
##Process control
JAVA input and output
Input
Two input methods:
Method 1: java.util.ScannerThe code is as follows:
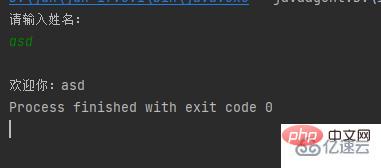
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { var sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("請輸入姓名:"); String name = sc.nextLine(); System.out.printf("%n歡迎你:%s", name); }}
Generate a Scanner object, output "Please enter your name:", return the input string and assign it to name, and output "%nWelcome %s" where %n represents a newline and %s represents nameResult:
Method 2: JOptionPane If the input content is confirmed, the string value will be nullpublic class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String w = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("請輸入詞匯:");
System.out.println(w);
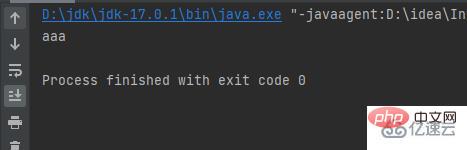
}}Result: 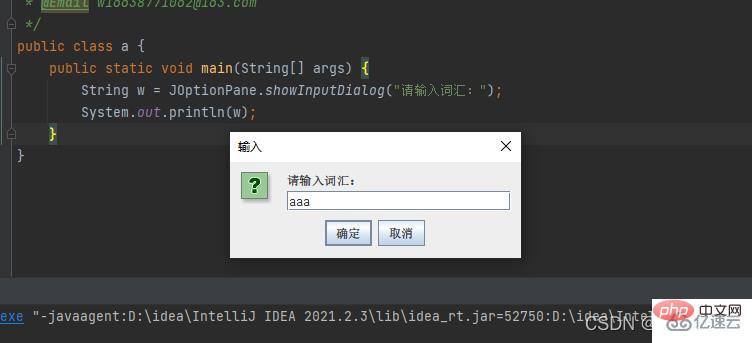
Three ways to output on the consoleMethod 1: System.out.print (); Output to the console
Method 2: System.out.println(); Output to the console and wrap
Method 3: System.out.printf(); Format the output to the console
Code demonstration:
The first method outputs directly without line breakspublic class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int w = 1;
int a = 2;
System.out.print(w);
System.out.print(a);
}}Result: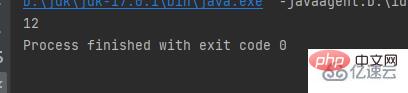
The second line feed outputpublic class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int w = 1;
int a = 2;
System.out.println(w);
System.out.println(a);
}}Result: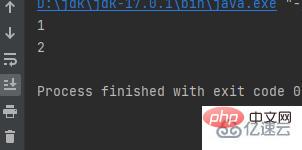
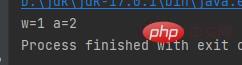
The third formatted outputResult:The meaning of %d It is an int type variable, that is, replace the first %d with the value of w, and replace the second %d with the value of a
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int w = 1; int a = 2; System.out.printf("w=%d a=%d", w, a); }}
Branch statement
if else
if() The condition in the brackets returns true as long as it is correct, and false if it is wrong.else means otherwise
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { if (1>2){ System.out.println("A"); }else { System.out.println("B"); } }}
Multiple judgments are as follows: If the first judgment is incorrect, the next judgment will be made. When the return value is true, it will be executed, otherwise else## will be executed.switch case default#
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { if (1 > 2) { System.out.println("A"); } else if (1 > 0) { System.out.println("B"); } else { System.out.println("C"); } }}
#switch multi-branch switch statement
switch(w) w in brackets is the judgment parameter, and the number after case is A value that matches w. When the value of w matches the value after the case, the statement in the current case is executedbreak means to exit the current judgment, which means that there is no need to judge again later
default means the default value, when there is no match The default is thispublic class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int w=1; String wk = ""; switch (w) { case 2: wk = "星期一"; break; case 3: wk = "星期二"; break; case 4: wk = "星期三"; break; case 5: wk = "星期四"; break; case 6: wk = "星期五"; break; case 7: wk = "星期六"; break; default: wk = "星期日"; break; } System.out.println(wk); }}result:
 Loop statement
Loop statement
for
for ( int i = 0; i < 5; i ) is divided into three parts. int i=0 is the initial value, i<5 is the loop condition, and i is the value of i plus 1 after executing this statement once. Exit the loop when i>5public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}} Result: 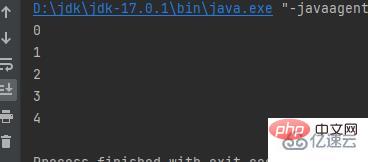 for in
for in
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int i : a) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}}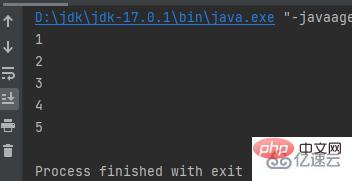 while do while
while do while
while(condition){ }
- Execute the statement if the condition is met, exit if not.
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 0; while (i < 5) { i++; System.out.println(i); } }}Result:
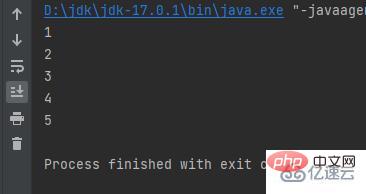
Different from while, do while is executed once Then judgeThe output is executed first and then judged. Therefore, the condition i<0 can also output once
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 0; do { i++; System.out.println(i); } while (i < 0); }}
The result is:
 break continue
break continue
break;Skip this time when i is divisible by 2 , proceed to the next cycle. When i is greater than 10, the loop ends.Terminate the current loop statement continue;
End this loop and immediately prepare to start the next loopint i = 0;while (++i < 20) { if (i % 2 == 0) continue; System.out.println(i); if (i > 10) break;}
The above is the detailed content of JAVA process control is implemented in this way. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 css dark mode toggle example
Jul 30, 2025 am 05:28 AM
css dark mode toggle example
Jul 30, 2025 am 05:28 AM
First, use JavaScript to obtain the user system preferences and locally stored theme settings, and initialize the page theme; 1. The HTML structure contains a button to trigger topic switching; 2. CSS uses: root to define bright theme variables, .dark-mode class defines dark theme variables, and applies these variables through var(); 3. JavaScript detects prefers-color-scheme and reads localStorage to determine the initial theme; 4. Switch the dark-mode class on the html element when clicking the button, and saves the current state to localStorage; 5. All color changes are accompanied by 0.3 seconds transition animation to enhance the user
 python parse date string example
Jul 30, 2025 am 03:32 AM
python parse date string example
Jul 30, 2025 am 03:32 AM
Use datetime.strptime() to convert date strings into datetime object. 1. Basic usage: parse "2023-10-05" as datetime object through "%Y-%m-%d"; 2. Supports multiple formats such as "%m/%d/%Y" to parse American dates, "%d/%m/%Y" to parse British dates, "%b%d,%Y%I:%M%p" to parse time with AM/PM; 3. Use dateutil.parser.parse() to automatically infer unknown formats; 4. Use .d
 css dropdown menu example
Jul 30, 2025 am 05:36 AM
css dropdown menu example
Jul 30, 2025 am 05:36 AM
Yes, a common CSS drop-down menu can be implemented through pure HTML and CSS without JavaScript. 1. Use nested ul and li to build a menu structure; 2. Use the:hover pseudo-class to control the display and hiding of pull-down content; 3. Set position:relative for parent li, and the submenu is positioned using position:absolute; 4. The submenu defaults to display:none, which becomes display:block when hovered; 5. Multi-level pull-down can be achieved through nesting, combined with transition, and add fade-in animations, and adapted to mobile terminals with media queries. The entire solution is simple and does not require JavaScript support, which is suitable for large
 VSCode settings.json location
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:12 AM
VSCode settings.json location
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:12 AM
The settings.json file is located in the user-level or workspace-level path and is used to customize VSCode settings. 1. User-level path: Windows is C:\Users\\AppData\Roaming\Code\User\settings.json, macOS is /Users//Library/ApplicationSupport/Code/User/settings.json, Linux is /home//.config/Code/User/settings.json; 2. Workspace-level path: .vscode/settings in the project root directory
 css full page layout example
Jul 30, 2025 am 05:39 AM
css full page layout example
Jul 30, 2025 am 05:39 AM
Full screen layout can be achieved using Flexbox or Grid. The core is to make the minimum height of the page the viewport height (min-height:100vh); 2. Use flex:1 or grid-template-rows:auto1frauto to make the content area occupy the remaining space; 3. Set box-sizing:border-box to ensure that the margin does not exceed the container; 4. Optimize the mobile experience with responsive media query; this solution is compatible with good structure and is suitable for login pages, dashboards and other scenarios, and finally realizes a full screen page layout with vertical centering and full viewport.
 How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
To correctly handle JDBC transactions, you must first turn off the automatic commit mode, then perform multiple operations, and finally commit or rollback according to the results; 1. Call conn.setAutoCommit(false) to start the transaction; 2. Execute multiple SQL operations, such as INSERT and UPDATE; 3. Call conn.commit() if all operations are successful, and call conn.rollback() if an exception occurs to ensure data consistency; at the same time, try-with-resources should be used to manage resources, properly handle exceptions and close connections to avoid connection leakage; in addition, it is recommended to use connection pools and set save points to achieve partial rollback, and keep transactions as short as possible to improve performance.
 Full-Stack Web Development with Java, Spring Boot, and React
Jul 31, 2025 am 03:33 AM
Full-Stack Web Development with Java, Spring Boot, and React
Jul 31, 2025 am 03:33 AM
Selecting the Java SpringBoot React technology stack can build stable and efficient full-stack web applications, suitable for small and medium-sized to large enterprise-level systems. 2. The backend uses SpringBoot to quickly build RESTfulAPI. The core components include SpringWeb, SpringDataJPA, SpringSecurity, Lombok and Swagger. The front-end separation is achieved through @RestController returning JSON data. 3. The front-end uses React (in conjunction with Vite or CreateReactApp) to develop a responsive interface, uses Axios to call the back-end API, and ReactRouter
 Java Performance Optimization and Profiling Techniques
Jul 31, 2025 am 03:58 AM
Java Performance Optimization and Profiling Techniques
Jul 31, 2025 am 03:58 AM
Use performance analysis tools to locate bottlenecks, use VisualVM or JProfiler in the development and testing stage, and give priority to Async-Profiler in the production environment; 2. Reduce object creation, reuse objects, use StringBuilder to replace string splicing, and select appropriate GC strategies; 3. Optimize collection usage, select and preset initial capacity according to the scene; 4. Optimize concurrency, use concurrent collections, reduce lock granularity, and set thread pool reasonably; 5. Tune JVM parameters, set reasonable heap size and low-latency garbage collector and enable GC logs; 6. Avoid reflection at the code level, replace wrapper classes with basic types, delay initialization, and use final and static; 7. Continuous performance testing and monitoring, combined with JMH






