 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 ERP Shifts To Industry 5.0 To Enable Smarter, Human-Centric Operations
ERP Shifts To Industry 5.0 To Enable Smarter, Human-Centric Operations
ERP Shifts To Industry 5.0 To Enable Smarter, Human-Centric Operations
Jul 30, 2025 am 11:10 AMIn recent years, Industry 4.0 technologies including AI, IoT and robotics have continued to improve efficiency by automating tasks and connecting systems across ERP and supply chains. But as I look ahead to the rest of 2025 and beyond, I see the conversation shifting. Industry 5.0 emphasizes human-machine collaboration — where, for example, AI agents assist humans rather than replacing them, and systems are built to support human creativity, judgment and sustainability. One theme in an article I wrote earlier this year, “ERP Leveled Up in 2024 — Where Is It Headed in 2025?,” was to explore how Industry 4.0 and 5.0 are shaping the next generation of ERP.
The global Industry 5.0 market reflects this momentum — valued at $82.57 billion in 2025 and projected to reach $2.15 trillion by 2037, with a CAGR of 30.7%. This growth is fueled by AI-enabled ERP, enterprise-wide data integration and the increasing adoption of technologies including IoT, IIoT and digital twins.
In short, ERP systems are being reengineered for a new era. Thanks to AI agents, context-aware automation and the other technologies discussed here, ERP is moving beyond transaction processing to actively detect disruptions, support real-time decisions and adapt on the fly. It’s no longer just a back-office system — it’s becoming a critical driver of intelligent operations.
How Industry 4.0 And 5.0 Are Enhancing Today’s Operations
Industry 5.0 emphasizes the collaboration between humans and machines to create synergistic relationships that enhance productivity and workplace satisfaction. The obvious example of this is the use of AI. Already today, AI is seemingly everywhere in production facilities. Among many other impacts, this changes how we use ERP. Instead of ERP systems being limited to traditional planning tools, they are now smart platforms that can provide real-time operational data and forward-looking insights. Organizations can use this to streamline their processes and make more informed decisions.
A specific example is using AI assistants in manufacturing and operations. These tools help planners, engineers and frontline workers handle data, flag issues and draft reports or maintenance logs — accelerating results while keeping humans in control. The AI assistant software market was valued at $8.5?billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $35.7?billion by 2033, growing at a 17.5% CAGR. Modern ERP platforms reflect this shift by embedding AI directly into workflows — not just to automate, but to improve how users interact with data through personalized dashboards, smart alerts and context-aware suggestions.
Personalization represents a core principle of Industry 5.0. Modern manufacturing systems support hyper-customization through additive manufacturing, smart product configurators and flexible production lines. AI algorithms predict customer needs and adjust configurations in real time, while 3-D printing enables cost-effective production of custom parts. These systems rely on evolved ERP platforms that integrate customer data, production capacity and material availability to deliver custom goods at scale.

The Rapidly Emerging Role Of AI Agents
In an Industry 5.0 context, AI agents are emerging as a key link between human expertise and intelligent automation. Deloitte projects that 25% of enterprises using generative AI will deploy autonomous AI agents in 2025, doubling to 50% by 2027. It’s not hard to see why: The World Economic Forum identifies AI agents as capable of achieving up to 14% cost savings through intelligent automation.
Unlike traditional rule-based systems, AI agents interpret real-time data, learn from patterns and act within defined boundaries. They go beyond basic automation, evolving from content generators (as in generative AI) into autonomous problem solvers capable of reasoning, planning and taking action.
AI agents are already performing practical, high-impact tasks in today’s manufacturing and industrial environments. They predict equipment failures using sensor data and automatically trigger maintenance workflows in ERP or CMMS systems. They adjust production schedules in real time when delays, material shortages or demand fluctuations occur. AI agents also help optimize inventory levels by analyzing usage trends and supplier lead times, reducing overstock and stockouts.
In manufacturing, AI agents can also help manage quality control by analyzing production data — often using computer vision, which for years now has allowed machines to interpret visual information from cameras to detect defects or irregularities. When a problem is identified, the AI can automatically adjust the process and coordinate with other systems to correct it. It also communicates with upstream and downstream processes to ensure the fix is carried through the entire line. This speeds up corrections, reduces waste and minimizes the need for manual inspection. Another area for waste reduction is energy management, where AI agents can monitor consumption patterns and recommend adjustments to improve efficiency.
What’s different now is how agentic AI enables autonomous, context-aware coordination across systems. They work across systems such as MES, ERP and SCM, managing entire sequences of interrelated tasks — not just one-off actions. If a supplier delay occurs, an agent might reschedule production, reassign inventory, update material availability in the ERP and adjust delivery timelines in the SCM system. It can also flag these changes for human review before moving forward. This “human-in-the-loop” approach lets AI handle routine coordination and data entry, while keeping planners in control of the critical decisions.
AI agents are making ERP systems more adaptive, enabling faster actions and smarter collaboration across the enterprise — an essential step forward in the practical realization of Industry 5.0. In this context, ERP systems must continue to evolve into coordination platforms that manage multi-agent execution and workflows, interfacing with external ecosystems and internal operations. These systems will require open APIs and real-time data processing capabilities to function as orchestration layers between AI agents, IoT systems (more on that in a moment) and external partners, enabling seamless communication and coordination across diverse manufacturing environments.
IoT And Industrial IoT Data In Action
IoT and IIoT systems provide the foundation for real-time sensor data to drive autonomous operations. The industrial IoT market is projected to reach $275.7 billion by 2025, with manufacturing, energy and logistics sectors heavily investing in IIoT solutions. These devices continuously monitor temperature, vibration, pressure or other variables across factory floors and other industrial sites, feeding data directly into ERP systems and analytics platforms for faster, more accurate decision making.
Current adoption rates show that 62% of manufacturers have embraced IoT technologies in their manufacturing or assembly processes, with 43% leveraging real-time location systems. Yet only 18% of manufacturers have real-time visibility into their operations, making advanced IoT solutions crucial for bridging operational gaps.
As touched on earlier, IoT data can combine with AI to power predictive maintenance and automated quality control systems that detect early signs of equipment failure and automatically initiate repairs. Modern predictive maintenance systems also leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze vast sensor data streams, identifying subtle anomalies and patterns that might indicate equipment problems. This early detection capability allows manufacturers to schedule maintenance precisely when needed, avoiding both unexpected breakdowns and unnecessary maintenance interventions.
In supply chains, IoT sensors embedded in transport vehicles, warehouses and supplier facilities provide real-time insights on goods movement, environmental conditions and delivery timelines, enabling AI agents to dynamically reroute deliveries or reorder inventory. In all of these examples, we again see common themes of reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Data Infrastructure Requirements For Industry 4.0 And 5.0
As operations become increasingly autonomous, harmonized data enables interoperability across systems and vendors. Standardized data formats provide the foundation for intelligent agents and ERP platforms to share and act on information effectively, which is essential for cross-enterprise collaboration in complex multi-tier supply chains.
Digital twins are becoming standard practice, with the market projected to reach $73.5 billion by 2027. These virtual replicas of physical assets simulate operations using real-time data, allowing businesses to test changes, optimize processes and predict outcomes without disrupting live environments. Modern digital twins integrate real-time data from sensors, IoT devices and enterprise systems, creating continuously updated virtual replicas that provide instant insights into performance.
Scalable infrastructure built on cloud, edge computing and API-driven platforms is essential for supporting these advanced capabilities. Edge computing is significant for manufacturing, where milliseconds can make substantial differences in the performance of robotics, predictive maintenance and automated quality assurance. By processing data locally, edge systems ensure continuous operation even during connectivity outages, reducing bandwidth costs and improving response times.
Sustainability And Human-Centricity In Industry 5.0
Sustainability and human-centricity are central to how Industry 5.0 is implemented. Rather than focusing solely on economic efficiency and scale, organizations are also embedding environmental responsibility and workforce well-being into how systems are designed and operated.
On the sustainability front, ERP and supply chain systems equipped with AI agents are helping companies monitor energy use, track emissions and reduce waste in real time. These systems support practical goals such as optimizing transportation routes, choosing lower-impact materials and improving asset utilization. As reporting requirements and environmental expectations grow, these capabilities are becoming essential to day-to-day operations.
Human-centricity means designing systems that work with people, not just around them. AI agents can reduce manual workload by handling repetitive tasks, surfacing relevant information and supporting faster decision making, freeing employees to focus on tasks requiring human judgment or creativity. In practice, this improves not just efficiency but also job satisfaction and workplace safety.
Industry 5.0 is not about replacing what came before, but expanding how organizations think about performance. By integrating sustainability and human factors directly into ERP and operational workflows, companies can better balance productivity with long-term resilience.
The Future Of ERP Starts With Industry 5.0
Industry 5.0 concepts are already prompting a major rethink of how ERP systems are designed. We’re moving away from rigid, monolithic architectures toward more modular, event-driven systems supporting real-time data processing, human-machine collaboration and AI agents that actively participate in day-to-day operations. ERP isn’t just about automating transactions anymore — it’s about enabling systems that are smarter, more sustainable and more aligned with strategic outcomes. That means cleaner data, better context and platforms that can evolve alongside the business.
AI agents will be central to this shift. Instead of merely reacting to inputs, they’ll guide processes, anticipate disruptions and help teams make faster, more informed moves. But that only works if ERP systems are built to support it — which mandates architectures that are flexible, integrated and capable of managing both structured and unstructured data at scale.
This is just the beginning. As we look ahead to Industry 6.0, which is expected to take shape around 2050, ERP will need another overhaul. We’ll be entering an era of hyper-autonomy, where intelligent agents make decisions with minimal human involvement, and technologies like quantum computing and nanotechnology take center stage. Quantum alone could unlock new capabilities in materials science, chemistry, drug discovery, finance, economics, climate modeling and advanced physics simulations. And it only makes sense to predict that these new applications will drive ERP systems that are more complex, faster and more innovative than we see today.
In an upcoming article, I’ll explore how ERP platforms need to evolve to support a future defined by autonomy, intelligence and paradigm-level innovation.
The above is the detailed content of ERP Shifts To Industry 5.0 To Enable Smarter, Human-Centric Operations. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Investing is booming, but capital alone isn’t enough. With valuations rising and distinctiveness fading, investors in AI-focused venture funds must make a key decision: Buy, build, or partner to gain an edge? Here’s how to evaluate each option—and pr
 AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). Heading Toward AGI And
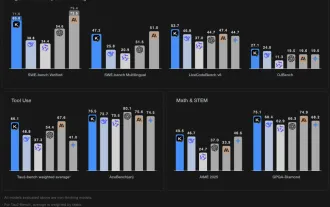 Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Remember the flood of open-source Chinese models that disrupted the GenAI industry earlier this year? While DeepSeek took most of the headlines, Kimi K1.5 was one of the prominent names in the list. And the model was quite cool.
 Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). For those readers who h
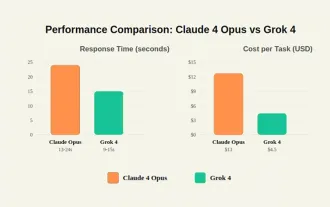 Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
By mid-2025, the AI “arms race” is heating up, and xAI and Anthropic have both released their flagship models, Grok 4 and Claude 4. These two models are at opposite ends of the design philosophy and deployment platform, yet they
 Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
For example, if you ask a model a question like: “what does (X) person do at (X) company?” you may see a reasoning chain that looks something like this, assuming the system knows how to retrieve the necessary information:Locating details about the co
 This Startup Built A Hospital In India To Test Its AI Software
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:14 AM
This Startup Built A Hospital In India To Test Its AI Software
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:14 AM
Clinical trials are an enormous bottleneck in drug development, and Kim and Reddy thought the AI-enabled software they’d been building at Pi Health could help do them faster and cheaper by expanding the pool of potentially eligible patients. But the
 Senate Kills 10-Year State-Level AI Ban Tucked In Trump's Budget Bill
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:16 AM
Senate Kills 10-Year State-Level AI Ban Tucked In Trump's Budget Bill
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:16 AM
The Senate voted 99-1 Tuesday morning to kill the moratorium after a last-minute uproar from advocacy groups, lawmakers and tens of thousands of Americans who saw it as a dangerous overreach. They didn’t stay quiet. The Senate listened.States Keep Th





