which means “3 * factorial(3-1)”, now it’ll be the fourth call, and the value will be 2, which means “2 * factorial(2-1)”. The int value will be one in the next recursive call, which will terminate the function here. While every call was made, its value was saved in a Stack, which is a LIFO method. So, for the final Output, the result will be “5*4*3*2*1 = 120.”
Compared to other methods, Recursion is quite difficult to understand and to implement, but if understood well and implemented wisely, it is a good tool.
Output:
It is highly recommended to use Recursion only in the case where writing an iterative code can be quite complex.
Now that we have learned various methods for implementing Factorial Calculations in Java Let’s explore a Built-in function that does the same work in a single line.
Example 4 – Using built-in Function
*) IntMath
Understanding the need for arithmetic operations over a value, a few functions specific to certain value types were written, we will see the Integer type value in work.
IntMath is a class for arithmetic calculations on an int value. IntMath class comes with a range of arithmetic operations, including factorial.
Syntax:
factorial (int n)
Conclusion –?Factorial in Java
We started with an introduction to java and how to run a java program. Then we learned about Factorial Calculation and various methods, including Recursion, to accomplish it.
Towards the end, we learned about IntMath; a Java Function primarily focused on Arithmetic operations. Java is a widely-used programming language; it comes with many features; in this article, we learned about Factorial Calculations in Java, which is a tiny aspect.
The above is the detailed content of Factorial in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Laravel lazy loading vs eager loading
Jul 28, 2025 am 04:23 AM
Laravel lazy loading vs eager loading
Jul 28, 2025 am 04:23 AM
Lazy loading only queries when accessing associations can easily lead to N 1 problems, which is suitable for scenarios where the associated data is not determined whether it is needed; 2. Emergency loading uses with() to load associated data in advance to avoid N 1 queries, which is suitable for batch processing scenarios; 3. Emergency loading should be used to optimize performance, and N 1 problems can be detected through tools such as LaravelDebugbar, and the $with attribute of the model is carefully used to avoid unnecessary performance overhead.
 Integrating PHP with Machine Learning Models
Jul 28, 2025 am 04:37 AM
Integrating PHP with Machine Learning Models
Jul 28, 2025 am 04:37 AM
UseaRESTAPItobridgePHPandMLmodelsbyrunningthemodelinPythonviaFlaskorFastAPIandcallingitfromPHPusingcURLorGuzzle.2.RunPythonscriptsdirectlyfromPHPusingexec()orshell_exec()forsimple,low-trafficusecases,thoughthisapproachhassecurityandperformancelimitat
 python memory management example
Jul 28, 2025 am 01:10 AM
python memory management example
Jul 28, 2025 am 01:10 AM
Python's memory management is based on reference counting and garbage collection mechanisms. 1. The reference counting mechanism ensures that objects are released immediately when the reference number is 0. The return value of sys.getrefcount() is 1 more than the actual reference because it increases its reference itself; 2. Circular references cannot be cleaned through reference counting, and it depends on the generational recycling of the gc module. Calling gc.collect() can recycle unreachable objects; 3. In actual development, long-term holding of large object references should be avoided. We can use weakref weak references, timely place None to release memory, and use tracemalloc to monitor memory allocation; 4. Summary: Python combines reference counting and garbage collection to manage memory, developers can use tools and optimize reference pipes.
 Laravel raw SQL query example
Jul 29, 2025 am 02:59 AM
Laravel raw SQL query example
Jul 29, 2025 am 02:59 AM
Laravel supports the use of native SQL queries, but parameter binding should be preferred to ensure safety; 1. Use DB::select() to execute SELECT queries with parameter binding to prevent SQL injection; 2. Use DB::update() to perform UPDATE operations and return the number of rows affected; 3. Use DB::insert() to insert data; 4. Use DB::delete() to delete data; 5. Use DB::statement() to execute SQL statements without result sets such as CREATE, ALTER, etc.; 6. It is recommended to use whereRaw, selectRaw and other methods in QueryBuilder to combine native expressions to improve security
 Reactive Programming in Java with Project Reactor and Spring WebFlux
Jul 29, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Reactive Programming in Java with Project Reactor and Spring WebFlux
Jul 29, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Responsive programming implements high concurrency, low latency non-blocking services in Java through ProjectReactor and SpringWebFlux. 1. ProjectReactor provides two core types: Mono and Flux, supports declarative processing of asynchronous data flows, and converts, filters and other operations through operator chains; 2. SpringWebFlux is built on Reactor, supports two programming models: annotation and functional. It runs on non-blocking servers such as Netty, and can efficiently handle a large number of concurrent connections; 3. Using WebFlux Reactor can improve the concurrency capability and resource utilization in I/O-intensive scenarios, and naturally supports SSE and WebSo.
 Notepad find and replace with regex capture groups
Jul 28, 2025 am 02:17 AM
Notepad find and replace with regex capture groups
Jul 28, 2025 am 02:17 AM
Use regular expression capture group in Notepad to effectively reorganize text. First, you need to open the replacement dialog box (Ctrl H), select "Search Mode" as "regular expression", 1. Use () to define the capture group, such as (\w ) to capture words; 2. Use \1 and \2 to reference the corresponding group in the replacement box; 3. Example: Exchange the name "JohnDoe" as "Doe, John", find (\w )\s (\w ), replace it with \2,\1; 4. Date format conversion 2023-12-25 to 25/12/2023, find (\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2}), replace it with \3/\2/\1; 5. Log reordering can extract time, level, ID and other information
 Optimizing Memory Usage in Java Applications
Jul 28, 2025 am 02:40 AM
Optimizing Memory Usage in Java Applications
Jul 28, 2025 am 02:40 AM
UseefficientdatastructureslikeArrayListoverLinkedListandprimitivecollectionstoreduceoverhead;2.Minimizeobjectcreationbyreusingobjects,usingStringBuilderforconcatenation,andcachingexpensiveobjects;3.Preventmemoryleaksbynullifyingreferences,usingstatic
 Using MapStruct for Painless Bean Mapping in Java
Jul 28, 2025 am 03:20 AM
Using MapStruct for Painless Bean Mapping in Java
Jul 28, 2025 am 03:20 AM
MapStruct is a compile-time code generator used to simplify mapping between JavaBeans. 1. It automatically generates implementation classes by defining interfaces to avoid manually writing lengthy set/get mapping code; 2. It has type-safe, no runtime overhead, supports automatic mapping of the same name fields, custom expressions, nested objects and collection mapping; 3. It can be integrated with Spring and uses @Mapper(componentModel="spring") to inject mapper into Springbean; 4. Simple configuration, just introduce mapstruct dependencies and annotationProcessorPaths inserts






