 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 What are the types of exceptions in java? Introduction to the classification of java exceptions and their characteristics
What are the types of exceptions in java? Introduction to the classification of java exceptions and their characteristics
What are the types of exceptions in java? Introduction to the classification of java exceptions and their characteristics
May 28, 2025 pm 05:24 PMExceptions in Java are divided into three types: detected exceptions, unchecked exceptions and errors. 1. The detected exception needs to be processed or declared in the code, such as IOException. 2. Unchecked exceptions are caused by logical errors, such as NullPointerException, and do not require forced processing. 3. Errors such as OutOfMemoryError are usually unrecoverable.

Exception handling in Java is an indispensable part of programming. Understanding the classification and characteristics of exceptions not only allows us to write more robust code, but also handle it more calmly when facing exceptions. So, what are the types of exceptions in Java? Let's take a deeper look.
In Java, exceptions are mainly divided into two categories: Checked Exceptions and Unchecked Exceptions . In addition, there is another special category: Errors . These three types of exceptions have their own characteristics and handling methods. Let's interpret them one by one below.
The detected exception refers to the exception that must be processed or declared when writing code, such as IOException , SQLException , etc. These exceptions are usually caused by external conditions, such as file failure or database connection failure. The characteristic of checked exceptions is that they are checked by the compiler at compile time, and if not captured or declared, the code will not be compiled. This design is designed to force developers to handle possible exceptions, thereby improving code robustness.
For example, if we want to read a file, we must deal with possible IOException :
try {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("example.txt"));
String line = reader.readLine();
// Process file content} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("File cannot be read: " e.getMessage());
} Unchecked exceptions are different. They are usually caused by program logic errors, such as NullPointerException , ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException , etc. These exceptions are not checked at compile time, and developers can choose to handle them, but they can also not be handled. The characteristic of non-checked exceptions is that they are usually avoidable and can be reduced through good programming practices and code review.
For example, if we accidentally access the illegal index of an array:
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(numbers[3]); // This throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException Errors are the most serious exception types in Java. They usually represent system-level errors, such as OutOfMemoryError , StackOverflowError , etc. Errors are usually irrecoverable, and developers cannot handle them by catching them, and can only try to avoid errors.
For example, when memory is insufficient, OutOfMemoryError may be thrown:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (true) {
list.add("Memory Leak"); // This will cause OutOfMemoryError
}In actual development, the following points need to be considered when handling exceptions:
- Checked exceptions : Make sure that these exceptions are properly handled or declared in the code to avoid compilation errors. At the same time, the rational use of detected exceptions can improve the readability and maintainability of the code because it clarifies possible exceptions.
- Unchecked exceptions : Although the compiler will not force these exceptions, good programming habits and code review can reduce the occurrence of such exceptions. Using the
try-catchblock to handle possible unchecked exceptions can improve the robustness of the code. - Error : Although errors are usually unrecoverable, errors can be reduced through reasonable resource management and code optimization. For example, avoid memory leaks, use recursion rationally, etc.
When handling exceptions, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- Granularity of exceptions : Don't abuse exceptions, too much exception handling will make the code complicated and difficult to maintain. Exception handling should be used only if necessary.
- Exception information : When an exception is thrown, detailed exception information is provided, which is helpful for debugging and problem location.
- Exception chain : Use exception chain (
Throwable'sinitCausemethod) to retain information about the original exception, helping to understand the cause of the exception more comprehensively.
In short, understanding exception classification and its characteristics in Java is the key to writing robust code. By rationally using detected exceptions, unchecked exceptions and errors, the reliability and maintainability of the code can be improved. Hope this article can help you better understand and handle exceptions in Java.
The above is the detailed content of What are the types of exceptions in java? Introduction to the classification of java exceptions and their characteristics. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to limit user resources in Linux? How to configure ulimit?
May 29, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
How to limit user resources in Linux? How to configure ulimit?
May 29, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
Linux system restricts user resources through the ulimit command to prevent excessive use of resources. 1.ulimit is a built-in shell command that can limit the number of file descriptors (-n), memory size (-v), thread count (-u), etc., which are divided into soft limit (current effective value) and hard limit (maximum upper limit). 2. Use the ulimit command directly for temporary modification, such as ulimit-n2048, but it is only valid for the current session. 3. For permanent effect, you need to modify /etc/security/limits.conf and PAM configuration files, and add sessionrequiredpam_limits.so. 4. The systemd service needs to set Lim in the unit file
 What is Middleware in Laravel? How to use it?
May 29, 2025 pm 09:27 PM
What is Middleware in Laravel? How to use it?
May 29, 2025 pm 09:27 PM
Middleware is a filtering mechanism in Laravel that is used to intercept and process HTTP requests. Use steps: 1. Create middleware: Use the command "phpartisanmake:middlewareCheckRole". 2. Define processing logic: Write specific logic in the generated file. 3. Register middleware: Add middleware in Kernel.php. 4. Use middleware: Apply middleware in routing definition.
 Free Korean comics online viewing free comics entrance Free Korean comics online reading free pull-down
Jun 12, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
Free Korean comics online viewing free comics entrance Free Korean comics online reading free pull-down
Jun 12, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
With the vigorous development of the Internet, Korean comics (Korean comics) have won the love of more and more readers around the world with their exquisite painting style, fascinating plots and rich and diverse themes. If you want to travel anywhere, in the exciting Korean comic world, it is crucial to find a stable, free and resource-rich online reading platform. This article will provide you with a detailed guide to watching Korean comics online for free comics, helping you easily start your Korean comic journey.
 Redis master-slave replication failure troubleshooting process
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
Redis master-slave replication failure troubleshooting process
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
The steps for troubleshooting and repairing Redis master-slave replication failures include: 1. Check the network connection and use ping or telnet to test connectivity; 2. Check the Redis configuration file to ensure that the replicaof and repl-timeout are set correctly; 3. Check the Redis log file and find error information; 4. If it is a network problem, try to restart the network device or switch the alternate path; 5. If it is a configuration problem, modify the configuration file; 6. If it is a data synchronization problem, use the SLAVEOF command to resync the data.
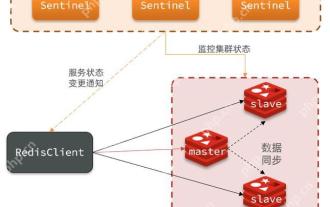 Quick location and handling of Redis cluster node failures
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Quick location and handling of Redis cluster node failures
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
The quick location and processing steps for Redis cluster node failure are as follows: 1. Confirm the fault: Use the CLUSTERNODES command to view the node status. If the fail is displayed, the node will fail. 2. Determine the cause: Check the network, hardware, and configuration. Common problems include memory limits exceeding. 3. Repair and restore: Take measures based on the reasons, such as restarting the service, replacing the hardware or modifying the configuration. 4. Notes: Ensure data consistency, select appropriate failover policies, and establish monitoring and alarm systems.
 How does the overflow property manage content that exceeds an element's boundaries?
Jun 09, 2025 am 12:16 AM
How does the overflow property manage content that exceeds an element's boundaries?
Jun 09, 2025 am 12:16 AM
The overflow attribute handles overflow content by hiding, scrolling or automatically adjusting. The main values ??include 1. Hidden direct cropping; 2. Scroll always displays scroll bars; 3. Auto displays scroll bars as needed; 4. Overflow-x and overflow-y can control horizontal and vertical overflow respectively. 1. overflow:hidden is used to avoid overflow of content; 2. overflow:scroll is suitable for chat windows or fixed-size sidebars to keep the interface consistent; 3. overflow:auto is suitable for tables or user-generated content to achieve flexible scrolling; 4. Note when setting overflow-x and overflow-y independently
 Kucoin appoints two high-profile executives to complete its European leadership team
Jun 12, 2025 am 10:45 AM
Kucoin appoints two high-profile executives to complete its European leadership team
Jun 12, 2025 am 10:45 AM
Global cryptocurrency exchange Kucoin recently completed the formation of its European leadership team, appointing two highly-watched executives. This personnel change is part of Kucoin’s accelerated layout in the EU market, especially in response to the upcoming cryptoasset management regulations (MICAR). Currently, the company is advancing the relevant licensing process through the Austrian Financial Markets Authority (FMA) and introducing senior experts from traditional finance and crypto to strengthen its management. KucoinEU is currently actively communicating with the FMA to achieve full compliance operations with the goal of providing a complete cryptocurrency service within the European Economic Area (EEA). At this stage, the company has not yet conducted business within the EU or EEA and is about to obtain the corresponding license.
 Performance comparison and joint application scenarios between Redis and RabbitMQ
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Performance comparison and joint application scenarios between Redis and RabbitMQ
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Redis and RabbitMQ each have their own advantages in performance and joint application scenarios. 1.Redis performs excellently in data reading and writing, with a latency of up to microseconds, suitable for high concurrency scenarios. 2.RabbitMQ focuses on messaging, latency at milliseconds, and supports multi-queue and consumer models. 3. In joint applications, Redis can be used for data storage, RabbitMQ handles asynchronous tasks, and improves system response speed and reliability.





