Ejb is denoted as Enterprise Java Bean Component, also called server-side software components; it will mainly be used as the applications’ business logic. The web containers used for runtime environments include the software components, computer security, servlet lifecycle management, transaction processing, and web services.EJb is the architecture style written in the Java programming languages running on the server-side of the computer network, so it has followed the client-server model in the applications. And also, ejb is the java bean technology to distribute the web components on the client-side it has the feature called reusable components in multiple web applications.
Start Your Free Software Development Course
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
Syntax:
The basic syntax of the EJB model in java programming as follows.
import javax.ejb.*;
import java packages;
class classname
{
Main? method()
{
-----Some programming logics----
}
}
The above codes are basic steps for developing the application using ejb packages.
How to use EJB in Java Works?
- In EJB, the java bean class will use more than one annotation for the ejb specifications, which will be helpful for satisfying the user requirements based on the business purpose.EJB has a different set of versions and has followed the feature like JNDI(java naming directory interface). One of the resources in servers jndi is the directory service is used for locating or allocating the resource, like ejb, data source, and JMS queue services. The servers have a default scheme name for the jndi resources, but it should be overridden if we changed the configuration part’s name.
- EJB will work on java beans; it has two different types 1. Session beans and 2.Message Driven BeansSession beans. Session beans will be used for client-server interactions; it encapsulates the application’s business logic through programmatically by the client invocation will be done by either local machine or remote machine bean will be used by the client with the help of web services. Session beans will be three different categories 1. Stateless,2.Stateful and 3.Singleton.Stateless beans when the client use these type of beans there is no permanent state in web containers, so they are thread-safe performance wise very fast when compared to stateful beans. These beans are shared with multiple clients at the same time.
- Stateful beans can store the states in containers; once the client terminates the session, these states are also destroyed in the server. Singelton beans it has a single instance session for the entire lifecycle of that application; these beans also shared the states with multiple clients. These beans are thread-safe, so developers will use them more easily, and performance also fast compared to stateful beans.
- Message Driven Beans(MDB) is the type of bean that is used as the type of message asynchronous like JMS message listeners, but it will receive the message response as JMS messages instead of the events. We can map the messages using jndi services whenever the message receives the container calls the MDB beans using the onMessage() method for further process. The whole process of the MDB using the onMessage() method will be a single transaction. If suppose message process is a rollback, the receiver message again redelivered.
Examples to Implement EJB in Java
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Interface:
package JPAEJB;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface CustomerInterface {
void addBooks(String name);
List getBooks();
}
Implementation:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import JPAEJB.CustomerInterface;
@Stateless
public class CustomerClass implements CustomerInterface {
List<String>books;
public CustomerClass() {
books = new ArrayList<String>();
}
public void addBooks(String name) {
books.add(name);
}
public List<String> getBooks() {
return books;
}
}
CustomerInterface:
import JPAEJB.CustomerInterface;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class CustomerInterfaceImplem {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties p;
InitialContext c;
{
p = new Properties();
try {
p.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
c = new InitialContext(p);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CustomerInterfaceImplem cust = new CustomerInterfaceImplem();
cust.testStatelessEjb();
}
private void show() {
System.out.println("Welcome to my domain");
System.out.print("Options \n1. Add the Books\n2. Exit \nEnter your Choice: ");
}
private void StatelessEjb() {
try {
intc = 1;
CustomerInterface cust =
(CustomerInterface)ctx.lookup("CustomerInterface/remote");
while (c != 2) {
String books;
show();
String str = brConsoleReader.readLine();
c = Integer.parseInt(str);
if (c == 1) {
books = brConsoleReader.readLine();
cust.addBooks(books);
}elseif (c == 2) {
break;
}
}
List<String>books1 = cust.getBooks();
System.out.println(books1.size());
for (inti = 0; i<books1.size(); ++i) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + books1.get(i));
}
CustomerInterface cust1 =
(CustomerInterface)ctx.lookup("cust/remote");
List<String>books2 = cust.getBooks();
System.out.println(books2.size());
for (inti = 0; i<books2.size(); ++i) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + books2.get(i));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null) {
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
Sample Output:
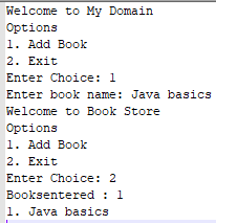
Example #2
EJB in Web Services:
package JPAEJB;
import java.util.List;
import Customers.CustomerInterfaceImplem;
public class Ejbclients{
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(CustomerInterface cust:getBooks()) {
System.out.println(cust.getBooks());
}
}
private static List
<CustomerInterface> getBooks() {
CustomerInterfaceImplem s =
new CustomerInterfaceImplem();
CustomerInterface c =
s.getCustomerInterfacePort();
return c.getBooks();
}
}
Example #3
EJB Security:
import javax.ejb.*
@Stateless
@DeclareRoles({"customer""books"})
public class CustSecurity implements CustomerInterface {
@RolesAllowed({"books"})
public void delete(CustomerInterface cust) {
System.out.println("customer delete the books");
}
@PermitAll
public void showBooks(CustomerInterface cust) {
System.out.println("customer viewed the books");
}
@DenyAll
public void deleteAll() {
System.out.println("customer delete all the books in libraries");
}
}
Security XML:
<?xml version="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE sun-ejb-jar PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Application Server 9.0 EJB 3.0//EN""http://www.sun.com/software/appserver/dtds/sun-ejb-jar_3_0-0.dtd"> <ejb-jar> <security-role-mapping> <role-name>customer</role-name> <group-name>customer-groups</group-name> </security-role-mapping> <security-role-mapping> <role-name>Books</role-name> <group-name>Books-group</group-name> </security-role-mapping> <enterprise-beans/> </ejb-jar>
Explanation: The above three examples are the same output we used different features of the ejb first example we use the customer will add and delete the books using jndi(java naming directory interface) second example we use the web service for customer done the operations through web final example we used the additional security.
Conclusion
Generally, EJB act as an interface outside of business logic applications; it has the? browser compatibility feature security-wise more when compared to other business logic frameworks. It also maintains the system-level transactions.
The above is the detailed content of EJB in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use JavaScript to determine whether two arrays are equal?
May 23, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to use JavaScript to determine whether two arrays are equal?
May 23, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
In JavaScript, you need to use a custom function to determine whether two arrays are equal, because there is no built-in method. 1) Basic implementation is to compare lengths and elements, but cannot process objects and arrays. 2) Recursive depth comparison can handle nested structures, but requires special treatment of NaN. 3) Special types such as functions and dates need to be considered, and further optimization and testing are required.
 How to correctly handle this pointing in a closure?
May 21, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
How to correctly handle this pointing in a closure?
May 21, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
The methods to correctly handle this pointing in JavaScript closures include: 1. Use arrow functions, 2. Use bind methods, 3. Use variables to save this. These methods ensure that this intrinsic function correctly points to the context of the external function.
 How to implement data encryption with JavaScript?
May 23, 2025 pm 11:12 PM
How to implement data encryption with JavaScript?
May 23, 2025 pm 11:12 PM
Using JavaScript to implement data encryption can use the Crypto-JS library. 1. Install and introduce the Crypto-JS library. 2. Use the AES algorithm for encryption and decryption to ensure that the same key is used. 3. Pay attention to the secure storage and transmission of keys. It is recommended to use CBC mode and environment variables to store keys. 4. Consider using WebWorkers when you need high performance. 5. When processing non-ASCII characters, you need to specify the encoding method.
 What are the four categories of Java? Description of Java Basic Type System Classification
May 20, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
What are the four categories of Java? Description of Java Basic Type System Classification
May 20, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
Java's four basic type systems include integer types, floating point types, character types and boolean types. 1. Integer types (byte, short, int, long) are used to store numerical values ??without decimals. Choosing the appropriate type can optimize memory and performance. 2. Float type (float, double) is used for decimal values. Pay attention to accuracy issues. If necessary, BigDecimal is used. 3. Character type (char) is based on Unicode and is suitable for single characters, but String may be required in international applications. 4. Boolean types are used for true and false values, simplifying logical judgments and improving code readability.
 How to copy and paste layer styles in PS?
May 16, 2025 am 06:00 AM
How to copy and paste layer styles in PS?
May 16, 2025 am 06:00 AM
Copying and pasting layer styles in Photoshop is a key trick to improve productivity. Let's dive into how to do it, and the various details and techniques you may encounter in the process. When we talk about copying and pasting layer styles in Photoshop, the first thing we need to understand is that layer styles refer to effects applied to layers, such as shadows, glows, bevels, and reliefs. Mastering this feature not only saves time, but also ensures consistent design. To copy the style of a layer, right-click the layer you want to copy and select Copy Layer Style. This will copy all the styles of the layer into the clipboard. Next, select the target layer you want to apply these styles, right-click it, and select Paste
 What does u mean in c language? Unsigned modification of u in c language
May 16, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
What does u mean in c language? Unsigned modification of u in c language
May 16, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
u is used in C language to declare unsigned integer constants. 1. The u suffix represents an unsigned integer, such as 10u. 2. The range of unsigned integers starts from 0 and does not contain negative numbers. They are suitable for large-range positive numbers and bit operations. 3. Pay attention to overflow and negative number processing issues when using unsigned integers.
 The difference between programming in Java and other languages ??Analysis of the advantages of cross-platform features of Java
May 20, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
The difference between programming in Java and other languages ??Analysis of the advantages of cross-platform features of Java
May 20, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
The main difference between Java and other programming languages ??is its cross-platform feature of "writing at once, running everywhere". 1. The syntax of Java is close to C, but it removes pointer operations that are prone to errors, making it suitable for large enterprise applications. 2. Compared with Python, Java has more advantages in performance and large-scale data processing. The cross-platform advantage of Java stems from the Java virtual machine (JVM), which can run the same bytecode on different platforms, simplifying development and deployment, but be careful to avoid using platform-specific APIs to maintain cross-platformity.
 After installing Nginx, the configuration file path and initial settings
May 16, 2025 pm 10:54 PM
After installing Nginx, the configuration file path and initial settings
May 16, 2025 pm 10:54 PM
Understanding Nginx's configuration file path and initial settings is very important because it is the first step in optimizing and managing a web server. 1) The configuration file path is usually /etc/nginx/nginx.conf. The syntax can be found and tested using the nginx-t command. 2) The initial settings include global settings (such as user, worker_processes) and HTTP settings (such as include, log_format). These settings allow customization and extension according to requirements. Incorrect configuration may lead to performance issues and security vulnerabilities.






