 web3.0
web3.0
 What are Maker and Taker? How to calculate the handling fee? A list of handling fees on popular exchanges
What are Maker and Taker? How to calculate the handling fee? A list of handling fees on popular exchanges
What are Maker and Taker? How to calculate the handling fee? A list of handling fees on popular exchanges
Jul 30, 2025 pm 09:33 PMTable of contents
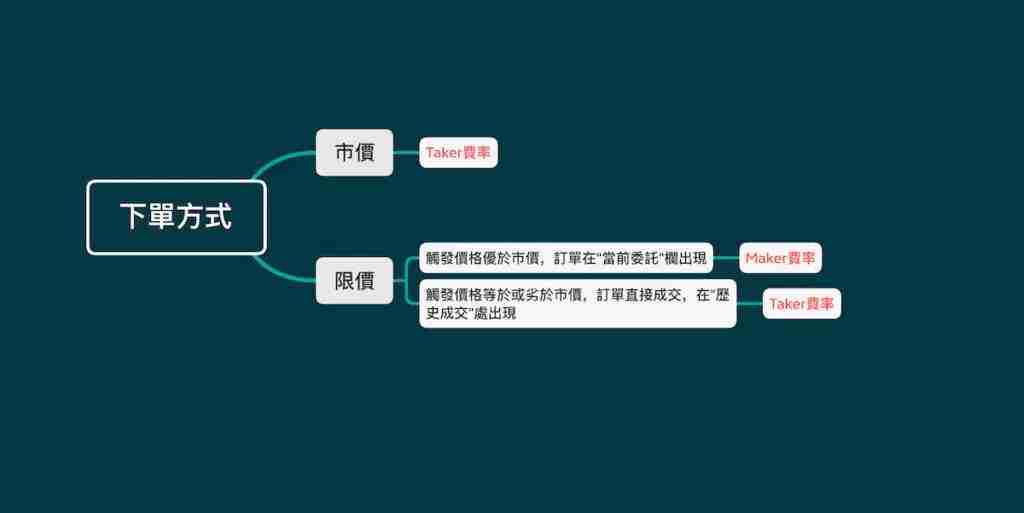
- What are Maker and pending orders? How to calculate Maker Fee
- Maker Fee Calculation Formula
- Is it necessary to use a limit order a Maker?
- What are Taker and Eat Order? How to calculate Taker Fee
- Taker Fee Calculation Formula
- How to determine whether you are a Maker or Taker
- Lazy Pack – Maker/taker fees for each virtual currency exchange
- Spot maker/taker fee lazy pack
- Contract maker/taker fee lazy pack
- How to reduce Maker/Taker transaction fees
- Can you make money by placing an order?
- Lazy Pack – Exchange organization that provides negative Maker handling fees
- What is the "Maker" function?
Many novice users who are new to the encryption world have heard of the words Maker and Taker, but in fact they may not know much about their specific scenarios. In addition, some users also have various doubts about the conversion between Maker and Taker. For example: I was Maker when I was placing an order, but why did I become Taker when I finally made a deal?
- Maker is the person who creates depth for exchanges, and Maker orders appear in the order book and will not be sold immediately.
- Taker is someone who eats the depth of the exchange. Taker orders will be traded immediately and will not appear in the order book.
- Maker fees are usually lower than Taker fees, and some exchanges even offer negative Maker rates, that is, you can earn a handling fee after Maker orders are completed.
- Users can switch between Maker and Taker identities through different order functions. This order is Maker, so the order you place can be Taker. Even in the same order, it is Maker when opening a position, and it can be Taker when closing the position.
What are Maker and pending orders? How to calculate Maker Fee
Maker is a pending order, also known as a liquidity provider. Specifically, it means that a user posts a certain quantity and price order, but there is no matching order in the market. Then this entrusted order will always be placed on the exchange's trading, waiting for other users to complete the transaction, which is equivalent to providing liquidity to the entire market, so it is called Maker.
To put it simply, Maker is actually the person who puts limit orders and waits for transactions. They provide market depth and are passive transactions. A limit order refers to a user buying or selling at the price of the digital currency specified by him, and the transaction can be completed when the market price fluctuates to the price set by the user.
So, let’s give an example to explain in detail how to make a Maker:
Taking using USDT to make the Maker to buy CET in the CET/USDT spot market as an example, the operation is roughly divided into the following steps:
- Assume that the latest transaction price of the CET/USDT market is 0.076502, and the current selling price is 0.076502, as shown in the figure;
- Select the [Price Limit] entrust type to [Always Valid];
- Set [buy price] and [buy volume], assuming that when the CET price fluctuates to 0.076430, buy 500;
- Confirm [Transaction Volume] and finally click [Buy CET].
After the commission is successfully set up, the order will be sent to the market and is in the position of buying 1. When the market price of CET fluctuates to 0.076430, the order will be gradually traded, realizing the entrusting strategy of makingr's price limit buying, while the same is true for the price limit selling.
Maker Fee Calculation Formula
The calculation formula of Maker Fee (only-party handling fee) is: transaction volume × Maker handling fee
- Example 1: User A traded an order worth USDT in the form of a pending order. The Maker fee charged by the exchange he used was 0.1%, so the handling fee for this order = 100 × 0.1% = 1 USDT
- Example 2: User B traded an order worth USDT in the form of a pending order. The Maker fee charged by the exchange he used is - 0.1%, so the handling fee for this order = 100 × - 0.1% = - 1 USDT. This thought that User B earned a USDT handling fee through this transaction.
Is it necessary to use a limit order a Maker?
The answer is no. The basis for judging whether it is a Maker is whether your order has created depth for the exchange. It can be simply understood as whether your order is immediately traded. When the limit price set by your order is exactly equal to the best market price, or even worse than the best price, then the limit order will be automatically sold at the best market price. The handling fee at this time is calculated in Take r, not Maker.
For example, if you place an order of USDT of 30,000 USDT, you can sell 1 Bitcoin, but the current market optimal price is 20,000. At this time, the exchange will not really buy your Bitcoin at a price of USDT of 30,000 USDT per card, but will be sold at USDT of 20,000 USDT of the market optimal price. The method for calculating the handling fee you need to give at this time is not 20,000 × Maker handling fee, but 20,000 × Taker handling fee.
What are Taker and Eat Order? How to calculate Taker Fee
Taker is a order taken, also known as a liquidity consumer. It means that users actively place a certain number of orders by checking the existing order prices in the exchange market, and immediately trade with existing orders posted, consuming liquidity in the market.
Simply put, Taker refers to the person who immediately places an order and queues up to make a deal and takes away the market depth, which is an active deal.
How to set up Taker? Let's give examples:
Take the use of USDT as a Taker to buy CET in the CET/USDT spot market as an example. The operation is roughly as follows:
- Assume that the latest transaction price of the CET/USDT market is 0.075433, and the current selling price is 0.075507, as shown in the figure;
- Select the [Price Limit] entrust type to [Always Valid];
- Set [buy price] and [buy volume], the purchase price is the current selling price of 0.075507, and the purchase volume is 99 CET;
- Confirm [Transaction Volume] and finally click [Buy CET];
After the commission is successful, the order will also be delivered to the market. Since the purchase quantity is less than the selling quantity, the order will be sold immediately at a price of 0.075507, realizing the entrusting strategy of Taker's price limit buying, and the same is true for Taker's price limit selling.
Taker Fee Calculation Formula
The calculation formula for Taker Fee (eating single-party handling fee) is: transaction volume × Taker handling fee
- Example 1: User A traded an order worth USDT in the form of a market price. The Taker fee charged by the exchange he used was 0.2%, so the handling fee for this order = 100 × 0.2% = 2 USDT
How to determine whether you are a Maker or Taker
Lazy Pack – Maker/taker fees for each virtual currency exchange
Spot maker/taker fee lazy pack
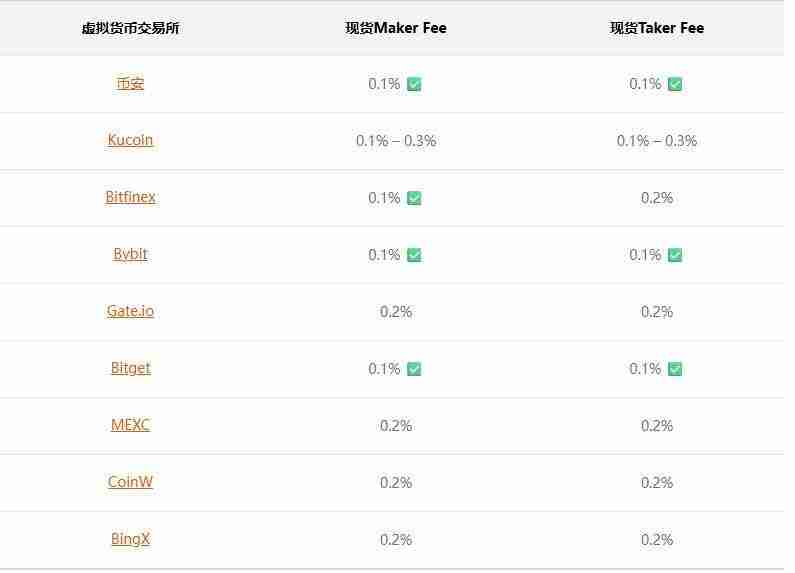
For ordinary users, the lowest spot handling fees are Binance, Kucoin, Bybit and Bitget.
Contract maker/taker fee lazy pack
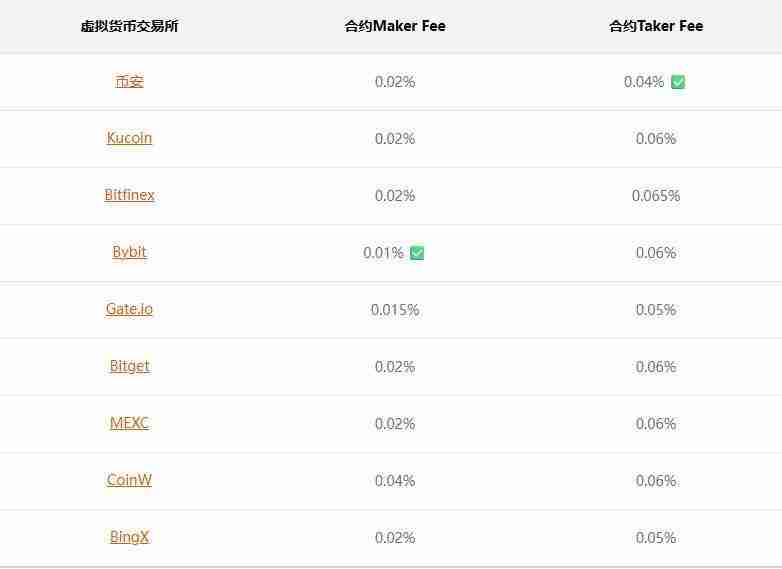
For ordinary users, Binance and Bybit have the lowest contract fees.
How to reduce Maker/Taker transaction fees
If you want to reduce the handling fee when trading virtual currencies, there are usually the following methods:
- Register through discount invitation link – Discount code lazy packs on major virtual currency exchanges
- Use platform coins to deduct handling fees
- Become a virtual currency exchange VIP
Can you make money by placing an order?
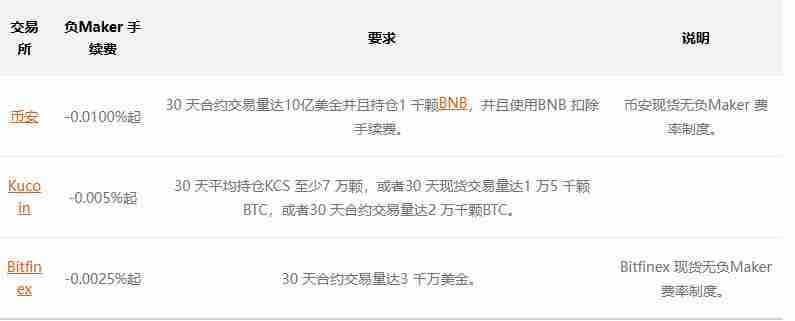
Someone should have noticed that in Example 2 of the Maker fee calculation method, the Maker fee with a negative number is listed. This is not a typo of the author, but a negative Maker rate that is real in this charging structure.
It can be imagined that if there are many people who place orders on an exchange, the number of orders is large, and the price difference of orders is small, then when a new user enters this virtual currency exchange, will he feel: "Well, the transaction volume of this exchange is large, and I can buy the coins I want quickly and conveniently, which should be trustworthy."
Therefore, many exchanges that adopt the Maker/Taker fee structure will make the Maker's fee rate lower than Taker's fee rate. Even setting the Maker fee to a negative number means that when you place an order and complete a transaction, not only do you not have to give a handling fee, but the exchange will also give you the handling fee in turn.
However, not all users can settle the handling fee at a negative Maker rate. Major virtual currency exchanges will require users to enjoy the discount of negative Maker rates after reaching a certain transaction volume, which is also one of the privileges of VIPs.
Lazy Pack – Exchange organization that provides negative Maker handling fees
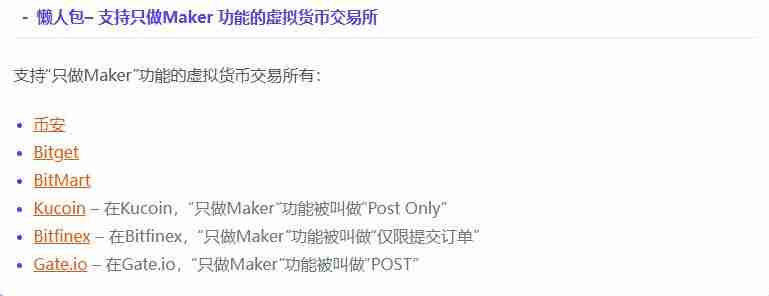
What is the "Maker" function?
"Maker only" is an advanced feature in limited orders. It can ensure that your order must appear in the order book and will not match the orders already in the order book, thus ensuring that your transaction fee must be a lower Maker rate.
Generally speaking, there are two purposes for using "Maker only":
- Guaranteed handling fees are lower Maker rates;
- Avoid losses caused by operating errors.
The first point is easy to understand, the Maker rate is usually lower than the Taker rate. Here we will explain the second point below. As we said above, sometimes our price limit trigger price will be set intentionally or unintentionally worse than the market's best price. If it is intentional, it's okay, but if we lose more or less 0 unintentionally, we will suffer losses after the order is executed. So when using the "Maker only" function, if you set up buying a virtual currency at a price higher than the current market price, the system will automatically cancel your order when you place an order, thus avoiding you buying a certain currency at a high price.
Similar functions vary in the names of each virtual currency exchange. Please refer to the lazy bag below for details.
Here's what Maker and Taker are? How to calculate the handling fee? This is the article about the list of handling fees on popular exchanges. For more comprehensive interpretations of Maker and Taker, please search for previous articles on this site or continue browsing the related articles below. I hope everyone will support this site in the future!
The above is the detailed content of What are Maker and Taker? How to calculate the handling fee? A list of handling fees on popular exchanges. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the websites for real-time price query of Bitcoin? Recommended websites that can view Bitcoin K-line and depth chart
Jul 31, 2025 pm 10:54 PM
What are the websites for real-time price query of Bitcoin? Recommended websites that can view Bitcoin K-line and depth chart
Jul 31, 2025 pm 10:54 PM
In the digital currency market, real-time mastering of Bitcoin prices and transaction in-depth information is a must-have skill for every investor. Viewing accurate K-line charts and depth charts can help judge the power of buying and selling, capture market changes, and improve the scientific nature of investment decisions.
 The Ethereum price rose by more than 20% in 7 days. What is the reason behind it?
Jul 31, 2025 pm 10:48 PM
The Ethereum price rose by more than 20% in 7 days. What is the reason behind it?
Jul 31, 2025 pm 10:48 PM
The recent surge of Ethereum price by more than 20% is mainly driven by four major factors: 1. The Cancun Upgrade is approaching, especially the "prototype data sharding" technology introduced by EIP-4844 will significantly reduce the transaction costs of Layer 2, improve network scalability, and attract investors to make advance arrangements; 2. The DeFi ecosystem continues to flourish, and the total value of locked positions (TVL) has grown steadily. New protocols such as liquid staking derivatives (LSD) and restaking (Restaking) have risen, increasing the rigid demand for ETH as a Gas fee and pledged assets; 3. The market has strong expectations for the approval of Ethereum spot ETF, believing that it will provide convenient channels for institutional investors, introduce a large amount of funds and enhance market confidence.
 Recommended market websites that support multiple currency trend analysis. A complete list of currency price market websites suitable for novices
Jul 31, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
Recommended market websites that support multiple currency trend analysis. A complete list of currency price market websites suitable for novices
Jul 31, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
For newbies who have just entered the currency circle, choosing a market website that supports real-time trend analysis of multiple currencies and is simple to operate can help you quickly understand the overall market and grasp the price changes and trends of each currency.
 How many Ethereum has issued in total? Where do ordinary people buy Ethereum?
Jul 31, 2025 pm 10:57 PM
How many Ethereum has issued in total? Where do ordinary people buy Ethereum?
Jul 31, 2025 pm 10:57 PM
1. Ordinary users can purchase Ethereum through mainstream digital asset trading platforms such as Binance, Ouyi OK, HTX Huobi, etc. The process includes registering an account, identity authentication, binding payment methods and trading through market or limit orders. The assets can be stored on the platform or transferred to personal money sacrificial pie; 2. Ethereum has no fixed issuance limit, with about 72 million initial issuance, and it is continuously issued through the PoS mechanism and the destruction mechanism is introduced due to EIP-1559, which may achieve deflation; 3. Before investing, you need to understand the risk of high volatility, enable two-factor verification to ensure account security, and learn asset custody methods such as hardware or software money sacrificial pie; 4. Ethereum is the core platform of decentralized applications, DeFi protocols and NFT ecosystem, supporting the operation of smart contracts and promoting digital asset rights confirmation and flow
 Top 10 trading software in the currency circle Download the top 10 exchange app in the currency circle
Jul 31, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Top 10 trading software in the currency circle Download the top 10 exchange app in the currency circle
Jul 31, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
This article lists the top ten trading software in the currency circle, namely: 1. Binance, a world-leading exchange, supports multiple trading modes and financial services, with a friendly interface and high security; 2. OKX, rich products, good user experience, supports multilingual and multiple security protection; 3. gate.io, known for strict review and diversified trading services, attaches importance to community and customer service; 4. Huobi, an old platform, has stable operations, strong liquidity, and has a great brand influence; 5. KuCoin, has large spot trading volume, rich currency, low fees, and diverse functions; 6. Kraken, a US compliance exchange, has strong security, supports leverage and OTC trading; 7. Bitfinex, has a long history, professional tools, suitable for high
 How to adjust the asset position in the currency circle to a suitable proportion according to market trends
Jul 31, 2025 pm 06:33 PM
How to adjust the asset position in the currency circle to a suitable proportion according to market trends
Jul 31, 2025 pm 06:33 PM
First, we need to judge the type of market trend. 1. The upward trend is manifested as a step-by-step price increase and the trading volume is moderately amplified. The position can be controlled at 60%-80%, and some returns can be gradually realized; 2. The downward trend is showing a continuous downward trend and the trading volume may fall in volume. The position should be reduced to 20%-40%, and the loss should be reduced in time to avoid the expansion of losses; 3. The sideways fluctuation trend is limited and the long and short balance is balanced. It is recommended that the position be kept at 40%-60%, and the range bands should be used; when adjusting, it is necessary to combine its own risk tolerance, avoid frequent operations, adhere to the diversified allocation of assets, and dynamically track trend changes to respond in a timely manner, ensure that the position strategy is consistent with the market trend, and ultimately achieve scientific asset management and risk control.
 What is Ethereum? What are the ways to obtain Ethereum ETH?
Jul 31, 2025 pm 11:00 PM
What is Ethereum? What are the ways to obtain Ethereum ETH?
Jul 31, 2025 pm 11:00 PM
Ethereum is a decentralized application platform based on smart contracts, and its native token ETH can be obtained in a variety of ways. 1. Register an account through centralized platforms such as Binance and Ouyiok, complete KYC certification and purchase ETH with stablecoins; 2. Connect to digital storage through decentralized platforms, and directly exchange ETH with stablecoins or other tokens; 3. Participate in network pledge, and you can choose independent pledge (requires 32 ETH), liquid pledge services or one-click pledge on the centralized platform to obtain rewards; 4. Earn ETH by providing services to Web3 projects, completing tasks or obtaining airdrops. It is recommended that beginners start from mainstream centralized platforms, gradually transition to decentralized methods, and always attach importance to asset security and independent research, to
 What is a digital currency strategy order? What should you pay attention to when doing a strategy order
Jul 31, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
What is a digital currency strategy order? What should you pay attention to when doing a strategy order
Jul 31, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
The digital currency strategy list is an operation plan based on preset rules and market analysis, used to guide digital currency transactions. The core is to respond to market fluctuations through early planning; 1. The strategy list includes entry opportunities, target points, and ways to deal with fluctuations, aiming to reduce operational arbitraryness; 2. It is necessary to formulate it in combination with your own risk tolerance and cognitive level to avoid blindly applying other people's strategies. Novice should start with simple strategies; 3. The strategy should be adjusted in a timely manner according to market dynamics, and continue to pay attention to industry information and emotional changes to maintain effectiveness; 4. Risk response plans must be planned in advance to avoid panic operations in emergencies, and potential risks should be reduced by diversifying investments to ensure overall stability. The above key points together form a complete and executable strategy system.




