Navigating the Complexities of Interconnected Data: Neo4j vs. Amazon Neptune
In today's data-rich world, efficiently managing intricate, interconnected information is paramount. While traditional databases remain relevant, they often struggle with highly relational data. Graph databases offer a superior solution, adeptly handling and querying complex relationships. This article delves into this technology, comparing two leading contenders: Neo4j and Amazon Neptune, and highlighting their transformative impact on data management.

Key Considerations:
- Graph databases like Neo4j and Amazon Neptune excel at managing complex, interconnected datasets, surpassing the capabilities of traditional relational databases.
- They leverage nodes, edges, and properties to represent and query relationships efficiently, providing clear visualizations of intricate connections.
- Neo4j, a prominent graph database, offers the Cypher query language, ACID compliance, and a rich ecosystem.
- Amazon Neptune, a managed AWS service, supports property and RDF graph models, boasting seamless integration and high availability.
- The optimal choice between Neo4j and Amazon Neptune depends on project specifics, team expertise, and infrastructure requirements.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Understanding Graph Databases
- Neo4j: A Leading Graph Database
- Core Features of Neo4j
- Amazon Neptune: A Managed Graph Database Service
- Core Features of Amazon Neptune
- Neo4j vs. Amazon Neptune: A Detailed Comparison
- Real-World Applications and Industry Adoption
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding Graph Databases:
Graph databases are purpose-built for storing and managing interconnected data, simplifying the representation and querying of complex relationships. Unlike table-based traditional databases, they utilize:
- Nodes: Representing individual entities or objects.
- Edges: Defining the relationships between these entities.
- Properties: Storing attributes associated with nodes and edges.
This structure facilitates efficient querying and visualization of intricate data relationships, making graph databases ideal for applications such as social networks, recommendation engines, and fraud detection systems.
Neo4j: A Leading Graph Database:
Launched in 2007, Neo4j is a robust and adaptable platform for managing interconnected data. Employing a property graph model, it stores data within nodes and edges, each capable of holding properties. This makes it exceptionally well-suited for applications like social networks, recommendation systems, fraud detection, and network management.

Core Features of Neo4j:
- Cypher Query Language: A dedicated graph query language enabling expressive and efficient data retrieval.
- ACID Compliance: Guarantees data consistency and reliable transactions, essential for mission-critical applications.
- Scalability and Performance: Delivers impressive performance for graph traversals and real-time queries through native graph storage and indexing.
- Extensive Ecosystem: Offers comprehensive tooling and integrations, supporting various programming languages, frameworks, and platforms.
Amazon Neptune: A Managed Graph Database Service:
Introduced by AWS in 2018, Amazon Neptune is a fully managed graph database service supporting both property graph and RDF graph models. As a managed service, it handles database administration complexities, including backups, recovery, and scaling, enabling developers to concentrate on application development.

Core Features of Amazon Neptune:
- Multi-Model Support: Supports both Apache TinkerPop's Gremlin (for property graphs) and SPARQL (for RDF graphs).
- Managed Service: Seamlessly integrates with other AWS services, providing automated backups, patching, and scaling.
- High Availability and Durability: Designed for enterprise-grade reliability with features like multi-AZ replication and automatic failover.
- Robust Security and Compliance: Integrates with AWS security services, offering features like VPC support, encryption, and compliance with industry standards.
Neo4j vs. Amazon Neptune: A Detailed Comparison:
| Feature | Neo4j | Amazon Neptune |
|---|---|---|
| Query Language | Cypher | Gremlin & SPARQL |
| Deployment | Self-managed or Neo4j Aura | Fully managed AWS service |
| Scalability | High | High, with seamless managed scaling |
| Ecosystem | Mature and extensive | Benefits from the AWS ecosystem |
| Data Model | Property Graph | Property Graph & RDF |
Real-World Applications and Industry Adoption:
Neo4j finds extensive use in finance, healthcare, and telecommunications for applications such as network optimization, fraud detection, and patient data management. Amazon Neptune is frequently chosen by businesses in retail, logistics, and social media that require scalable, managed graph database solutions.
Conclusion:
Graph databases are powerful tools for managing interconnected data, regardless of whether you're building a social network or optimizing a supply chain. Amazon Neptune offers the simplicity of a managed service with deep AWS integration, while Neo4j provides a mature ecosystem and specialized graph performance. The best choice depends on your specific project needs, team expertise, and existing infrastructure. The key takeaway is that understanding and leveraging the relationships within your data is crucial, and graph databases provide the tools to unlock that potential.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1: What is a graph database?
A: A graph database stores and manages highly interconnected data using nodes, edges, and properties, enabling efficient querying and visualization of complex relationships.
Q2: What are some examples of graph databases?
A: Examples include Neo4j, Amazon Neptune, ArangoDB, JanusGraph, and OrientDB.
Q3: What is considered the most popular graph database?
A: Neo4j is widely recognized as the most popular, known for its powerful Cypher query language, robust performance, and extensive ecosystem.
Q4: Is MongoDB a graph database?
A: No, MongoDB is a NoSQL document database, not specifically designed for graph data and complex relationships.
The above is the detailed content of Neo4j vs. Amazon Neptune: Graph Databases in Data Engineering. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Investing is booming, but capital alone isn’t enough. With valuations rising and distinctiveness fading, investors in AI-focused venture funds must make a key decision: Buy, build, or partner to gain an edge? Here’s how to evaluate each option—and pr
 AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). Heading Toward AGI And
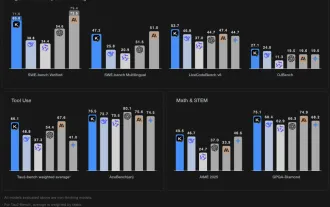 Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Remember the flood of open-source Chinese models that disrupted the GenAI industry earlier this year? While DeepSeek took most of the headlines, Kimi K1.5 was one of the prominent names in the list. And the model was quite cool.
 Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). For those readers who h
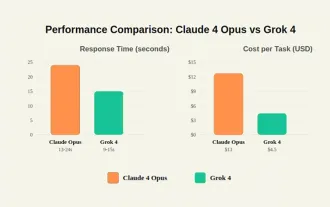 Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
By mid-2025, the AI “arms race” is heating up, and xAI and Anthropic have both released their flagship models, Grok 4 and Claude 4. These two models are at opposite ends of the design philosophy and deployment platform, yet they
 Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
For example, if you ask a model a question like: “what does (X) person do at (X) company?” you may see a reasoning chain that looks something like this, assuming the system knows how to retrieve the necessary information:Locating details about the co
 Senate Kills 10-Year State-Level AI Ban Tucked In Trump's Budget Bill
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:16 AM
Senate Kills 10-Year State-Level AI Ban Tucked In Trump's Budget Bill
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:16 AM
The Senate voted 99-1 Tuesday morning to kill the moratorium after a last-minute uproar from advocacy groups, lawmakers and tens of thousands of Americans who saw it as a dangerous overreach. They didn’t stay quiet. The Senate listened.States Keep Th
 This Startup Built A Hospital In India To Test Its AI Software
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:14 AM
This Startup Built A Hospital In India To Test Its AI Software
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:14 AM
Clinical trials are an enormous bottleneck in drug development, and Kim and Reddy thought the AI-enabled software they’d been building at Pi Health could help do them faster and cheaper by expanding the pool of potentially eligible patients. But the






