
These recent policy moves share a common sense of urgency. Billions are being funneled into AI infrastructure, workforce development, and data ecosystems, with clear decisions about which nations and corporations will gain access—and which will be left behind. The new AI Action Plans mark a shift toward more direct government intervention, aiming to reshape the fast-evolving AI landscape.
The United States: Prioritizing Speed and Security Through Deregulation
President Donald Trump made his intentions unmistakable when he introduced “Winning the AI Race: America’s AI Action Plan” on July 23. “To secure our future, we must harness the full power of American innovation,” he declared. Both his speech and the plan’s language pointed squarely at China as the primary strategic rival.
The U.S. strategy is built for rapid execution. It pushes to eliminate regulatory barriers that could delay AI research or deployment and discourages individual states from imposing their own restrictions. Federal funding will boost semiconductor manufacturing, expand data centers, and support AI-focused education and training. Government agencies are now instructed to adopt AI systems that reflect the administration’s concept of “objective truth,” while avoiding those deemed to carry “ideological bias.”
National security remains a cornerstone. The U.S. will strengthen export controls on cutting-edge AI hardware and software, while creating secure AI export packages for allied nations. Secretary of State Marco Rubio emphasized the stakes: “America sets the technological gold standard worldwide, and the world continues to run on American technology.”
Europe: Bridging the Compute Gap
Launched on April 9—weeks before the U.S. plan—the European Union’s AI Continent Action Plan aims to accelerate Europe’s AI ambitions, if not fully close the gap with the U.S. and China. A key weakness? Insufficient cloud infrastructure and data center capacity. The EU’s response: massive public-private investments in “AI factories” and “AI Gigafactories,” modeled after large-scale scientific endeavors like CERN but focused on computational power.
The plan also envisions a unified European data market through new European Data Spaces. These secure, shared datasets are designed to fuel AI training while complying with the EU’s stringent data privacy laws.
“Europe must become a global leader in AI innovation,” stated European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen.
Japan: Minimal Regulation, Maximum Flexibility
Japan has taken a lighter regulatory approach with its AI Promotion Act, enacted on May 28. Rather than imposing broad restrictions, the law establishes guiding principles and applies strict obligations only to a limited number of “high-risk” AI applications. The goal is to position Japan as the world’s most AI-friendly destination for investment and innovation.
A new AI Strategy Headquarters, led directly by the Prime Minister, will oversee coordination across ministries. This centralized structure is intended to speed up decision-making and resource allocation.
South Korea: Building AI on a Foundation of Trust
South Korea’s Strategy to Realize Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence, unveiled on May 13, centers on ethics and public confidence. The plan mandates that high-risk AI systems must notify users when they are active. Additionally, the government will conduct social impact assessments to monitor how AI affects everyday life. Officials stress the importance of building citizen trust from the ground up.
China: Expanding Domestically, Engaging Globally
China has rolled out two major AI initiatives in quick succession. The Digital China 2025 plan, released on May 16, seeks to embed AI across all economic sectors and significantly boost national computing capacity. Then, at the recent World AI Conference & High-Level Meeting on Global AI Governance, Beijing introduced an action plan for global AI governance and announced a new international AI governance body based in Shanghai.
Premier Li Qiang argued that the AI race should not be dominated by a few powerful nations or corporations. China pledged to share open-source tools and technological advances with developing countries, especially in the Global South—a direct contrast to U.S. export restrictions.
India’s Gujarat State: Local Ambition, Global Vision
Even subnational governments are joining the race. India’s Gujarat state recently approved its own Action Plan for Implementation of Artificial Intelligence, signaling that the AI competition now extends beyond national borders. The state aims to train 250,000 people in AI, establish “AI factories” in smaller cities, and use AI to modernize public services.
What’s Driving This Surge in AI Action Plans?
Several forces are pushing governments to act. First is the scarcity of computing power. Every national plan highlights compute infrastructure: Europe is building Gigafactories, China targets 300 EFLOPS of computing power, and the U.S. is expediting data center approvals.
Second is the growing talent gap. Demand for skilled AI professionals—both in government and industry—is outpacing supply. The U.S., EU, and India all acknowledge the need for more AI-trained workers, prompting a wave of new training initiatives.
Third is the recognition of AI as a national security imperative. Governments increasingly see AI as a strategic asset. Some are tightening export controls, while others are fast-tracking sovereign AI models or building international alliances through open-source collaboration.
Yet a major gap remains: the absence of a unified regulatory framework. The EU’s comprehensive AI Act will take effect next year, Japan is opting for minimal oversight, and the U.S. continues to favor deregulation. This regulatory misalignment creates significant challenges for multinational companies.
Will These Plans Unite the AI Market—or Divide It?
These national strategies raise a critical question: Will governments find common ground to maintain a connected global AI market? Or will competing visions fracture it into isolated blocs?
There are reasons for cautious optimism. Shared concerns—such as model safety, data integrity, and misuse—could foster basic international standards, particularly in model evaluation and cybersecurity. Initiatives like the G7’s Hiroshima AI Process are already working toward alignment.
But signs of fragmentation are growing. The U.S. is focused on preserving its technological lead through export controls. China is expanding influence by offering open-source tools and proposing a global AI governance hub. These divergent strategies may solidify into incompatible systems.
For AI developers, this could mean developing multiple versions of software, retraining models for different regions, and navigating a complex web of compliance rules. A unified global standard would simplify this—but geopolitical realities suggest otherwise.
The AI Race Is Accelerating
The global AI race is intensifying. The next phase will determine whether the world’s AI ecosystem becomes more integrated or increasingly fragmented. Governments aren’t waiting for technology to mature—they’re setting rules and building infrastructure now, each striving for a strategic edge.
As European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen warned: “The global race for AI isn’t slowing down. [The] Time to act is now.”
The above is the detailed content of Governments Worldwide Race To Lock In AI Leadership. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Investing is booming, but capital alone isn’t enough. With valuations rising and distinctiveness fading, investors in AI-focused venture funds must make a key decision: Buy, build, or partner to gain an edge? Here’s how to evaluate each option—and pr
 AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). Heading Toward AGI And
 Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Remember the flood of open-source Chinese models that disrupted the GenAI industry earlier this year? While DeepSeek took most of the headlines, Kimi K1.5 was one of the prominent names in the list. And the model was quite cool.
 Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). For those readers who h
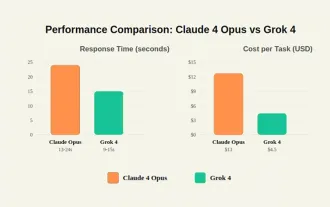 Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
By mid-2025, the AI “arms race” is heating up, and xAI and Anthropic have both released their flagship models, Grok 4 and Claude 4. These two models are at opposite ends of the design philosophy and deployment platform, yet they
 Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
For example, if you ask a model a question like: “what does (X) person do at (X) company?” you may see a reasoning chain that looks something like this, assuming the system knows how to retrieve the necessary information:Locating details about the co
 This Startup Built A Hospital In India To Test Its AI Software
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:14 AM
This Startup Built A Hospital In India To Test Its AI Software
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:14 AM
Clinical trials are an enormous bottleneck in drug development, and Kim and Reddy thought the AI-enabled software they’d been building at Pi Health could help do them faster and cheaper by expanding the pool of potentially eligible patients. But the
 Senate Kills 10-Year State-Level AI Ban Tucked In Trump's Budget Bill
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:16 AM
Senate Kills 10-Year State-Level AI Ban Tucked In Trump's Budget Bill
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:16 AM
The Senate voted 99-1 Tuesday morning to kill the moratorium after a last-minute uproar from advocacy groups, lawmakers and tens of thousands of Americans who saw it as a dangerous overreach. They didn’t stay quiet. The Senate listened.States Keep Th






