Introduction
Envision yourself in a supermarket queue, patiently awaiting your turn to purchase concert tickets for your favorite artist. This orderly process, where individuals join a line and proceed in a First In, First Out (FIFO) manner, is precisely what computer scientists refer to as a queue. Queues are fundamental Python data structures, invaluable for managing tasks, processing asynchronous data, and numerous other programming functions. This article explores Python queue implementation, provides a general overview, and highlights their significance.
Key Learning Points
- Grasp the concept of a queue and its programming importance.
- Master various Python queue implementation techniques.
- Explore common queue operations.
- Discover practical queue applications.
- Understand advanced queue types and their uses.
Table of Contents
- What is a Queue?
- Queue Operations
- Python Queue Implementation
- Using Lists
- Leveraging
collections.deque - Utilizing
queue.Queue
- Queue Applications
- Advanced Queue Types
- Priority Queues
- Double-Ended Queues (Deques)
- Circular Queues
- Blocking Queues
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Queue?
A queue is a linear data structure adhering to the First In, First Out (FIFO) principle. Data is added to the rear and removed from the front, ensuring the earliest added element is processed first.

Queue Operations
Essential queue operations include:
- Enqueue: Adds an element to the queue's rear. A full queue results in an overflow. Time complexity: O(1).
- Dequeue: Removes an element from the queue's front (FIFO). An empty queue causes an underflow. Time complexity: O(1).
- Peek (Front): Accesses the front element without removal. Time complexity: O(1).
- Rear (Back): Accesses the rear element. Time complexity: O(1).
- IsEmpty: Checks for emptiness. Time complexity: O(1).
- IsFull: Checks for fullness (for fixed-size queues). Time complexity: O(1).
- Size: Returns the queue's element count. Time complexity: O(1) in most implementations.
Python Queue Implementation
Several methods exist for implementing queues in Python:
Using Lists
Python lists can serve as queues, but are inefficient for large datasets due to the O(n) complexity of removing from the front.
class ListQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = []
# ... (rest of the methods remain the same)
Using collections.deque
The collections.deque object offers superior efficiency, providing O(1) complexity for appending and popping from both ends.
from collections import deque
class DequeQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = deque()
# ... (rest of the methods remain the same)
Using queue.Queue
The queue.Queue class is specifically designed for thread-safe queue management in multi-threaded environments.
from queue import Queue, Empty
class ThreadSafeQueue:
def __init__(self, maxsize=0):
self.queue = Queue(maxsize=maxsize)
# ... (rest of the methods remain the same)
Queue Applications
Queues find extensive use in diverse applications:
- Task Scheduling: Organizing tasks for sequential processing.
- Breadth-First Search (BFS): Graph traversal algorithm.
- Asynchronous Data Handling: Managing data flow in web servers.
- Buffering: Controlling data flow between producers and consumers.
- Print Spooling: Managing print jobs.
- Order Processing: Handling customer orders.
- Resource Allocation: Managing shared resources.
- Batch Processing: Processing jobs in batches.
- Networking: Managing network traffic.
- Operating Systems: Managing interrupts and processes.
- Simulations: Modeling real-world waiting lines.
Advanced Queue Types
Beyond basic queues, several specialized types exist:
Priority Queues
Elements are assigned priorities, with higher-priority elements dequeued first.
from queue import PriorityQueue # ... (example usage remains the same)
Double-Ended Queues (Deques)
Allow additions and removals from both ends.
from collections import deque # ... (example usage remains the same)
Circular Queues
Efficiently utilize array space by wrapping around.
class CircularQueue:
# ... (implementation remains the same)
Blocking Queues
Synchronize access between threads, blocking when full or empty.
import queue # ... (implementation remains the same)
Advantages of Queues
- Order Preservation: Maintains element order.
- Concurrency Management: Handles concurrent data processing effectively.
- Simplicity and Adaptability: Easy to implement and adapt to various needs.
Conclusion
Queues are fundamental data structures with broad applications. Understanding their implementation and usage is crucial for efficient programming. This article presented several Python implementations and highlighted their diverse applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Queue vs. Stack? Queues use FIFO; stacks use LIFO (Last In, First Out).
Q2. When to Use a Queue? Use queues for ordered processing, like task scheduling or BFS.
Q3. Is collections.deque Thread-Safe? No, use queue.Queue for thread safety.
Q4. Queues for Sorting? Priority queues enable priority-based sorting.
Q5. Real-World Queue Examples? Customer lines, print queues, web server requests.
The above is the detailed content of Queue in Python - Analytics Vidhya. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Investing is booming, but capital alone isn’t enough. With valuations rising and distinctiveness fading, investors in AI-focused venture funds must make a key decision: Buy, build, or partner to gain an edge? Here’s how to evaluate each option—and pr
 AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). Heading Toward AGI And
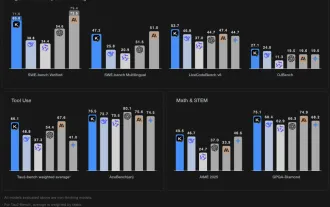 Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Remember the flood of open-source Chinese models that disrupted the GenAI industry earlier this year? While DeepSeek took most of the headlines, Kimi K1.5 was one of the prominent names in the list. And the model was quite cool.
 Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). For those readers who h
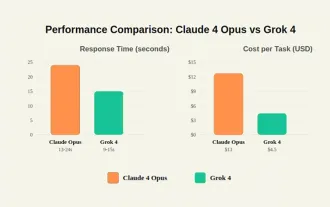 Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
By mid-2025, the AI “arms race” is heating up, and xAI and Anthropic have both released their flagship models, Grok 4 and Claude 4. These two models are at opposite ends of the design philosophy and deployment platform, yet they
 Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
For example, if you ask a model a question like: “what does (X) person do at (X) company?” you may see a reasoning chain that looks something like this, assuming the system knows how to retrieve the necessary information:Locating details about the co
 Senate Kills 10-Year State-Level AI Ban Tucked In Trump's Budget Bill
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:16 AM
Senate Kills 10-Year State-Level AI Ban Tucked In Trump's Budget Bill
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:16 AM
The Senate voted 99-1 Tuesday morning to kill the moratorium after a last-minute uproar from advocacy groups, lawmakers and tens of thousands of Americans who saw it as a dangerous overreach. They didn’t stay quiet. The Senate listened.States Keep Th
 This Startup Built A Hospital In India To Test Its AI Software
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:14 AM
This Startup Built A Hospital In India To Test Its AI Software
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:14 AM
Clinical trials are an enormous bottleneck in drug development, and Kim and Reddy thought the AI-enabled software they’d been building at Pi Health could help do them faster and cheaper by expanding the pool of potentially eligible patients. But the






