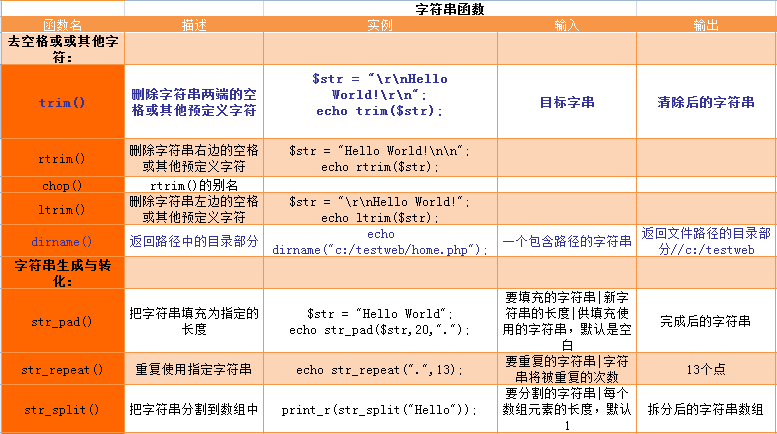
Statement of this Website

All resources on this website are contributed and published by netizens, or reprinted by major download sites. Please check the integrity of the software yourself! All resources on this website are for learning and reference only. Please do not use them for commercial purposes, otherwise you will be responsible for all consequences incurred! If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete and remove it. Contact information: admin@php.cn