NSF-Backed 'MaVila' AI Brings Factory Floors Into The LLM Era
Jul 19, 2025 am 11:08 AM
“MaVila is a highly advanced vision and language model tailored specifically for smart manufacturing, a field we've been deeply involved in for nearly a decade,” Lee stated in an interview with the NSF.
Key Strengths of MaVila
Most current industrial AI systems still depend on rule-based vision tools that struggle with unfamiliar part shapes or lighting conditions on the factory floor. What sets MaVila apart is its training on domain-specific data—thousands of labeled images, technical manuals, and sensor logs from CNC machines, wire-EDM units, and 3D printers. When presented with a newly printed titanium bracket, the model can identify a micro-crack and instantly recommend adjustments to the laser power. This task would typically require an on-site process engineer.
MaVila can analyze a milling machine, detect an anomaly, and propose an optimal cutting speed—all before a human operator can hit the emergency stop.
“Traditional large language models are built to process and generate text,” Lee explained. “But MaVila’s vision model is capable of interpreting both visual and textual information.”
In early lab trials, MaVila successfully detected deliberately introduced defects in 3D-printed components and proposed corrected print settings within seconds. The team then deployed the model on a mobile robot that captured images of a milling process, retrieved the correct torque specification from a PDF manual, and recommended a tool path adjustment—all while the machine was in operation.
Lee emphasized that control over specialized data will define the next wave of industrial AI.
“I believe the heart of the AI industry lies in the algorithms and models you develop,” he said. “But equally important is the data. Whoever controls the data holds the most value.”
His team has created one of the first publicly available benchmarks for smart manufacturing images, and further enhanced MaVila using a retrieval-augmented processing pipeline, enabling it to access the correct section of a manual during real-time interaction.
Since public datasets rarely address niche manufacturing scenarios, Lee’s team has spent years collecting high-resolution images of cutting tools, compiling sensor data from 3D printers, and digitizing operator manuals into a searchable database. This effort has led to a retrieval-enhanced system that allows MaVila to deliver accurate responses while a machine is still operating.
AI Gains Traction in Manufacturing Environments
Siemens is already bringing a similar solution to market. Its Industrial Copilot, integrated with the company’s TIA Portal, can generate PLC code and HMI interfaces, reducing development time and error rates. The tool will launch this summer.
NVIDIA is collaborating with Foxconn, Pegatron, and other firms to create full-scale digital replicas of their production lines. By simulating factory layouts before physical construction begins, these companies report quicker deployment and improved safety. BMW also claims its Virtual Factory has cut planning costs by up to 30% by simulating every robotic motion in a photorealistic environment.
These developments indicate that major manufacturers are embracing AI-powered assistants, but they also present a challenge for smaller suppliers who may lack the resources or data to compete.
Policy Support and Workforce Challenges
Government funding is increasingly supporting U.S. manufacturing. This spring, the NSF allocated $25.5 million in grants for “future manufacturing” initiatives, including digital twin development and “recyclofacturing”—a circular method that converts industrial metal waste directly into new materials, minimizing downcycling and lowering carbon emissions. However, a Deloitte report highlights an anticipated shortage of 2.1 million manufacturing workers in the U.S. by 2030, one reason Siemens promotes its copilot as a solution for bridging skill gaps.
Some experts caution that even the most sophisticated models can’t replace the need for fresh, proprietary data. Mid-sized manufacturers must decide how much internal knowledge they are willing to share with research institutions or pay to keep secure.
Lee acknowledges this challenge. His next goal is to establish pilot collaborations with at least three small and medium-sized manufacturers. Without real-world production data, the model risks remaining confined to academic use.
The success of MaVila now depends on whether factories are willing to provide sufficient images and logs to maintain the model’s effectiveness, and how easily it can be deployed.
If these barriers are overcome, U.S. factories could replace thick technical binders with an AI assistant capable of identifying issues, explaining them, and correcting them in real time—transforming static automation into intelligent, adaptive production systems and potentially giving American manufacturing the competitive edge it has long sought.
The above is the detailed content of NSF-Backed 'MaVila' AI Brings Factory Floors Into The LLM Era. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Investing is booming, but capital alone isn’t enough. With valuations rising and distinctiveness fading, investors in AI-focused venture funds must make a key decision: Buy, build, or partner to gain an edge? Here’s how to evaluate each option—and pr
 AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). Heading Toward AGI And
 Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Remember the flood of open-source Chinese models that disrupted the GenAI industry earlier this year? While DeepSeek took most of the headlines, Kimi K1.5 was one of the prominent names in the list. And the model was quite cool.
 Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). For those readers who h
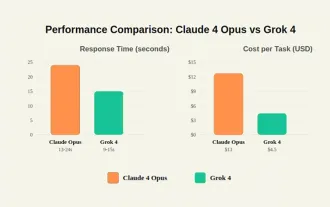 Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
By mid-2025, the AI “arms race” is heating up, and xAI and Anthropic have both released their flagship models, Grok 4 and Claude 4. These two models are at opposite ends of the design philosophy and deployment platform, yet they
 Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
For example, if you ask a model a question like: “what does (X) person do at (X) company?” you may see a reasoning chain that looks something like this, assuming the system knows how to retrieve the necessary information:Locating details about the co
 This Startup Built A Hospital In India To Test Its AI Software
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:14 AM
This Startup Built A Hospital In India To Test Its AI Software
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:14 AM
Clinical trials are an enormous bottleneck in drug development, and Kim and Reddy thought the AI-enabled software they’d been building at Pi Health could help do them faster and cheaper by expanding the pool of potentially eligible patients. But the
 Senate Kills 10-Year State-Level AI Ban Tucked In Trump's Budget Bill
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:16 AM
Senate Kills 10-Year State-Level AI Ban Tucked In Trump's Budget Bill
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:16 AM
The Senate voted 99-1 Tuesday morning to kill the moratorium after a last-minute uproar from advocacy groups, lawmakers and tens of thousands of Americans who saw it as a dangerous overreach. They didn’t stay quiet. The Senate listened.States Keep Th






