 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 The accuracy rate reaches 60.8%. Zhejiang University's chemical retrosynthesis prediction model based on Transformer was published in the Nature sub-journal
The accuracy rate reaches 60.8%. Zhejiang University's chemical retrosynthesis prediction model based on Transformer was published in the Nature sub-journal
The accuracy rate reaches 60.8%. Zhejiang University's chemical retrosynthesis prediction model based on Transformer was published in the Nature sub-journal
Aug 06, 2024 pm 07:34 PM
Editor | KX
Retrosynthesis is a critical task in drug discovery and organic synthesis, and AI is increasingly used to speed up the process.
Existing AI methods have unsatisfactory performance and limited diversity. In practice, chemical reactions often cause local molecular changes, with considerable overlap between reactants and products.
Inspired by this, Hou Tingjun’s team at Zhejiang University proposed to redefine single-step retrosynthetic prediction as a molecular string editing task, and iteratively refine the target molecular string to generate precursor compounds. And an edit-based retrosynthesis model EditRetro is proposed, which can achieve high-quality and diverse predictions.
Extensive experiments show that the model achieves excellent performance on the standard benchmark data set USPTO-50 K, with a top-1 accuracy of 60.8%.
The results show that EditRetro exhibits good generalization capabilities and robustness, highlighting its potential in the field of AI-driven chemical synthesis planning.
Related research titled "Retrosynthesis prediction with an iterative string editing model" was published in "Nature Communications" on July 30.

Paper link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-50617-1
Molecular synthesis path design is an important task in organic synthesis, which is important for biomedicine, pharmaceuticals and It is of great significance in various fields such as materials industry.
Retrosynthetic analysis is the most widely used method for developing synthetic routes. It involves using established reactions to iteratively break down molecules into simpler, easier-to-synthesize precursors.
In recent years, AI-driven retrosynthesis has facilitated the exploration of more complex molecules, greatly reducing the time and effort required to design synthetic experiments. Single-step retrosynthesis prediction is an important part of retrosynthesis planning. There are currently several deep learning-based methods with excellent results. These methods can be roughly divided into three categories: template-based methods, template-free methods, and semi-template-based methods.
Here, researchers focus on template-free retrosynthetic prediction. propose to redefine the problem as a molecular string editing task and propose EditRetro, an editing-based retrosynthetic model that can achieve high-quality and diverse predictions.

Illustration: Schematic diagram of the proposed EditRetro method based on molecular string retrosynthesis. (Source: Paper)
The core concept of this research is to generate reactant strings through an iterative editing process using Levenshtein operations. The approach draws inspiration from recent advances in edit-based sequence generation models. Specifically, operations from EDITOR, an editing-based Transformer designed for neural machine translation, are employed.
EditRetro Overview
The EditRetro model contains three editing operations, namely sequence relocation, placeholder insertion and marker insertion, to generate reactant strings. It is implemented by a Transformer model, which consists of an encoder and three decoders, both consisting of stacked Transformer blocks.
- Relocation decoder: Relocation operations include basic token editing operations such as retain, delete, and reorder. It can be compared to the process of identifying reaction centers, including reordering and deleting atoms or groups to obtain synthons.
- Placeholder decoder: The placeholder insertion strategy (classifier) ??predicts the number of placeholders to insert between adjacent tokens. It plays a crucial role in determining the structure of reactants, similar to identifying the positions of added atoms or groups in intermediate synthons obtained from the sequence repositioning stage.
- Token decoder: token insertion strategy (classifier), responsible for generating candidate tokens for each placeholder. This is crucial to determine the actual reactants that can be used to synthesize the target product. This process can be viewed as a similar process done by synthons, combined with placeholder insertion operations.
EditRetro model improves generation efficiency through its non-autoregressive decoder. Although incorporating additional decoders to iteratively predict editing operations, EditRetro performs editing operations in parallel within each decoder (i.e., non-autoregressive generation).
When given a target molecule, the encoder takes its string as input and generates the corresponding hidden representation, which is then used as input to the decoder’s cross-attention module. Similarly, the decoder also takes the product string as input on the first iteration. During each decoding iteration, the three decoders are executed sequentially.
Better than baseline, generate accurate reactants
????? ?? ???? ??? ?? USPTO-50K ? USPTO-FULL?? ??? ??? ??????. ???? ?? ??? ??? ? ??? ??? ??? ?? ??? R-SMILES ? ??? ?? ?? ??? Graph2Edits? ???? ?? ??? ???? ?? ???? ??? ?????.

EditRetro ???? ??? ??? ?? USPTO-50K? ?? ???? ???? EditRetro? 60.8%? ?? 1? ?? ?? ???? ??? ??? ???? ??? ??????.

?? ??? USPTO-FULL ??? ???? ?? 1?? ??? ?? ???? 52.2%? ?? ?? ???? ???? ?? ????? ? ??? ???????.

EditRetro? ?? RoundTrip ? MaxFrag ??? ???? ?? ???? ? ?? ??? ?????. ?? EditRetro? ??? ??? ????? ??? ? ??? ?????.
?? EditRetro? ? ??? ?? ??? ?? ??? ??? ?????. ? ??? ??? ???? ??? ??? ???? ???? ???? ??? ???? ? ??? ???. ??? ??? ?? ??? ??? ?? ??? ?? ??? ?? ???? ??? ? ????. ?? ??? ??? ?? ???? ????? ??? ?? ??? ???? ?? ???? ???? ????. ? ? ?? ??? ?? ???? ??? ???? ???? ????.
?? ??? ?? ??, ?? ?? ? ?? ?? ??? ??? ? ? ??? ???? EditRetro? ???? ???????. ??? ??? ???? ?????? EditRetro? ???? ???? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ? ?? ??? ?????.
??? ?? ??? ???
?? 4?? ??? ??? ?? ?????? EditRetro? ????? ??? ?? ? ???? ?????.
?? ???? EditRetro? ???? ???? ?? ??? ??? ??? ?? ??? ?? ??? ??????. ???? ??? ?? ??? ??? ??? ?? 4?? ?? ???, ? ??????(febuxostat), ?????(osimertinib), GPX4? ????? ????, DDR1 ??? ??? INS015_037? ??????.

??: EditRetro? ??? ??? ??. (??: ??)
? ?? ?? ?? ??? ??? ?? ?? ???? ??? ??? ????? ???? ??? ?? 2?? ?????. ??? 16?? ?? ?? ? 10?? ?? ???? 1?????. ??? ??? ?? ??? ???? EditRetro? ???? ???? ?????.
? ??? ??? ???? ???? ???? ?? ?? ??? ?????? ??? ?? ???? ???? ?? ????? ?? ??? ?????.
The above is the detailed content of The accuracy rate reaches 60.8%. Zhejiang University's chemical retrosynthesis prediction model based on Transformer was published in the Nature sub-journal. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
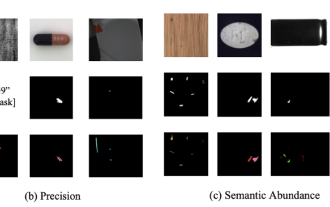 Breaking through the boundaries of traditional defect detection, 'Defect Spectrum' achieves ultra-high-precision and rich semantic industrial defect detection for the first time.
Jul 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
Breaking through the boundaries of traditional defect detection, 'Defect Spectrum' achieves ultra-high-precision and rich semantic industrial defect detection for the first time.
Jul 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
In modern manufacturing, accurate defect detection is not only the key to ensuring product quality, but also the core of improving production efficiency. However, existing defect detection datasets often lack the accuracy and semantic richness required for practical applications, resulting in models unable to identify specific defect categories or locations. In order to solve this problem, a top research team composed of Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Guangzhou and Simou Technology innovatively developed the "DefectSpectrum" data set, which provides detailed and semantically rich large-scale annotation of industrial defects. As shown in Table 1, compared with other industrial data sets, the "DefectSpectrum" data set provides the most defect annotations (5438 defect samples) and the most detailed defect classification (125 defect categories
 NVIDIA dialogue model ChatQA has evolved to version 2.0, with the context length mentioned at 128K
Jul 26, 2024 am 08:40 AM
NVIDIA dialogue model ChatQA has evolved to version 2.0, with the context length mentioned at 128K
Jul 26, 2024 am 08:40 AM
The open LLM community is an era when a hundred flowers bloom and compete. You can see Llama-3-70B-Instruct, QWen2-72B-Instruct, Nemotron-4-340B-Instruct, Mixtral-8x22BInstruct-v0.1 and many other excellent performers. Model. However, compared with proprietary large models represented by GPT-4-Turbo, open models still have significant gaps in many fields. In addition to general models, some open models that specialize in key areas have been developed, such as DeepSeek-Coder-V2 for programming and mathematics, and InternVL for visual-language tasks.
 Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Aug 08, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Aug 08, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Editor |KX To this day, the structural detail and precision determined by crystallography, from simple metals to large membrane proteins, are unmatched by any other method. However, the biggest challenge, the so-called phase problem, remains retrieving phase information from experimentally determined amplitudes. Researchers at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark have developed a deep learning method called PhAI to solve crystal phase problems. A deep learning neural network trained using millions of artificial crystal structures and their corresponding synthetic diffraction data can generate accurate electron density maps. The study shows that this deep learning-based ab initio structural solution method can solve the phase problem at a resolution of only 2 Angstroms, which is equivalent to only 10% to 20% of the data available at atomic resolution, while traditional ab initio Calculation
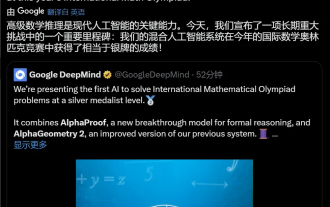 Google AI won the IMO Mathematical Olympiad silver medal, the mathematical reasoning model AlphaProof was launched, and reinforcement learning is so back
Jul 26, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
Google AI won the IMO Mathematical Olympiad silver medal, the mathematical reasoning model AlphaProof was launched, and reinforcement learning is so back
Jul 26, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
For AI, Mathematical Olympiad is no longer a problem. On Thursday, Google DeepMind's artificial intelligence completed a feat: using AI to solve the real question of this year's International Mathematical Olympiad IMO, and it was just one step away from winning the gold medal. The IMO competition that just ended last week had six questions involving algebra, combinatorics, geometry and number theory. The hybrid AI system proposed by Google got four questions right and scored 28 points, reaching the silver medal level. Earlier this month, UCLA tenured professor Terence Tao had just promoted the AI ??Mathematical Olympiad (AIMO Progress Award) with a million-dollar prize. Unexpectedly, the level of AI problem solving had improved to this level before July. Do the questions simultaneously on IMO. The most difficult thing to do correctly is IMO, which has the longest history, the largest scale, and the most negative
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 PRO | Why are large models based on MoE more worthy of attention?
Aug 07, 2024 pm 07:08 PM
PRO | Why are large models based on MoE more worthy of attention?
Aug 07, 2024 pm 07:08 PM
In 2023, almost every field of AI is evolving at an unprecedented speed. At the same time, AI is constantly pushing the technological boundaries of key tracks such as embodied intelligence and autonomous driving. Under the multi-modal trend, will the situation of Transformer as the mainstream architecture of AI large models be shaken? Why has exploring large models based on MoE (Mixed of Experts) architecture become a new trend in the industry? Can Large Vision Models (LVM) become a new breakthrough in general vision? ...From the 2023 PRO member newsletter of this site released in the past six months, we have selected 10 special interpretations that provide in-depth analysis of technological trends and industrial changes in the above fields to help you achieve your goals in the new year. be prepared. This interpretation comes from Week50 2023
 The accuracy rate reaches 60.8%. Zhejiang University's chemical retrosynthesis prediction model based on Transformer was published in the Nature sub-journal
Aug 06, 2024 pm 07:34 PM
The accuracy rate reaches 60.8%. Zhejiang University's chemical retrosynthesis prediction model based on Transformer was published in the Nature sub-journal
Aug 06, 2024 pm 07:34 PM
Editor | KX Retrosynthesis is a critical task in drug discovery and organic synthesis, and AI is increasingly used to speed up the process. Existing AI methods have unsatisfactory performance and limited diversity. In practice, chemical reactions often cause local molecular changes, with considerable overlap between reactants and products. Inspired by this, Hou Tingjun's team at Zhejiang University proposed to redefine single-step retrosynthetic prediction as a molecular string editing task, iteratively refining the target molecular string to generate precursor compounds. And an editing-based retrosynthetic model EditRetro is proposed, which can achieve high-quality and diverse predictions. Extensive experiments show that the model achieves excellent performance on the standard benchmark data set USPTO-50 K, with a top-1 accuracy of 60.8%.
 SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
Editor | KX In the field of drug research and development, accurately and effectively predicting the binding affinity of proteins and ligands is crucial for drug screening and optimization. However, current studies do not take into account the important role of molecular surface information in protein-ligand interactions. Based on this, researchers from Xiamen University proposed a novel multi-modal feature extraction (MFE) framework, which for the first time combines information on protein surface, 3D structure and sequence, and uses a cross-attention mechanism to compare different modalities. feature alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that this method achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting protein-ligand binding affinities. Furthermore, ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness and necessity of protein surface information and multimodal feature alignment within this framework. Related research begins with "S





